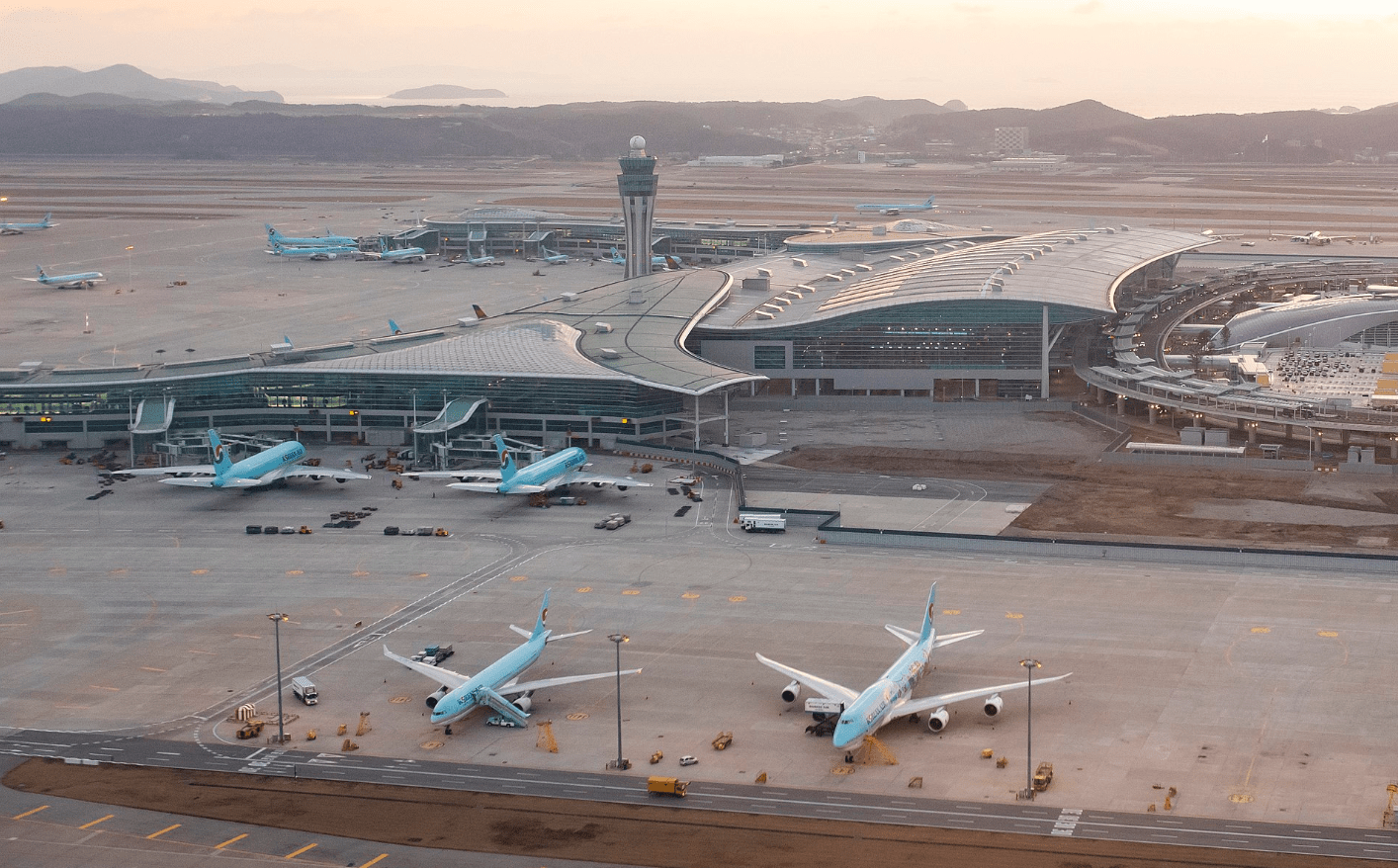
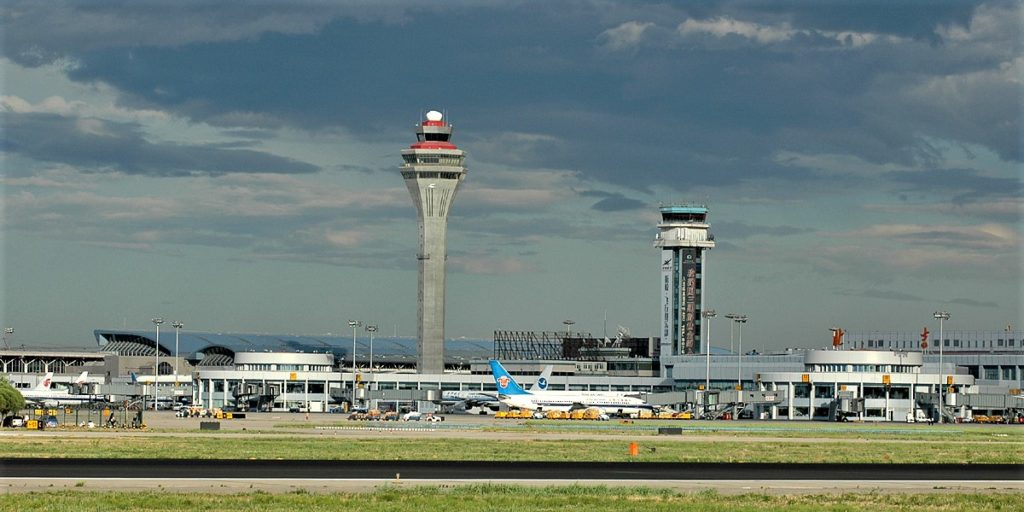
Beijing Capital International Airport
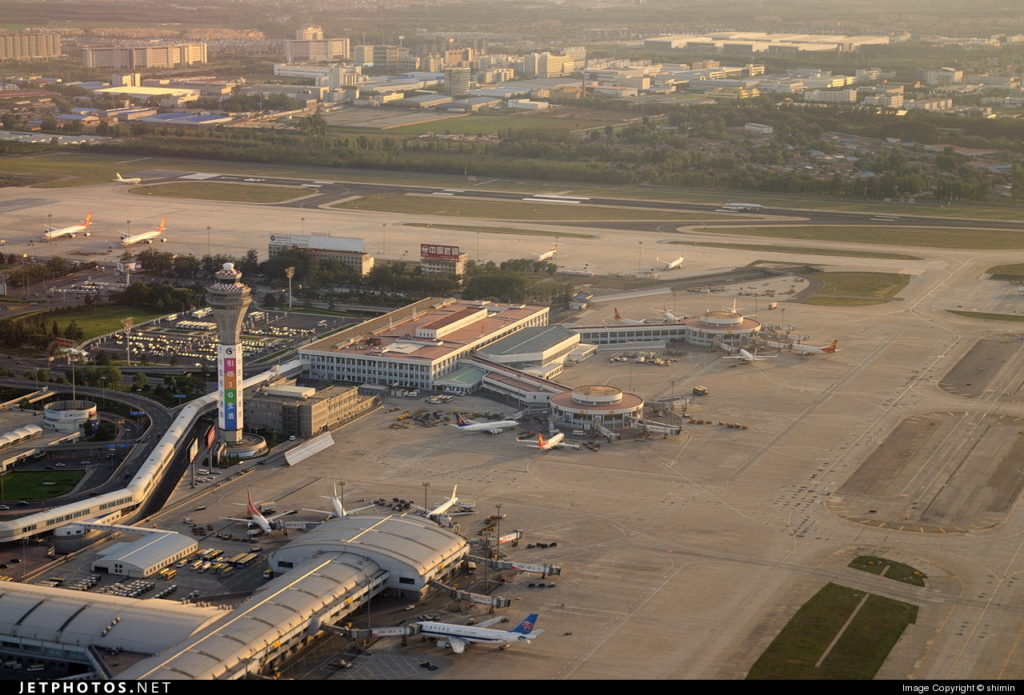

Source: JETPHOTOS.NET
| IATA: PEK ICAO: ZBAAWMO: 54511 | |
| Airport type | Public |
| Operator | Beijing Capital International Airport Company Limited |
| Serves | Beijing |
| Location | Chaoyang & Shunyi Districts, Beijing |
| Opened | 1 March 1958 |
| Hub for | Air ChinaChina Eastern AirlinesChina Southern AirlinesHainan Airlines |
| Focus city for | Sichuan AirlinesShenzhen AirlinesShandong Airlines |
| Elevation AMSL | 116 ft / 35 m |
| Coordinates |  40°04′21″N 116°35′51″ECoordinates: 40°04′21″N 116°35′51″ECoordinates:  40°04′21″N 116°35′51″E 40°04′21″N 116°35′51″E |
| Website | en.bcia.com.cn |
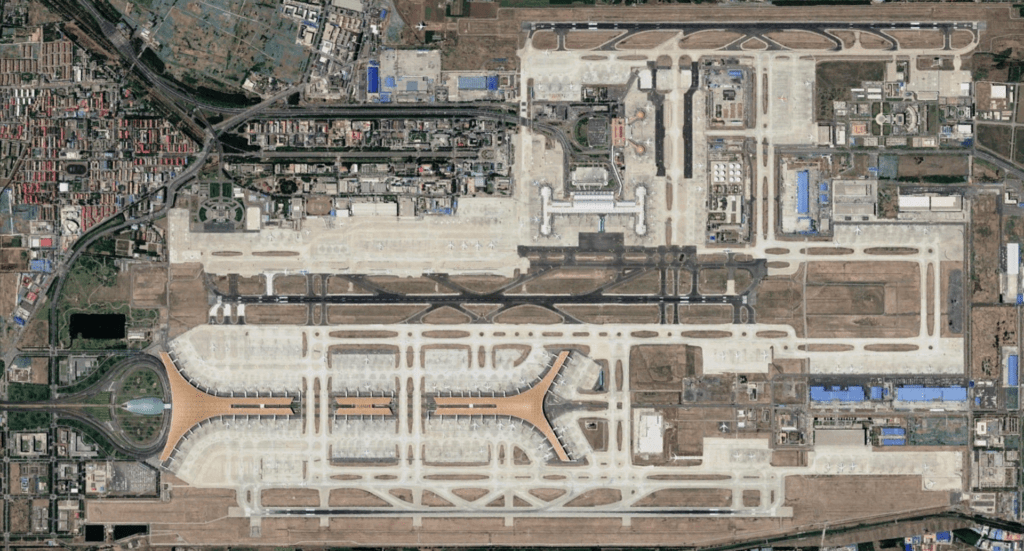
Beijing Capital International Airport (IATA: PEK, ICAO: ZBAA) is the main international airport serving Beijing. It is located 32 km (20 mi) northeast of Beijing’s city center, in an enclave of Chaoyang District and the surroundings of that enclave in suburban Shunyi District. The airport is owned and operated by the Beijing Capital International Airport Company Limited, a state-controlled company. The airport’s IATA Airport code, PEK, is based on the city’s former romanized name, Peking.
Beijing Capital has rapidly ascended in rankings of the world’s busiest airports in the past decade. It had become the busiest airport in Asia in terms of passenger traffic and total traffic movements by 2009. It has been the world’s second busiest airport in terms of passenger traffic since 2010. The airport registered 557,167 aircraft movements (take-offs and landings), ranking 6th in the world in 2012. In terms of cargo traffic, Beijing airport has also witnessed rapid growth. By 2012, the airport had become the 13th busiest airport in the world by cargo traffic, registering 1,787,027 tons.
From September 2019, all Oneworld & Skyteam flights from Beijing Capital International Airport were transferred to the new Beijing Daxing International Airport except Cathay Pacific and Cathay Dragon.

Source: Yaoleilei
Terminals
Ground view of Terminals 1 (foreground) and Terminal 2 (with blue roof, in background) in 2005. Terminal 2’s air traffic control tower in the background has since been demolished
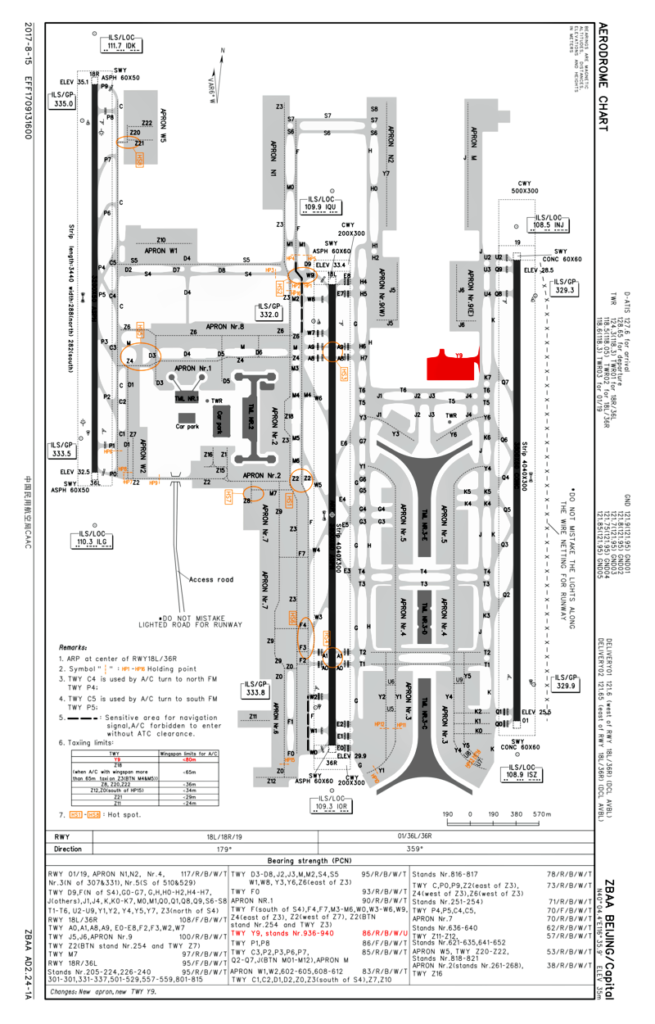
The airport has three terminals. Terminal 1 serves the domestic routes of Hainan Airlines and its subsidiaries (while its international, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan flights operate from Terminal 2). Terminal 2 serves China Southern Airlines, China Eastern Airlines, SkyTeam (excluding China Airlines, which uses Terminal 3), Oneworld members American Airlines and SriLankan Airlines, and also other domestic and international flights. Terminal 3, the newest terminal, serves Air China, Star Alliance, Oneworld members (excluding American Airlines and SriLankan Airlines, which uses Terminal 2), plus SkyTeam member China Airlines, and some other domestic and international flights that do not operate from either Terminals 1 or 2.
Terminal 1
Terminal 1, with 60,000 m2 (650,000 sq ft) of space, opened on 1 January 1980, and replaced the smaller existing terminal, which had been in operation since 1958. Terminal 1 was closed for renovation from 1 November 1999 to 20 September 2004, during which all airlines operated from Terminal 2. Featuring 16 gates, it was the operational base for the domestic routes of China Southern Airlines and a few other airlines such as XiamenAir and Chongqing Airlines, and was originally planned to handle domestic traffic excluding those to Hong Kong and Macau.
With the opening of Terminal 3, the terminal was closed for light refurbishment, and its airlines were moved to Terminal 2 on 20 May 2008. Terminal 1 reopened for a second time on 27 June 2008, and became the operational base for all domestic flights operated by the HNA Group including those of Hainan Airlines, Grand China Air, Beijing Capital Airlines and Tianjin Airlines, while all HNA Group’s international, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan flights remain in Terminal 2.

Source: 颐园新居
Terminal 2
Terminal 2 opened on 1 November 1999, with a floor area of 336,000 m2 (3,620,000 sq ft). This terminal was used to replace Terminal 1 while the latter was undergoing renovation, cramping all airlines despite being far bigger than Terminal 1. It can handle twenty aircraft at docks connecting directly to the terminal building. Prior to the opening of Terminal 3, all international flights (and the majority of domestic flights) operated from this terminal. This terminal now houses China Eastern Airlines, China Southern Airlines, Hainan Airlines (all international, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan flights), SkyTeam (excluding China Airlines, which uses Terminal 3), Oneworld members American Airlines and SriLankan Airlines, Air Koryo, and other domestic and international flights other than those operated by Air China, Shanghai Airlines, Star Alliance members and Oneworld members. A gate capable of handling the A380 (gate 21) was also built at the terminal.
Terminals 1 and 2 are linked by a public walkway that takes about 10–15 minutes to traverse. Shuttle buses connect all three terminals.

Source: 颐园新居
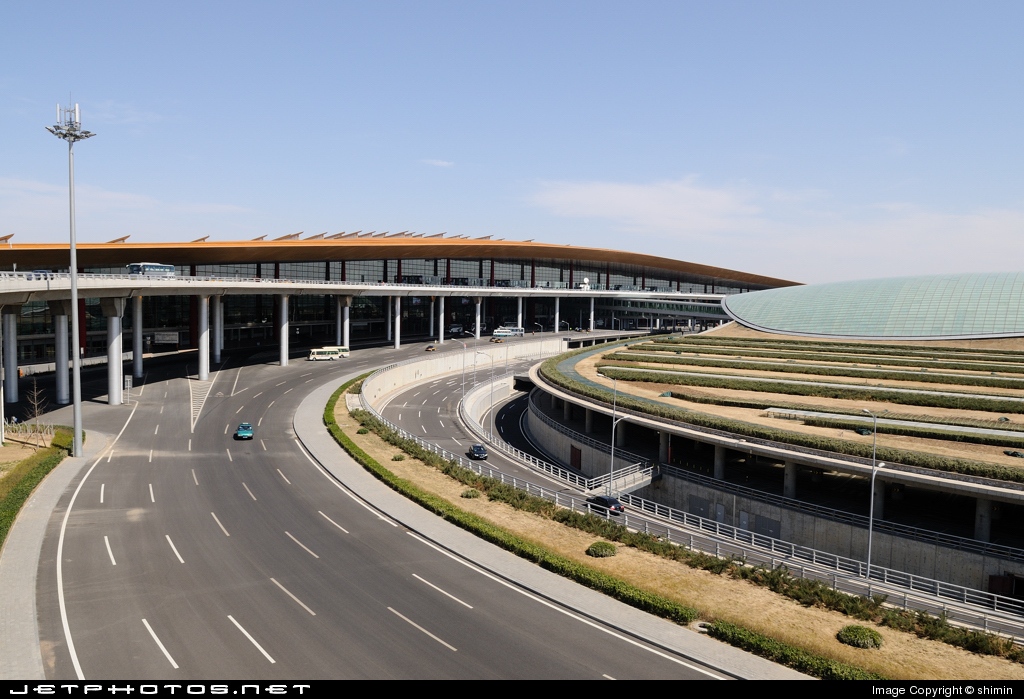
Terminal 3
Construction of Terminal 3 started on 28 March 2004, and the terminal opened in two stages. Trial operations commenced on 29 February 2008, when seven airlines including El Al Israel Airlines, Qantas, Qatar Airways, Shandong Airlines and Sichuan Airlines moved into the terminal. Twenty other airlines followed when the terminal became fully operational on 26 March 2008. Currently, it mainly houses Air China, Star Alliance, Oneworld (excluding American Airlines and SriLankan Airlines, which uses Terminal 2), SkyTeam member China Airlines, and other domestic and international flights that are not operated from Terminal 2. Star Alliance members LOT Polish Airlines, Scandinavian Airlines, Lufthansa, Austrian Airlines, United Airlines, Air Canada, Turkish Airlines, Thai Airways International, Singapore Airlines, All Nippon Airways, Asiana Airlines, and Air China use Terminal 3-E as part of the Move Under One Roof program to co-locate alliance members.
Terminal 3 was designed by a consortium of Netherlands Airport Consultants (NACO), UK Architect Foster and Partners, and ARUP. Lighting was designed by UK lighting architects Speirs and Major Associates. The budget for the expansion is US$3.5 billion. Much larger in size and scale than the other two terminals, Terminal 3 was the largest airport terminal-building complex in the world to be built in a single phase, with 986,000 m2 (10,610,000 sq ft) in total floor area at its opening. It features a main passenger terminal (Terminal 3C) and two satellite concourses (Terminal 3D and Terminal 3E), all of the five floors above ground and two underground, with the letters “A and B” omitted to avoid confusion with the existing Terminals 1 and 2. Only two concourses were initially opened, namely, Terminal 3C dedicated for domestic flights and Terminal 3E for international flights. Terminal 3D officially opened on 18 April 2013. The newly opened concourse is temporarily used solely by Air China for some of its domestic flights.
Terminal 3 of the BCIA is currently the second-largest airport passenger terminal building in the world. Its title as the world’s largest passenger terminal was surrendered on 14 October 2008 to Dubai International Airport’s Terminal 3, which has 1,713,000 m2 (18,440,000 sq ft) of floor space.
On 20 July 2013, a man in a wheelchair detonated small homemade explosives in Terminal 3 of the Beijing International Airport. The bomber, reported to be Ji Zhongxing, was injured and taken to a hospital for his injuries. No other people were hurt.

Source: JETPHOTOS.NET
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
| Air Algérie | Algiers |
| AirAsia X | Kuala Lumpur–International |
| Air Astana | Almaty, Nur-Sultan |
| Air Canada | Toronto–Pearson, Vancouver |
| Air China | Aksu, Athens, Auckland, Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Baotou, Barcelona, Bayannur, Beihai, Budapest, Busan, Changchun, Changsha, Changzhi, Changzhou, Chaoyang, Chengdu, Chiang Mai, Chifeng, Chongqing, Copenhagen, Dali, Dalian, Dandong, Daqing, Datong, Dazhou, Delhi, Dubai–International, Dunhuang, Düsseldorf, Frankfurt, Fukuoka, Fuyang, Fuyuan, Fuzhou, Ganzhou, Geneva, Guangyuan, Guangzhou, Guilin, Guiyang, Haikou, Hailar, Hami, Hangzhou, Hanoi, Harbin, Havana, Hefei, Hiroshima, Ho Chi Minh City, Hohhot, Hong Kong, Hotan, Houston–Intercontinental, Huangshan, Huizhou, Islamabad, Jakarta–Soekarno-Hatta, Jeju, Jiamusi, Jiansanjiang, Jieyang, Jingdezhen, Jinggangshan, Johannesburg–O.R. Tambo, Karachi, Karamay, Kashgar, Korla, Kuala Lumpur–International, Kunming, Lanzhou, Lhasa, Lijiang, Linfen, Liupanshui, Liuzhou, London–Heathrow, Los Angeles, Madrid, Manila, Melbourne, Mianyang, Milan–Malpensa, Minsk, Montréal–Trudeau, Moscow–Sheremetyevo, Mudanjiang, Mumbai, Munich, Nagoya–Centrair, Naha, Nanchang, Nanjing, Nanning, Nantong, Newark, New York–JFK, Nice, Ningbo, Nur-Sultan, Ordos, Osaka–Kansai, Panama City–Tocumen, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Phnom Penh, Phuket, Pyongyang, Qingdao, Qiqihar, Rome–Fiumicino, San Francisco, Sanya, São Paulo–Guarulhos, Sapporo–Chitose, Sendai, Seoul–Gimpo, Seoul–Incheon, Shanghai–Hongqiao, Shanghai–Pudong, Shaoyang, Shenyang, Shenzhen, Shihezi, Shiyan, Singapore, Songyuan, Stockholm–Arlanda, Sydney, Taipei–Taoyuan, Taiyuan, Taizhou, Tokyo–Haneda, Tokyo–Narita, Tonghua, Tongliao, Turpan, Ulaanbaatar, Ulanhot, Ulanqab, Urumqi, Vancouver, Vienna, Warsaw–Chopin, Washington–Dulles, Weihai, Wenzhou, Wuhai, Wuhan, Xiamen, Xi’an, Xichang, Xilinhot, Xining, Yancheng, Yangon, Yangzhou, Yanji, Yantai, Yibin, Yichang, Yinchuan, Yining, Yiwu, Yuncheng, Zhangjiajie, Zhanjiang, Zhengzhou, Zhuhai, Zunyi–Maotai, Zunyi–Xinzhou |
| Air France | Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| Air Koryo | Pyongyang |
| Air Macau | Macau |
| All Nippon Airways | Osaka–Kansai, Tokyo–Haneda, Tokyo–Narita |
| American Airlines | Dallas/Fort Worth, Los Angeles |
| Asiana Airlines | Seoul–Gimpo, Seoul–Incheon |
| Austrian Airlines | Vienna |
| Azerbaijan Airlines | Baku |
| Cambodia Angkor Air | Siem Reap, Sihanoukville |
| Cathay Dragon | Hong Kong |
| Cathay Pacific | Hong Kong |
| Cebu Pacific | Kalibo, Manila |
| China Airlines | Kaohsiung, Taipei–Taoyuan |
| China Eastern Airlines | Baoshan, Changzhou, Chengdu, Chiang Mai, Chongqing, Dali, Dalian, Delhi, Denpasar/Bali, Dongying, Enshi, Fukuoka, Guangzhou, Haikou, Hangzhou, Harbin, Hefei, Huai’an, Jiagedaqi, Jiayuguan, Jining, Kunming, Lanzhou, Lianyungang, Linyi, Luoyang, Lüliang, Luzhou, Mangshi, Nanchang, Nanjing, Naypyidaw, Ningbo, Pu’er, Qianjiang, Qingdao, Saipan, Shanghai–Hongqiao, Shanghai–Pudong, Shenzhen, Sydney, Taiyuan, Tengchong, Vientiane, Wenzhou, Wuhan, Wuxi, Xiamen, Xi’an, Xining, Xishuangbanna, Yantai, Yinchuan, Zhangye, Zhaotong Seasonal: Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi |
| China Southern Airlines | Amsterdam, Beihai, Changchun, Changsha, Chengdu, Chongqing, Dalian, Ganzhou, Guangzhou, Guilin, Guiyang, Haikou, Hangzhou, Harbin, Heihe, Korla, Kunming, Mohe, Nanning, Phnom Penh, Sanya, Seoul–Gimpo, Seoul–Incheon, Shanghai–Hongqiao, Shenyang, Shenzhen, Tashkent, Tbilisi, Tehran–Imam Khomeini, Urumqi, Wuhan, Xi’an, Yining, Yiwu, Zhangjiajie, Zhuhai |
| China Southern Airlines operated by Chongqing Airlines | Chongqing, Diqing |
| Dalian Airlines | Dalian |
| Donghai Airlines | Shenzhen, Yichang |
| EgyptAir | Cairo |
| El Al | Tel Aviv |
| Emirates | Dubai–International |
| Ethiopian Airlines | Addis Ababa |
| Etihad Airways | Abu Dhabi (ends 31 May 2020), Nagoya–Centrair (ends 31 May 2020) |
| EVA Air | Taipei–Taoyuan |
| Finnair | Helsinki |
| Fiji Airways | Nadi |
| Grand China Air | Guilin, Harbin, Sanya, Yinchuan |
| Hainan Airlines | Almaty, Anqing, Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Berlin–Tegel, Boston, Brussels, Changchun, Changsha, Chengdu, Chicago–O’Hare, Chongqing, Dalian, Dongying, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Guiyang, Haikou, Hailar, Hangzhou, Harbin, Hohhot, Irkutsk, Jiamusi, Kunming, Lanzhou, Manchester, Manzhouli, Moscow–Sheremetyevo, Mudanjiang, Nanchang, Nanning, Ningbo, Osaka–Kansai, Oslo–Gardermoen, Phuket, Saint Petersburg, San Jose (CA), Sanming, Sanya, Seattle/Tacoma, Shanghai–Hongqiao, Shanghai–Pudong, Shenzhen, Taipei–Taoyuan, Tel Aviv, Tokyo–Haneda, Tokyo–Narita, Toronto–Pearson, Urumqi, Weifang, Wenzhou, Wuhai, Wuhan, Xiamen, Xi’an, Xining, Yan’an, Yichang, Yulin Seasonal: Dublin |
| Hong Kong Airlines | Hong Kong |
| Japan Airlines | Tokyo–Haneda, Tokyo–Narita |
| Jeju Air | Daegu |
| Jiangxi Air | Nanchang |
| KLM | Amsterdam |
| Korean Air | Busan, Jeju, Seoul–Gimpo, Seoul–Incheon |
| Loong Air | Hangzhou |
| LOT Polish Airlines | Warsaw–Chopin |
| Lucky Air | Mangshi, Tengchong |
| Lufthansa | Frankfurt, Munich |
| Mahan Air | Tehran–Imam Khomeini |
| MIAT Mongolian Airlines | Ulaanbaatar |
| NordStar Airlines | Krasnoyarsk–Yemelyanovo |
| Pakistan International Airlines | Islamabad, Lahore, Tokyo–Narita |
| Philippine Airlines | Kalibo, Manila |
| Qatar Airways | Doha |
| Scandinavian Airlines | Copenhagen |
| Shandong Airlines | Chongqing, Fuzhou, Guilin, Hangzhou, Jinan, Nanyang, Qingdao, Rizhao, Weihai, Xiamen, Yantai, Zhuhai |
| Shanghai Airlines | Hangzhou, Shanghai–Hongqiao |
| Shenzhen Airlines | Chengdu, Nanning, Nantong, Osaka–Kansai, Quanzhou, Shenzhen, Wuxi, Xiangyang, Yichun |
| Sichuan Airlines | Baise, Chengdu, Chongqing, Kunming, Panzhihua, Sanya, Urumqi, Wanzhou, Xichang, Xishuangbanna, Zhongwei |
| Singapore Airlines | Singapore |
| Sky Angkor Airlines | Siem Reap |
| SriLankan Airlines | Colombo–Bandaranaike |
| Thai AirAsia | Seasonal: Chiang Mai |
| Thai Airways | Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Phuket |
| Tibet Airlines | Lhasa |
| Turkish Airlines | Istanbul |
| Turkmenistan Airlines | Ashgabat |
| United Airlines | Chicago–O’Hare, Newark, San Francisco, Washington–Dulles |
| Uzbekistan Airways | Tashkent |
| Vietnam Airlines | Hanoi Seasonal: Nha Trang |
Source: AirportStudio
Cargo
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| AirBridgeCargo | Moscow–Sheremetyevo |
| Air China Cargo | Anchorage, Atlanta, Chicago–O’Hare, Frankfurt, Los Angeles, Nanjing, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Seoul–Incheon, Shanghai–Pudong, Tokyo–Narita, Taipei–Taoyuan |
| Air Koryo | Pyongyang |
| Asiana Cargo | Seoul–Incheon |
| Cargolux | Luxembourg City |
| China Airlines Cargo | Taipei–Taoyuan |
| China Cargo Airlines | Shanghai–Pudong |
| China Postal Airlines | Shanghai–Pudong, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Hangzhou, Nanjing |
| DHL Aviation operated by Air Hong Kong | Hong Kong |
| EVA Air Cargo | Tapei–Taoyuan |
| Etihad Cargo | Abu Dhabi, Almaty |
| FedEx Express | Seoul–Incheon, Shanghai–Pudong, Osaka–Kansai |
| Korean Air Cargo | Seoul–Incheon |
| Lufthansa Cargo | Frankfurt |
| SF Airlines | Guangzhou, Hangzhou, Shanghai–Pudong, Wuxi, Shenzhen, Macau |
| Suparna Airlines | Hangzhou, Shenzhen |
Ground transportation
Intra-terminal transportation
Terminal 3 consists of three sub-concourses. Both domestic and international travellers check in at concourse T3C. Gates for domestic flights are in T3C, and gates for domestic flights operated by Air China are also located in concourse T3D. All international, Hong Kong, and Macau, and Taiwan flights are handled in concourse T3E.
In conjunction with the construction of the new terminal, Bombardier Transportation installed a 2 km (1.2 mi) automated people mover which connects T3C and T3E via T3D in a 2–5-minute one-way trip. The line uses Innovia APM 100 vehicles running at 6-minute intervals at a maximum speed of 55 kilometres per hour (34 mph).

Inter-terminal transportation
The airport provides a free inter-terminal shuttle bus between Terminals 1/2 and 3. They operate every 10 minutes from 6 am to 11 pm, and every 30 minutes from 11 pm till 6 am. Terminals 1 and 2 are connected by a lengthy corridor.
Rail
Beijing Capital International Airport is served by the Capital Airport Express, a dedicated rail link operated as part of the Beijing Subway system. The 28.1 km (17.5 mi) line runs from Terminal 3 to Terminal 2 and then to the city with stops at Sanyuanqiao and Dongzhimen. The line opened on 19 July 2008, in time for the 2008 Summer Olympics. A one-way trip takes approximately 16–20 minutes and costs ¥25. The running hours are 6:35-23:10 for T2, 6:20-22:50 for T3 and 6:00-22:30 for Dongzhimen.
Bus
There are 18 bus routes to and from points throughout the city including Xidan, Beijing railway station, Beijing South railway station, Beijing West railway station, Zhongguancun, Fangzhuang and Shangdi. The airport buses run to each of the three terminals and cost up to ¥30 per ride depending on the route. The airport buses accept only paper tickets that are sold at each terminal and certain bus stops in the city. The airport also offers intercity bus services to and from neighboring cities including Tianjin, Qinhuangdao, Baoding, Langfang and Tangshan.
Car
Toll plaza at Xiaotianzhu on the Airport Expressway, which goes to Terminals 1 and 2.Toll plaza on the 2nd Airport Expressway and entrance to parking garage at Terminal 3.
The airport is accessible by four expresses tollways. Two of these run directly from northeastern Beijing to the airport. The other two connect to the airport from nearby highways.
- The Airport Expressway is a 20 km (12 mi) toll road that runs from the northeastern 3rd Ring Road at Sanyuanqiao directly to Terminals 1 and 2. It was built in the 1990s and has served as the primary road connection to the city.
- The 2nd Airport Expressway, opened in 2008, is a 15.6 km (9.7 mi) toll road that runs east from Yaojiayuan Lu at the eastern 5th Ring Road and then north to Terminal 3.
- The Northern Airport Line, opened in 2006, is an 11.3 km (7.0 mi) toll road that runs east from the Jingcheng Expressway to Terminals 1 and 2.
- The Southern Airport Line, opened in 2008, is a toll road that runs parallel and to the south of the Northern Airport Line from the Jingcheng Expressway to the eastern Sixth Ring Road at the Litian Bridge. This highway crosses the Airport Expressway and 2nd Airport Expressway, and enables drivers on the former to reach Terminal 3 and the latter to head to Terminals 1 and 2.
- 2009 – 1st on the ranking of the World’s Best Airport by Condé Nast Traveler magazine, based on its satisfaction survey.
- 2011 – 3rd Best Airport Worldwide of the Airport Service Quality Awards by Airports Council International.
Source: Civil Aviation Administration of China
Source: wikipedia




















