Aviation
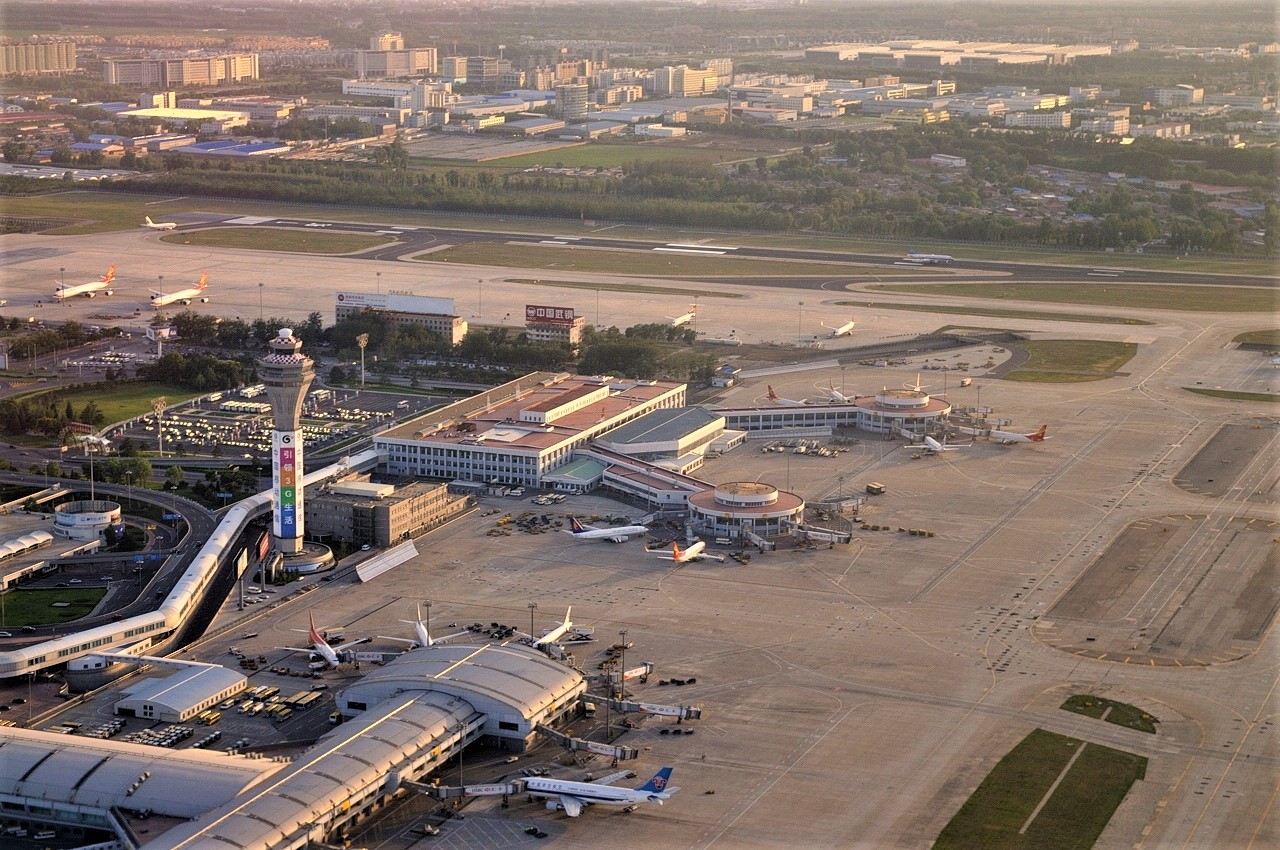
Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport
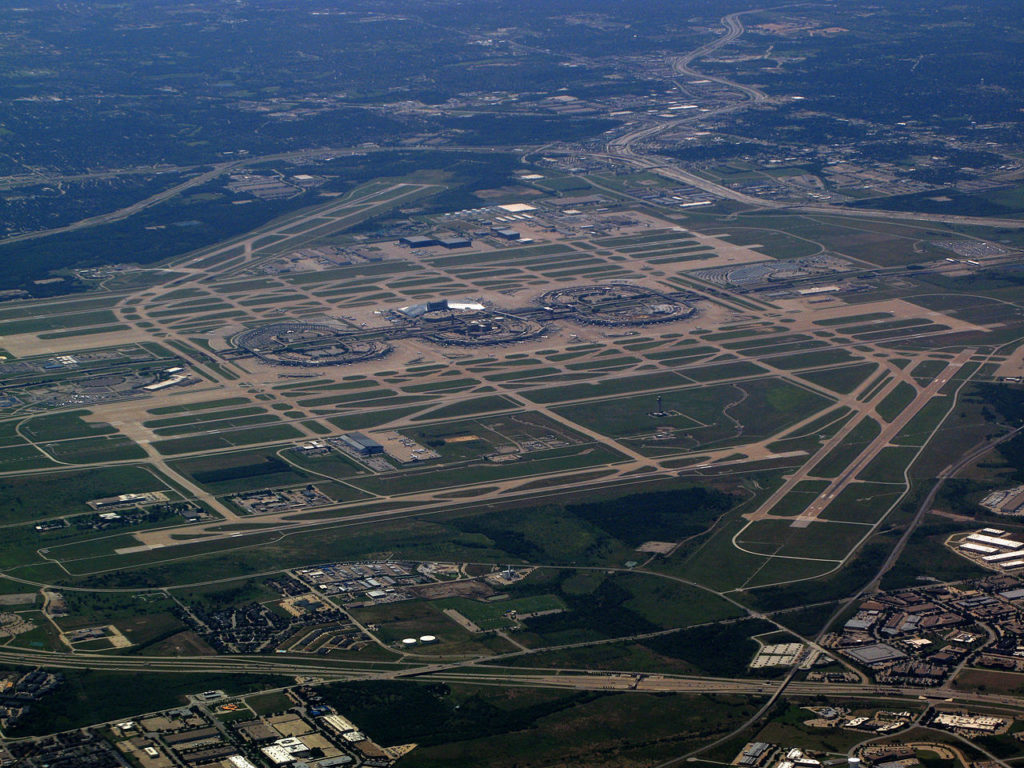

Source: Tom Walsh
| IATA: DFW ICAO: KDFW FAA LID: DFW WMO: 72259 | |
| Airport type | Public |
| Owner | Cities of Dallas and Fort Worth |
| Operator | DFW Airport Board |
| Serves | Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex |
| Location | Dallas and Tarrant counties, Texas |
| Opened | September 23, 1973; 46 years ago |
| Hub for | American Airlines Cargo Ameriflight UPS Airlines |
| Focus city for | Spirit Airlines Sun Country Airlines |
| Elevation AMSL | 607 ft / 185 m |
| Coordinates | |
| Website | dfwairport.com |
Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport (IATA: DFW, ICAO: KDFW, FAA LID: DFW), often known colloquially as Dallas Airport or DFW Airport, is the primary international airport serving the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex area in the U.S. state of Texas.
It is the largest hub for American Airlines, which is headquartered near the airport. It is the fourth busiest airport in the world by aircraft movements and the fifteenth busiest airport in the world by passenger traffic in 2017. It is the ninth busiest international gateway in the United States and the second busiest international gateway in Texas. American Airlines at DFW is the second largest single airline hub in the world and the United States, behind Delta’s Atlanta hub. In 2019, DFW set a new passenger traffic record in its 45 year history, serving 75,066,956 passengers.
Located roughly halfway between the major cities of Dallas and Fort Worth, DFW spills across portions of Dallas and Tarrant counties, and includes portions of the cities of Irving, Euless, Grapevine and Coppell] At 17,207 acres (6,963 hectares; 27 square miles), DFW is larger than the island of Manhattan, and is the second largest airport by land area in the United States, after Denver International Airport. It has its own post office ZIP code, 75261, and United States Postal Service city designation (“DFW Airport, TX”), as well as its own police, fire protection and emergency medical services. The members of the airport’s board of directors are appointed by the “owner cities” of Dallas and Fort Worth, with a non-voting member chosen from the airport’s four neighboring cities on a rotating basis.
As of January 2020, DFW Airport has service to 260 destinations, including 67 international and 193 domestic destinations within the U.S. In surpassing 200 destinations, DFW joined a small group of airports worldwide with that distinction.
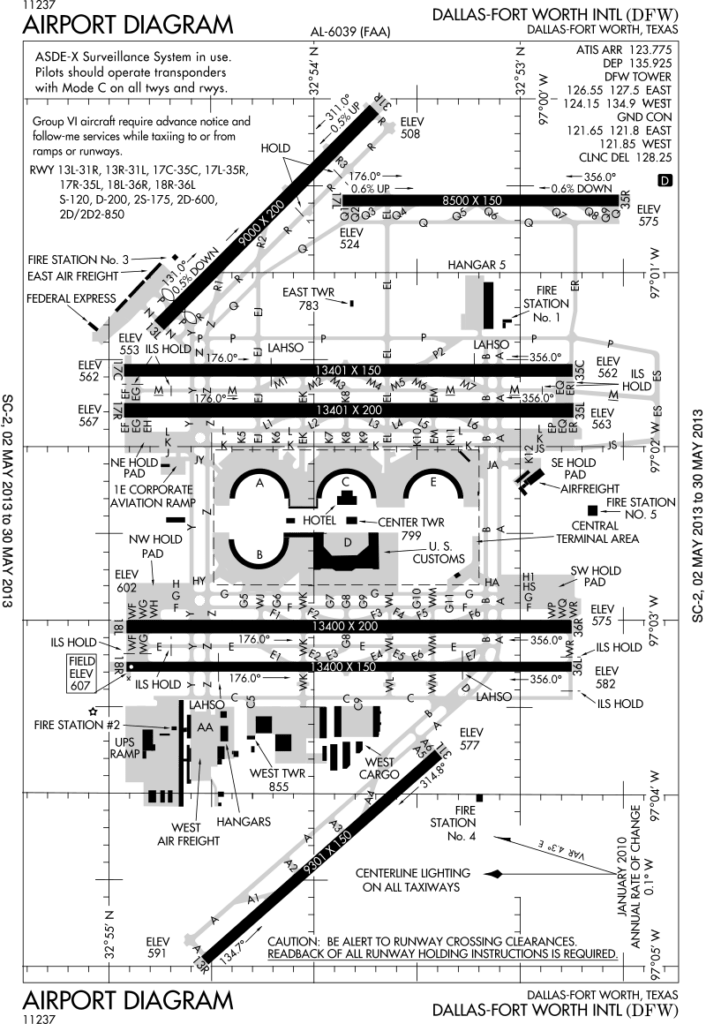

Source: FAA Airport Diagrams
Terminals and facilities


Source: Vmzp85
Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport has five terminals and 182 gates. The airport is designed with expansion in mind and can theoretically accommodate up to 13 terminals and 260 gates, although this level of expansion is unlikely to be reached in the foreseeable future. The first four terminals were designed by Hellmuth, Obata and Kassabaum and Brodsky, Hopf & Adler. The terminals at DFW are semicircular (except for the newest terminal, Terminal D, which is a “square U” shape) and built around the airport’s central north–south arterial road, International Parkway. Until the late 1990s, they were designated by a number (2 being northernmost, 4 being southernmost) and a letter suffix (“E” for East, “W” for West). This system was later scrapped and the terminals are now lettered from A to E. Terminals A, C, and E (from north to south) are on the east side of the airport, while Terminals B and D (from north to south) are on the west side.
DFW’s terminals are designed to minimize the distance between a passenger’s car and airplane, and to reduce traffic around terminals. A consequence of this layout is that connecting passengers had to walk extremely long distances between gates (in order to walk from one end of the semicircular concourse to the other, one must walk the entire length; there were no shortcuts or moving walkways between the ends). The original people mover train (Airtrans APM, later the American Airlines TrAAin) was notoriously slow (17 mph (27 km/h)), uni-directional (running only in a counter-clockwise direction) and was located outside the secured area (thus requiring travelers to go through security again). It was replaced by Skylink in April 2005 after serving approximately 250 million passengers. Skylink serves all five terminals at a considerably higher speed (up to 35 mph (56 km/h)), is bi-directional, and is located inside the secured area. Terminal Link connects all terminals with a shuttle bus system on the non-secure side.
DFW Airport tentatively completed a $2.7 billion “Terminal Renewal and Improvement Program” (TRIP), which encompassed renovations of three of the original four terminals (A, B, and E). Work on the project began following the conclusion of Super Bowl XLV in February 2011. Terminal A was the first terminal to undergo these renovations which were completed in January 2017 at a cost of about $1 billion. This was followed by the completion of Terminal E in August 2017 and Terminal B in December 2017. While Terminal C was originally part of the multibillion-dollar renovations, American Airlines in 2014 asked to delay renovations of the terminal. Terminal C is now slated to be renovated along with the project to construct a new terminal, Terminal F, to be completed sometime in 2025.
Terminal A
Terminal A has 26 gates. Originally named “Terminal 2E”, it is fully occupied by American Airlines for domestic flights and some international departures. Prior to the opening of Terminal D, Terminal A operated most of American Airlines’ international flights at the airport.
A satellite terminal near Terminal A was used due to gate restraints. Passengers were taken to the satellite via shuttle buses from gate A6. The satellite terminal was abandoned in 2005 when all American Eagle flights were consolidated into Terminals B and D. It now serves as a Corporate Aviation terminal for private and corporate aircraft, reopening in December 2010.
As of January 2017, renovations in Terminal A are now completed.
Terminal B
Terminal B has 47 gates. This terminal was called “Terminal 2W” when the airport was opened. It was occupied by Braniff International Airways, which was the largest carrier to open DFW in 1974. Braniff was its main occupant until May 1982. The Inter-Faith Chapel near United’s former gates commemorates the airline. By the early 1990s, Terminal 2W housed most carriers other than American and Delta. Prior to the opening of Terminal D, all foreign flag carriers operated from this terminal. AirTran Airways, Frontier Airlines, Midwest Airlines, and US Airways (including the former America West Airlines) relocated to Terminal E in 2006. On December 13, 2009, United moved to Terminal E to join its new alliance (and later merger) partner Continental, at which point American Eagle became the sole operator in Terminal B. The terminal contains an American Airlines Admirals Club.
Along with the TRIP improvements, a new 10-gate stinger concourse off of Terminal B was constructed between gates B28 and B33 to accommodate growth. The stinger concourse makes Terminal B the largest terminal at DFW in terms of number of gates.
Terminal C
Terminal C has 28 gates. American Airlines operates all the gates at Terminal C, originally called “Terminal 3E”, for only domestic flights. The terminal contains an American Airlines Admirals Club. The Hyatt Regency DFW Airport hotel is directly adjacent to this terminal. A twin hotel building stood across International Parkway but was demolished for the construction of Terminal D.
Terminal C has not started their TRIP Improvements. DFW Airport CEO Sean Donohue has been in talks with American about the future of Terminal C. They will either destroy it once the future Terminal F is finished, or renovate and keep it for other carriers to use so American and other airlines do not have to give up gate space. Announced on May 20, 2019, Terminal C will be renovated along with the project to construct a new terminal, Terminal F, both to be completed by 2025.
Terminal D
Terminal D has 26 gates. It is DFW’s international terminal, capable of handling 32,000 passengers daily or 11.7 million passengers annually. All international flights without border preclearance arrive in Terminal D. The terminal features 200 ticketing positions and a federal inspection facility capable of processing 2,800 passengers per hour. The terminal officially opened on July 23, 2005.
The eight-level parking garage has over 8,100 parking spaces and uses a Smart Technology System that lets guests know which floors are full. Air-conditioned skybridges with moving walkways and elevators connect the garage to the terminal, and an arrivals canopy roof shields pedestrians from inclement weather as they enter and exit the terminal. The 298-room Grand Hyatt DFW Hotel is directly connected to the terminal. In addition, Terminal D hosts a Minute Suites hotel located inside security. The terminal contains an American Airlines Admirals Club, a British Airways Lounge, a Korean Air Lounge, a Lufthansa Lounge, and a Qantas Business Lounge and an American Express Centurion Lounge.
On May 7, 2014, Qantas announced an upgauge to A380 service beginning in September 2014, and the Airport announced that gates 15 and 16 were being renovated to accommodate the A380 in anticipation of the new service. Terminal D had been designed with the A380 in mind;[54] however, loading the double-deck aircraft requires three gates with a separate jet bridge to serve first class and business class passengers on the upper level, so the renovations included the addition of gate 16X. On September 29, 2014, a Qantas A380–sporting a commemorative cowboy hat and bandana on the Kangaroo tail logo–inaugurated service at the remodeled gates. Qantas Flights 7 and 8 continue to use A380s and remain the longest non-stop flights to and from DFW Airport.
Terminal E
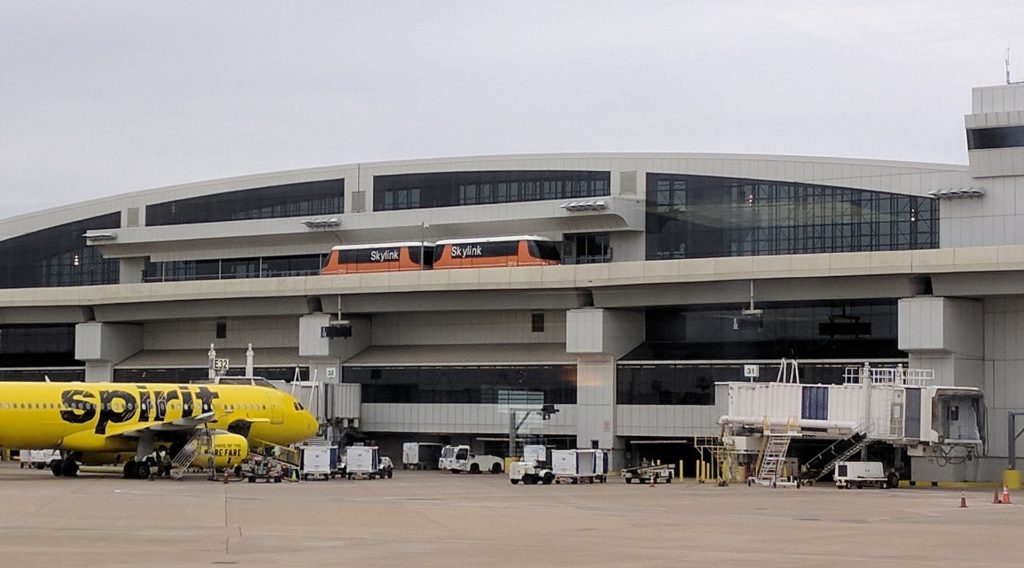


Source: Baseball Watcher
Terminal E has 41 gates. Originally called Terminal 4E, it was occupied primarily by Delta Air Lines until Delta closed its hub in 2005 and retained only flights to its other hubs. Delta branded the terminal “Easy Street” and marketed this term to passengers. Today, the terminal is used by all U.S.-based carriers at the airport other than Sun Country, and by Air Canada Express USCBP precleared flights from Canada. Terminal E was formerly the only terminal at DFW in which American Airlines had no presence, but this changed after their merger with US Airways, when they combined gates.
The terminal previously had customs facilities that were used when Delta operated flights to Frankfurt in the early 1990s, and when Air France and Aeroméxico used to serve DFW before the International Terminal D was constructed. In the 2000s, SkyTeam partner airlines Continental and Northwest moved to gates adjacent to Delta. Terminal E is connected to the other terminals by Skylink, but lacks a walkway to the other terminals. The terminal includes a Delta Sky Club as well as a United Club.
Terminal E is distinctive in that it has a satellite terminal connected by an underground walkway. The satellite, opened in 1988 to accommodate Delta and was later used by Delta Connection. It was briefly used in 2009 to house federal workers who evacuated New Orleans International Airport during Hurricane Gustav. It was refurbished and reopened in 2013 to house US Airways and Spirit Airlines while Terminal E was renovated. In April 2018, DFW Airport and American Airlines announced a $20 million renovation to the satellite terminal, which converted 9 existing mainline gates to 15 regional gates, along with updating interior fixtures such as carpet, elevators, escalators and moving walkways. American planned to have renovations completed by then and was fully moved into the terminal on May 3, 2019.
Terminal F (future)
On May 20, 2019, DFW airport, along with American Airlines, announced plans to build a 6th terminal. The proposed project is estimated to cost $3–3.5 billion and expected to finish as soon as 2025. Along with the addition of up to 24 new gates to Terminal F, renovations of Terminal C are planned to take place, as it is the last terminal which has not been updated in recent years.[63] The goal of the new terminal is to “provide the region with the growth it needs to compete with international business centers,” according to CEO of DFW Airport, Sean Donohue.

Ground transportation


intersects the airport
Source: DFW airport streets
The International Parkway Toll Road intersects the airport
A consolidated rental car facility is located at the south end of the airport and connected to all terminals by a dedicated network of shuttle buses. Hosting ten rental car companies, the center was completed in March 2000.
The DFW Airport area is served by International Parkway (partially State Highway 97 Spur), which runs through the center of the airport, connecting to Airport Freeway (State Highway 183) on the southern side of the airport and John W. Carpenter Freeway (State Highway 114) on the northern side. International Parkway continues north of State Highway 114, carrying the State Highway 121 designation for a short while until its interchange with the Lyndon B. Johnson Freeway (I-635), where State Highway 121 continues north as the Sam Rayburn Tollway.
Bus routes serving the airport are operated by Dallas Area Rapid Transit (DART) and Trinity Metro. DART operates route 408 from Downtown Irving/Heritage Crossing Station and Southwestern Medical District/Parkland Station to the Remote South Parking facility, and Trinity Metro operates the TRE Link bus route from CentrePort/DFW Airport station.
Three rail systems serve the airport: DART Light Rail, TEXRail, and the Trinity Railway Express. DART operates light rail from DFW Airport station located at Terminal A.[66] This provides direct rail service on the Orange Line to Dallas and Las Colinas (with a later extension to DFW Airport North station). TEXRail is a commuter rail service between Terminal B and T&P Station. DFW Airport is additionally served by the Trinity Railway Express commuter rail line at CentrePort/DFW Airport Station via shuttle bus to the Remote South parking lot. The line serves both downtown Dallas and downtown Fort Worth.
Other facilities
The facility at 1639 West 23rd Street is located on the airport property and in the City of Grapevine.[67][68][69] Tenants include China Airlines, Lufthansa Cargo,[71] and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
The DFW Airport Department of Public Safety provides the airport with its own police, fire protection, and emergency medical services.
The DFW International Airport headquarters is located nearby at 2400 Aviation Drive, DFW Airport, TX 75261.
In 1995, the airport opened Founders’ Plaza, an observation park dedicated to the founders of DFW Airport. The site offered a panoramic view of the south end of the airport and hosted several significant events, including an employee memorial the day after the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks and the airport’s 30th anniversary celebration in 2004.[75] As part of the perimeter taxiway project, Founders’ Plaza was closed in 2007 and moved to a new location surrounding a 50-foot (15 m)-tall beacon on the north side of the airport in 2008. The 6-acre (2.4 ha) plaza features a granite monument and sculpture, post-mounted binoculars, piped-in voices of air traffic controllers and shade pavilions. In 2010, a memorial honoring Delta Air Lines Flight 191 was dedicated at the plaza.
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
| Aeroméxico Connect | Mexico City | |
| Air Canada Express | Montréal–Trudeau, Toronto–Pearson, Vancouver | |
| Air France | Seasonal: Paris–Charles de Gaulle | |
| Alaska Airlines | Portland (OR), Seattle/Tacoma | |
| American Airlines | Albuquerque, Amarillo, Atlanta, Aruba, Austin, Baltimore, Birmingham (AL), Beijing–Capital, Belize City, Bogotá, Boise, Boston, Buenos Aires–Ezeiza, Burbank, Cancún, Charleston (SC), Charlotte, Chicago–O’Hare, Cincinnati, Cleveland, Colorado Springs, Columbia (SC), Columbus–Glenn, Cozumel, Denver, Des Moines, Destin/Fort Walton Beach, Detroit, Eagle/Vail, El Paso, Fayetteville/Bentonville, Fort Lauderdale, Fort Myers, Frankfurt, Fresno, Grand Cayman, Grand Rapids, Greensboro, Greenville/Spartanburg, Guadalajara, Guatemala City, Guayaquil, Hartford, Hong Kong, Honolulu, Houston–Intercontinental, Indianapolis, Jackson Hole, Jacksonville (FL), Kahului, Kansas City, Knoxville, Las Vegas, Liberia (CR), Lima, Little Rock, London–Heathrow, Los Angeles, Louisville, Lubbock, Madison, Madrid, Memphis, Mexico City, Miami, Midland/Odessa, Milwaukee, Minneapolis/St. Paul, Montego Bay, Monterey, Montrose, Nashville, New Orleans, Newark, New York–JFK, New York–LaGuardia, Norfolk, Oklahoma City, Omaha, Ontario, Orange County, Orlando, Palm Springs, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Pensacola, Philadelphia, Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Pittsburgh, Portland (OR), Puerto Vallarta, Quito, Raleigh/Durham, Reno/Tahoe, Richmond, Roatan, Sacramento, St. Louis, St. Thomas, Salt Lake City, San Antonio, San Diego, San Francisco, San Jose (CA), San José de Costa Rica, San José del Cabo, San Juan, San Salvador, Santiago de Chile, São Paulo–Guarulhos, Savannah, Seattle/Tacoma, Seoul–Incheon, Shanghai–Pudong, Spokane, Tampa, Tokyo–Haneda (begins July 7, 2020),[81] Tokyo–Narita, Toronto–Pearson, Tucson, Tulsa, Vancouver, Washington–Dulles, Washington–National, West Palm Beach, Wichita Seasonal: Amsterdam, Anchorage, Bozeman, Dublin, Fairbanks, Glacier Park/Kalispell (begins June 4, 2020), Gunnison/Crested Butte, Hayden/Steamboat Springs, Ixtapa/Zihuatanejo, Kailua–Kona, Key West, Montreal–Trudeau, Munich, Nassau, Portland (ME) (begins June 6, 2020), Providenciales, Punta Cana, Rome–Fiumicino, St. Kitts, San Pedro Sula, Santa Barbara, Santo Domingo–Las Américas, Sarasota, Tegucigalpa | |
| American Eagle | Abilene, Aguascalientes, Albuquerque, Alexandria, Amarillo, Aspen, Augusta (GA), Bakersfield, Baton Rouge, Beaumont, Billings, Birmingham (AL), Bismarck, Bloomington/Normal, Boise, Bozeman, Brownsville, Buffalo, Calgary, Cedar Rapids/Iowa City, Champaign/Urbana, Charleston (SC), Chattanooga, Cheyenne, Chihuahua, Cincinnati, College Station, Colorado Springs, Columbia (MO), Corpus Christi, Dayton, Del Rio, Des Moines, Destin/Fort Walton Beach, Durango (CO), Durango (MX), El Paso, Evansville, Fargo, Fayetteville/Bentonville, Flagstaff, Fort Smith, Fort Wayne, Gainesville, Garden City, Grand Island, Grand Junction, Grand Rapids, Greensboro, Greenville/Spartanburg, Gulfport/Biloxi, Harlingen, Harrisburg, Hattiesburg/Laurel (MS) (ending June 30, 2020), Houston–Hobby, Houston–Intercontinental, Huntsville, Jackson (MS), Jackson Hole, Joplin, Kansas City, Killeen/Fort Hood, Knoxville, Lafayette, Lake Charles, Laredo, Lawton, León/Del Bajío, Lexington, Little Rock, Longview, Louisville, Lubbock, Madison, Manhattan (KS), McAllen, Memphis, Meridian (MS) (ending June 30, 2020), Midland/Odessa, Milwaukee, Missoula, Mobile, Moline/Quad Cities, Monroe, Monterey (CA), Monterrey, Montgomery, Montrose, Morelia, Nashville, Oaxaca, Oklahoma City, Omaha, Panama City (FL), Pensacola, Peoria, Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Querétaro, Rapid City, Roswell, St. George (UT), St. Louis, San Angelo, San Luis Obispo, San Luis Potosí, Santa Barbara, Santa Fe, Shreveport, Sioux City, Sioux Falls, South Bend, Springfield (IL), Springfield/Branson, Stillwater, Tallahassee, Texarkana, Toronto–Pearson, Torreón/Gómez Palacio, Tri–Cities (TN), Tulsa, Tyler, Waco, Wichita, Wichita Falls, Wilmington (NC), Yuma, Zacatecas Seasonal: Acapulco, Asheville, Cleveland, Eagle/Vail, Glacier Park/Kalispell, Hilton Head, Huatulco, Ixtapa/Zihuatanejo, Key West, Mazatlán, Montreal–Trudeau, Myrtle Beach, Santa Rosa, Sarasota, Traverse City | |
| Avianca El Salvador | San Salvador | |
| Boutique Air | Carlsbad (NM), Greenville (MS), Victoria (TX) | |
| British Airways | London–Heathrow | |
| Delta Air Lines | Atlanta, Detroit, Los Angeles, Minneapolis/St. Paul, New York–JFK, New York–LaGuardia, Salt Lake City, Seattle/Tacoma (begins June 8, 2020) | |
| Delta Connection | Cincinnati, New York–JFK (ends June 7, 2020) | |
| Emirates | Dubai–International | |
| Frontier Airlines | Denver, Las Vegas, Newark, Orlando, Philadelphia Seasonal: Cincinnati | |
| Interjet | Mexico City | |
| Japan Airlines | Tokyo–Haneda | |
| JetBlue | Boston | |
| Korean Air | Seoul–Incheon | |
| Lufthansa | Frankfurt | |
| Qantas | Sydney | |
| Qatar Airways | Doha | |
| Southern Airways Express | El Dorado (AR), Harrison (AR), Hot Springs | |
| Spirit Airlines | Atlanta, Baltimore, Cancún, Chicago–O’Hare, Detroit, Fort Lauderdale, Las Vegas, Los Angeles, New Orleans, New York–LaGuardia, Orlando, Philadelphia, Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Tampa Seasonal: Boston, Cleveland, Myrtle Beach, San Diego, San José del Cabo, Seattle/Tacoma | |
| Sun Country Airlines | Las Vegas Seasonal: Cancún, Cozumel, Liberia (CR) (begins June 13, 2020), Minneapolis/St. Paul, Montego Bay, Puerto Vallarta (begins June 5, 2020), Punta Cana, San José del Cabo (begins June 3, 2020) | |
| United Airlines | Chicago–O’Hare, Denver, Houston–Intercontinental, Newark, San Francisco, Washington–Dulles | |
| United Express | Denver, Houston–Intercontinental, San Francisco, Washington–Dulles | |
| Volaris | Durango (MX), Guadalajara, León/Del Bajío , Zacatecas |
Cargo
| Aerologic | Chicago–O’Hare, Frankfurt |
| AirBridgeCargo Airlines | Amsterdam, Chicago–O’Hare, Frankfurt, Los Angeles, Moscow–Sheremetyevo |
| Air China Cargo | Anchorage, Beijing–Capital, New York–JFK, Shanghai–Pudong |
| Amazon Air | Allentown/Bethlehem, Cincinnati, Ontario, Sacramento, Tampa |
| Ameriflight | Amarillo, Brownwood, Cincinnati, Clinton (OK), Lubbock, McAllen, Midland/Odessa, Nashville, New Orleans, Oklahoma City, Pampa (TX), Phoenix–Sky Harbor, San Angelo, San Antonio, Smyrna (TN), Tulsa, Waco, Wichita, Wichita Falls |
| Amerijet International | Sacramento |
| Asiana Cargo | Atlanta, Chicago–O’Hare, Seattle/Tacoma |
| ASL Airlines Belgium | Atlanta, Liège |
| Avianca Cargo | Bogotá |
| Cargojet | Hamilton, Mexico City, Toronto–Pearson |
| Cargolux | Chicago–O’Hare, Houston–Intercontinental, Los Angeles, Mexico City |
| Cargolux Italia | Milan–Malpensa |
| Cathay Pacific Cargo | Anchorage, Atlanta, Houston–Intercontinental, Los Angeles |
| China Airlines Cargo | Anchorage, Atlanta, Chicago–O’Hare, Shanghai–Pudong, Taipei–Taoyuan |
| DHL Aviation | Cincinnati, El Paso, Hong Kong, Los Angeles |
| Empire Airlines | Lubbock |
| EVA Air Cargo | Anchorage, Atlanta, Chicago–O’Hare, Los Angeles, Seattle/Tacoma, Taipei–Taoyuan |
| FedEx Express | Fort Lauderdale, Indianapolis, Los Angeles, Memphis, Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Seattle/Tacoma |
| Korean Air Cargo | Anchorage, Atlanta, Guadalajara[citation needed] |
| Lufthansa Cargo | Frankfurt, Guadalajara, Mexico City |
| Martinaire | Abilene, Addison, Amarillo, Fort Worth-Meacham, Lubbock, Oklahoma City, Palestine, Pampa (TX), Shreveport, Temple, Tyler, Wichita Falls |
| Nippon Cargo Airlines | Anchorage, Chicago–O’Hare, Tokyo–Narita |
| Qantas Freight | Beijing–Capital, Chongqing |
| Qatar Airways Cargo | Doha, Atlanta, Liège, Luxembourg, Panama City–Tocumen |
| Silk Way West Airlines | Chicago–O’Hare |
| Singapore Airlines Cargo | Anchorage, Brussels, Chicago–O’Hare, Cincinnati, Los Angeles, Seattle/Tacoma |
| UPS Airlines | Albuquerque, Amarillo, Atlanta, Austin, Boston, Chicago–O’Hare, Chicago/Rockford, Columbia (SC), El Paso, Greenville/Spartanburg, Houston–Intercontinental, Little Rock, Los Angeles, Louisville, Memphis, Miami, Newark, Oakland, Ontario, Orlando, Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Portland (OR), San Antonio, San Bernardino, San Jose (CA), Spokane, Tampa Seasonal: Hartford, Honolulu, Knoxville, Minneapolis/St. Paul, Philadelphia |


Accidents and incidents
- August 2, 1985: Delta Air Lines Flight 191, a Lockheed L-1011 on a Fort Lauderdale–Dallas/Fort Worth–Los Angeles route, crashed near the north end of runway 17R (now 17C) after encountering a severe microburst on final approach; the crash killed 8 of 11 crew members, 128 of 152 passengers on board and one person on the ground.
- March 24, 1987: The pilot of a Metroflight Convair CV-580, registration number N73107, operating for American Eagle Airlines on a commuter flight bound for Gregg County Airport, lost directional control during a crosswind takeoff. The left-hand wing and propeller struck the runway and the nose landing gear collapsed as the craft slid off the runway and onto an adjacent taxiway; 8 passengers and 3 crew aboard the airliner suffered minor or no injuries. The crash was attributed to the pilot’s decision to disregard wind information and take off in weather conditions that exceeded the rated capabilities of the aircraft; the pilot’s “overconfidence in [his/her] personal ability” was cited as a contributing factor in the accident report.
- May 21, 1988: An American Airlines McDonnell Douglas DC-10-30, registration number N136AA, operating as AA Flight 70 bound for Frankfurt Airport, overran Runway 35L after automatic warning signals prompted the flight crew to initiate a rejected takeoff. The jetliner continued to accelerate for several seconds before slowing, and did not stop until it had run 1,100 feet (335 m) past the runway threshold, collapsing the nose landing gear. 2 crew were seriously injured and the remaining 12 crew and 240 passengers escaped safely; the aircraft was severely damaged and was written off. Investigators attributed the overrun to a shortcoming in the design standards that were used when the DC-10 was built; there had been no requirement to test whether partially worn (as opposed to brand-new) brake pads were capable of stopping the aircraft during a rejected takeoff and 8 of the 10 worn pad sets on N136AA had failed.
- August 31, 1988: Delta Air Lines Flight 1141, a Boeing 727 bound for Salt Lake City International Airport, crashed after takeoff, killing 2 of 7 crew members and 12 of 101 passengers on board.
- April 14, 1993: The pilot of American Airlines Flight 102, a McDonnell Douglas DC-10-30, registration number N139AA, lost directional control during a crosswind landing in rainy conditions after arriving from Honolulu International Airport. The jetliner slid off runway 17L and dug into deep mud, collapsing the nose landing gear and tearing off the left-hand engine and much of the left wing. A fire in the left-hand wheel well was rapidly extinguished by firefighters who arrived almost immediately from the nearby DFW/DPS Fire Station. 2 passengers suffered serious injuries while using the evacuation slides to escape from the steeply tilted fuselage; the remaining 187 passengers and all 13 crew evacuated safely. The aircraft was written off.
- October 1, 1993: Martinaire Flight 639, a Cessna 208B Caravan cargo aircraft, registration number N9762B, was blown off Runway 17L by jet blast after arriving from Tulsa International Airport, sustaining substantial damage to the left wing. The pilot and sole occupant was not injured. The pilot had disregarded a safety advisory from air traffic control and attempted to taxi behind a McDonnell Douglas MD-11 as it was cleared for takeoff.
- May 23, 2001: The right main landing gear of an American Airlines Fokker 100, registration number N1419D, operating as AA Flight 1107, collapsed upon landing on runway 17C after a scheduled flight from Charlotte/Douglas International Airport. The pilot was able to maintain directional control and stop the aircraft on the runway. The incident was attributed to metal fatigue caused by a manufacturing flaw in the right main gear; there were no serious injuries to the 88 passengers or 4 crew, but the aircraft was badly damaged and was written off.
Source: wikipedia.















