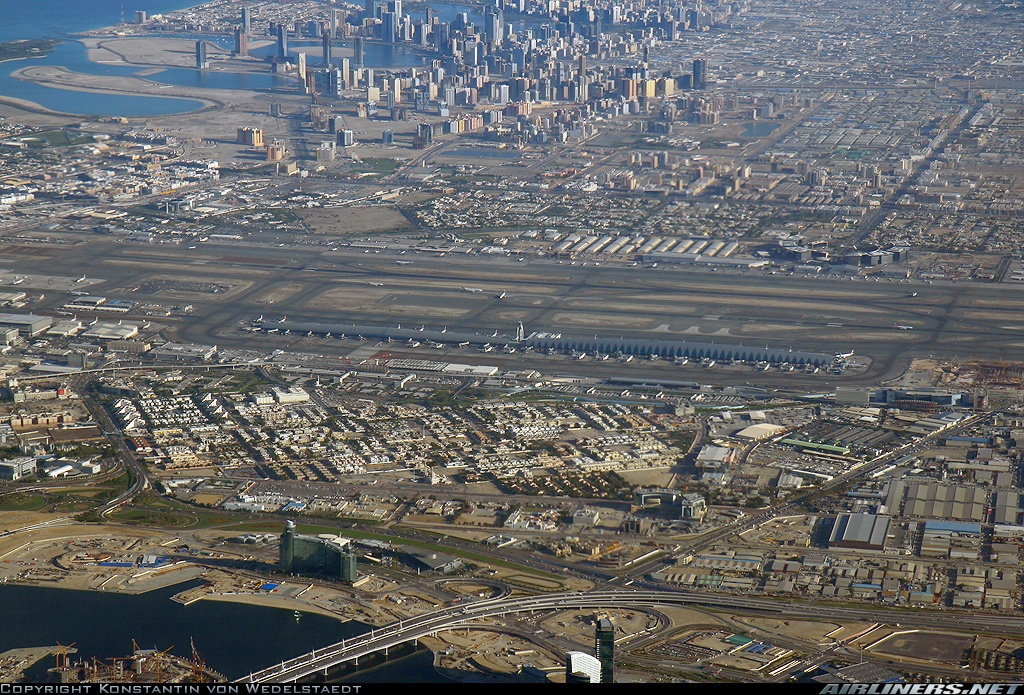
Moscow Sheremetyevo International Airport
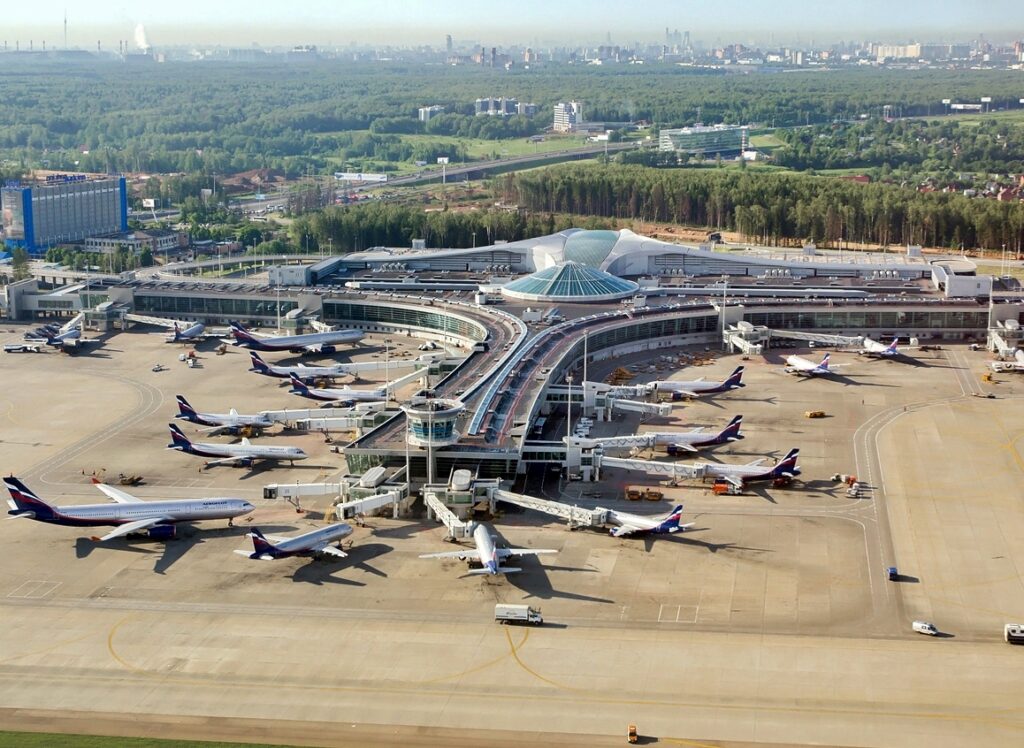

Source: Photo http://cdn-www.airliners.net/aviation-photos/photos/0/2/0/2166020.jpg
| ATA: SVO ICAO: UUEE LID: ШРМ | |
| Airport type | Public |
| Operator | International Airport Sheremetyevo |
| Serves | Moscow, Russia |
| Location | Khimki, Moscow Oblast |
| Hub for | Aeroflot Rossiya Airlines Nordwind Airlines Pegas Fly Royal Flight |
| Elevation AMSL | 192 m / 630 ft |
| Coordinates | |
| Website | svo.aero |
Sheremetyevo Alexander S. Pushkin International Airport (Russian: Международный аэропорт Шереметьево имени А.С. Пушкина, IPA: [ʂɨrʲɪˈmʲetʲjɪvə] Mezhdunarodnyy aeroport Sheremet’yevo imeni A.S. Pushkina) (IATA: SVO, ICAO: UUEE) is one of four international airports that serve the city of Moscow. It is the busiest airport in Russia, as well as the eighth-busiest airport in Europe. Originally built as a military airbase, Sheremetyevo was converted into a civilian airport in 1959, and in a 2019 contest, was named after Russian poet Alexander Pushkin.
The airport comprises six terminals: four international terminals (one under construction), one domestic terminal, and one private aviation terminal. It is located 29 km (18 mi) northwest of central Moscow, in the city of Khimki, Moscow Oblast.
In 2017, the airport handled about 40.1 million passengers and 308,090 aircraft movements. During 2018, the airport reported a 14.3% increase in passengers for a total of 45.8 million. There was also a 15.9% increase in aircraft traffic year over year. Sheremetyevo serves as the main hub for Russian flag carrier Aeroflot and its branch Rossiya Airlines, Nordwind Airlines and its branch Pegas Fly, Royal Flight, and Ural Airlines.

Terminals
Sheremetyevo International Airport has four operating passenger terminals and one special terminal reserved for the use of private and business aviation. The airport’s four passenger terminals are divided into two groups based on geographical location: the Northern Terminal Complex and the Southern Terminal Complex. The current terminal naming system was introduced in December 2009; previously, the terminals were numbered: Sheremetyevo-1 (now Terminal B), Sheremetyevo-2 (now Terminal F), and Sheremetevo-3 (now Terminal D).
Terminal A
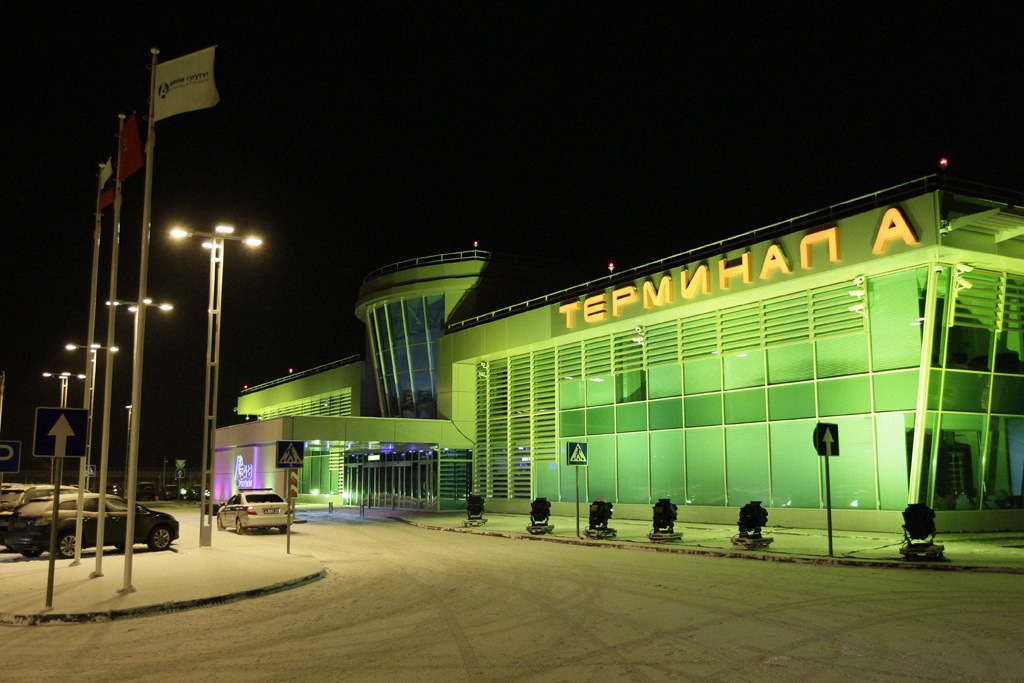

Source: RIA Novosti archive, image #1007581,
http://visualrian.ru/ru/site/gallery/#1007581
Digital / Цифра
Opened on 16 January 2012, Terminal A handles servicing of business and private aviation out of Sheremetyevo. The terminal occupies an area of 3,000 square metres (32,000 sq ft) and can carry an annual capacity of 75,000 passengers.
Northern Terminals
Terminal B
Terminal B – originally named Sheremetyevo-1 – has two iterations.
The first iteration was constructed and opened on 3 September 1964. The terminal, as Sheremetyevo-1, was known for its “flying-saucer”-like design, and was nicknamed “shot glass” by locals. Being 200 metres (660 ft) long and 40 metres (130 ft) wide, as well as having a volume exceeding 100,000 cubic metres (3,500,000 cu ft), the terminal can hold up to 800 people per hour. Formerly serving international flights, Sheremetyevo-1 would transition to serving domestic flights. Along with other Sheremetyevo terminals that underwent Latin lettering conventions, Sheremetyevo-1 was renamed Terminal B on 28 March 2010. Terminal B was then demolished in August 2015 to be reconstructed as a larger and more modern terminal which began in October 2015.

Source: A.Savin (Wikimedia Commons · WikiPhotoSpace)
The new terminal B commenced its operations on 3 May 2018, with the Aeroflot’s flight to Saratov. All airlines that have domestic flights from Sheremetyevo and some flights of Aeroflot began shifting to Terminal B from Terminal D. Compared to the previous terminal B, that was demolished, new terminal will have an increased passenger capacity of 20 million passengers and will serve domestic flights only. As of November 2018, Aeroflot has consolidated all of its domestic services at Terminal B, with the exception of flights to far eastern destinations in Vladivostok, Khabarovsk and Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky. Flights to the eastern Russian shore and some short-haul (including all domestic flights served by widebodies) continue out of SVO’s Terminal D.
The terminal is connected by an interterminal underground passage with Sheremetyevo’s southern terminals and the Aeroexpress railway station.
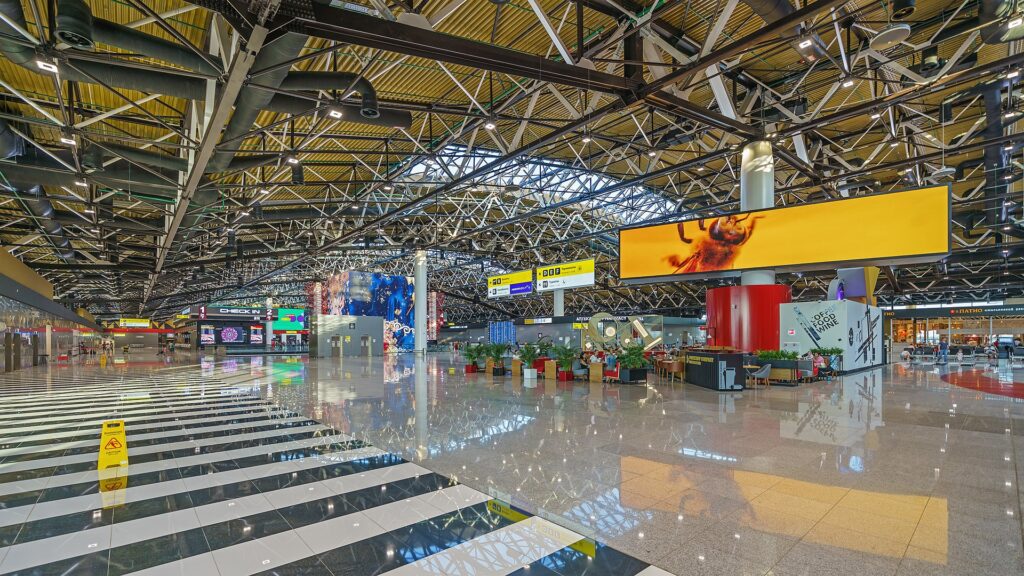
Terminal C
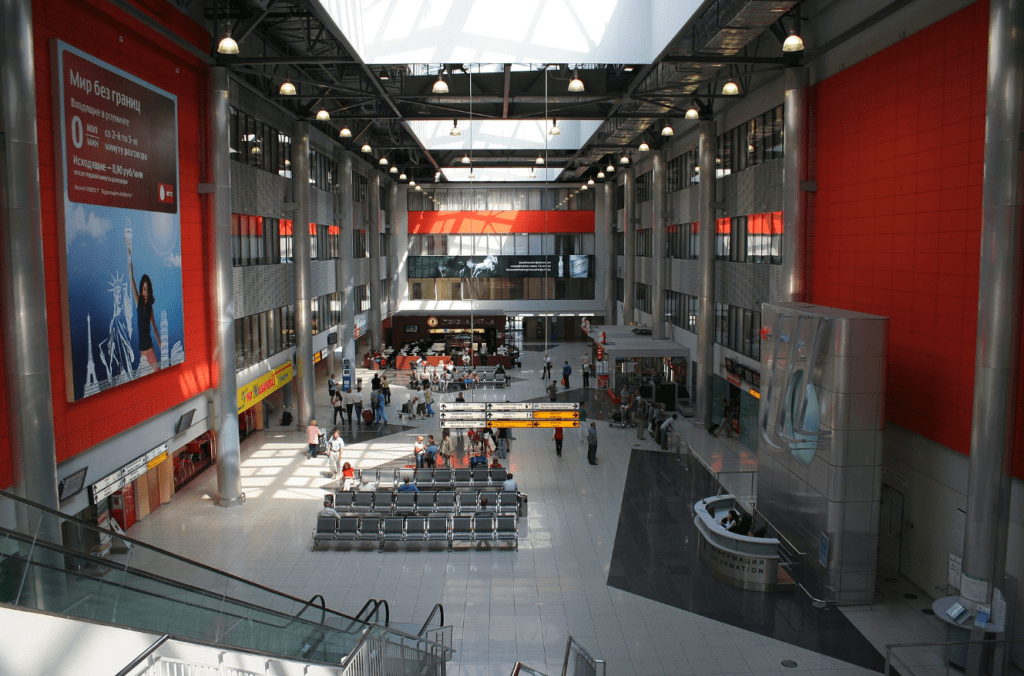
Source: A.Savin (Wikimedia Commons · WikiPhotoSpace)
On 12 March 2007, Sheremetyevo opened the former Terminal C for the servicing of international charter flights to maximize location convenience for all areas in the airport. Located adjacent to the former Terminal B, Terminal C served from 5 to 6 million passengers. The role of Terminal C diminished as passengers for international flights for the airport were distributed among Terminal D and Terminal E. As part of Sheremetyevo’s long-term redevelopment plan, Terminal C was closed on 1 April 2017 to be demolished for construction of a newer terminal.
Integrated with the now-reconstructed domestic Terminal B, the new Terminal C was designed to serve up to 20 million passengers. The first section of the new Terminal C opened on 17 January 2020, with a planned capacity of 20 million passengers. It is called Terminal C1, and some international flights were transferred to that new terminal. Another part called Terminal C2 is scheduled to be opened in 2026, and will add another 10 million passengers capacity.
Southern Terminals
Terminal D
Terminal D, opened in November 2009, is adjacent to Terminal F. The 172,000 m2 (1,850,000 sq ft) building is a hub for Aeroflot and its SkyTeam partners, with capacity for 12 million passengers per year. Aeroflot had been trying to implement the project of a new terminal (Sheremetyevo-3) since January 2001. However, construction only began in 2005, with commissioning of the complex finally taking place on 15 November 2009. The acquisition of its own terminal was a condition of Aeroflot’s entry into the SkyTeam airline alliance, thus necessitating the construction. The main contractor for the build was a Turkish company Enka. Terminal D has 22 jetways and 11 remote stands. On 15 November 2009 at 9:15 a.m., the first flight from Terminal D (the new official name of Sheremetyevo-3) departed for the southern resort city of Sochi. Despite this, Aeroflot took a number of months (due to unexpected administrative delays) to transfer all of its international flights from Terminal F to D (a full transfer was originally planned for February 2010).Whilst previously Terminal D had remained a separate legal entity from the rest of Sheremetyevo Airport, in spring 2012, it became an integrated unit of “Sheremetyevo International Airport” JSC. As part of the deal, Aeroflot, VEB Bank, and VTB Bank, all of which had invested in the construction of Terminal D, became part shareholders in the airport as a whole. The basis for the architectural and artistic image of Terminal D is that of a giant swan with outstretched wings.Interior of Terminal D
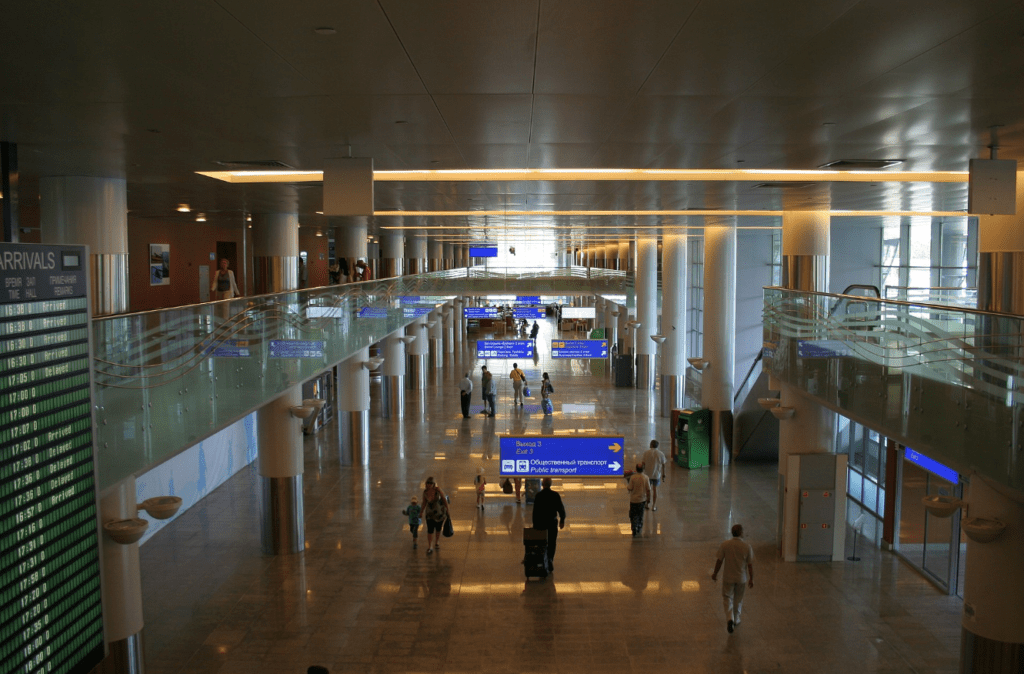

Source: A.Savin (Wikimedia Commons
· WikiPhotoSpace)
There is an official multi-storey parking at Terminal D connected with the main building by means of a pedestrian bridge. The parking size is about 4100 lots, however it has a relatively dense layout, so in most cases, it is difficult to get out of the car without hitting the neighbouring car.
Between 2014 and 2018, Terminal D used to be the only terminal at Sheremetyevo that was able to serve domestic flights. Even since new Terminal B was opened and commenced its services, Terminal D continues to operate non-Aeroflot domestic flights.
On 28 October 2018, Terminal D started handling all of Rossiya Airlines’ Moscow-originating domestic flights and its international service to Indonesia.
Terminal E
Terminal E opened in 2010 as a capacity expansion project, connecting terminals D and F. The terminal’s construction has allowed for the development of terminals D and F, as well as the railway station, into a single south terminal complex. The terminals of this complex are connected by a number of pedestrian walkways with travelators, thus allowing for passengers to move freely between its constituent facilities. In December 2010, a new chapel dedicated to St. Nicholas opened on the second floor of Terminal E. The terminal is used for international flights, primarily by Aeroflot and its SkyTeam partners. Terminal E has 8 jetway equipped gates. The V-Express Transit Hotel between security/passport check-ins provides short-term accommodations for passengers changing planes without having to present a visa for entering Russia. The hotel drew international attention in June 2013 when Edward Snowden checked into the hotel while seeking asylum.
Terminal F
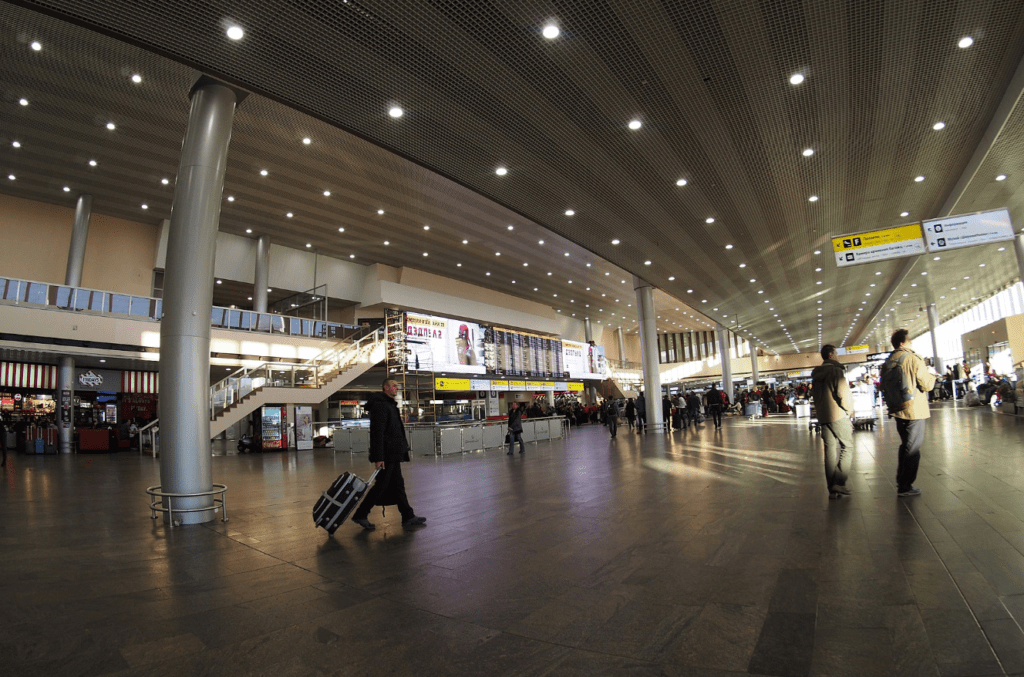

Source: Sheremetyevo F terminal
Opened on 6 May 1980 for Moscow’s Summer Olympics, Terminal F, previously Sheremetyevo-2, has 15 jetways and 21 remote aircraft stands. The terminal was designed to service 6 million passengers per year. Until the completion of the original Terminal C, it was the only terminal that serviced international flights. The design is a larger version of the one of Hannover-Langenhagen Airport by the same architects. A major reconstruction of the terminal and its interior space was completed by late 2009. For the convenience of passengers, the departures lounge and Duty Free zone were thoroughly modernised, whilst a number of partition walls were removed to create extra retail and lounge space.
It was announced that terminal F will be re-constructed after the construction of terminal C is completed.
Terminal G
In November 2019 it was announced that a new Terminal G will also be built. Construction is planned to begin in 2024.
Airlines and destinations
The following airlines serve the following destinations at Sheremetyevo International Airport.
Passenger
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Aeroflot | Abakan, Aktau, Aktobe, Alicante, Almaty, Amsterdam, Anapa, Antalya, Arkhangelsk, Astrakhan, Athens, Atyrau, Baku, Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Barcelona, Barnaul, Berlin–Brandenburg (begins 25 October 2020), Berlin–Schönefeld (ends 24 October 2020), Beijing–Daxing, Beirut, Belgorod, Belgrade, Bishkek, Bologna, Brussels, Bucharest, Budapest, Bukhara, Burgas, Cairo, Chelyabinsk, Chișinău, Colombo–Bandaranaike, Copenhagen, Delhi, Denpasar/Bali (resumes 28 October 2020), Dresden, Dubai–Al Maktoum, Dubai–International, Dublin, Düsseldorf, Frankfurt, Geneva, Gothenburg, Grozny, Guangzhou, Hamburg, Hanoi, Hanover, Havana, Helsinki, Ho Chi Minh City, Hong Kong, Istanbul, Irkutsk, Izhevsk, Kaliningrad, Karagandy, Kazan, Kemerovo, Khabarovsk, Khanty-Mansiysk, Kostanay, Krasnodar, Krasnoyarsk–International, Kyzylorda, Larnaca, Lisbon, Ljubljana, London–Heathrow, Los Angeles, Lyon, Madrid, Magadan, Magnitogorsk, Makhachkala, Málaga, Malé, Marseille, Miami, Milan–Malpensa, Mineralnye Vody, Minsk, Mumbai (resumes 29 March 2021), Munich, Murmansk, Nalchik, Naples, Nazran, New York–JFK, Nice, Nizhnekamsk, Nizhnevartovsk, Nizhny Novgorod, Novokuznetsk, Novosibirsk, Novy Urengoy, Nur-Sultan, Omsk, Orenburg, Orsk, Osaka–Kansai (resumes 29 March 2021), Osh, Oslo–Gardermoen, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Paris–Orly, Penza, Perm, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Phuket, Prague, Riga, Rome–Fiumicino, Rostov-on-Don, Saint Petersburg, Samara, Samarkand, Saransk, Saratov, Seoul–Incheon, Shanghai–Pudong, Shymkent, Simferopol, Singapore (resumes 25 December 2020), Sochi, Sofia, Stockholm–Arlanda, Stuttgart, Surgut, Syktyvkar, Tallinn, Tashkent, Tehran–Imam Khomeini, Tel Aviv, Tenerife–South, Thessaloniki, Tivat, Tokyo–Haneda, Tomsk, Tyumen, Ufa, Ulaanbaatar, Ulan-Ude, Ulyanovsk–Baratayevka, Valencia, Venice, Verona, Vienna, Vilnius, Vladikavkaz, Vladivostok, Volgograd, Voronezh, Warsaw–Chopin, Washington–Dulles, Yakutsk, Yaroslavl, Yekaterinburg, Yerevan, Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, Zagreb, Zürich Seasonal: Gelendzhik, Heraklion, Palma de Mallorca, Rimini (begins 3 July 2020), Split |
| Air Algérie | Algiers |
| airBaltic | Riga |
| Air China | Beijing–Capital |
| Air France | Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| Air Malta | Malta |
| Air Serbia | Belgrade |
| Alitalia | Rome–Fiumicino Seasonal: Catania, Palermo |
| Ariana Afghan Airlines | Kabul, Mazar-i-Sharif |
| Azur Air | Nha Trang Seasonal charter: Antalya |
| Beijing Capital Airlines | Hangzhou, Qingdao |
| Belavia | Minsk |
| Bulgaria Air | Sofia Seasonal: Burgas, Varna |
| Cham Wings Airlines | Damascus |
| China Eastern Airlines | Shanghai–Pudong, Xi’an |
| China Southern Airlines | Beijing–Daxing (begins 15 July 2020), Guangzhou, Lanzhou, Shenzhen, Ürümqi (resumes 20 June 2020), Wuhan |
| Czech Airlines | Prague |
| Ellinair | Thessaloniki |
| Finnair | Helsinki |
| Hainan Airlines | Beijing–Capital, Haikou |
| Iran Air | Seasonal: Tehran–Imam Khomeini |
| Japan Airlines | Tokyo–Haneda |
| KLM | Amsterdam |
| Korean Air | Seoul-Incheon |
| LOT Polish Airlines | Warsaw–Chopin |
| MIAT Mongolian Airlines | Berlin–Tegel, Ulaanbaatar |
| Nordwind Airlines | Blagoveshchensk, Bokhtar, Cheboksary, Chelyabinsk, Fergana, Hanover, Kazan, Khabarovsk, Krasnodar, Krasnoyarsk–International, Magnitogorsk, Mineralyne Vody, Nizhnekamsk, Nizhnevartovsk, Novosibirsk, Orenburg, Orsk, Perm, Rostov-on-Don, Saint Petersburg, Samara, Saratov, Simferopol, Sochi, Turkmenabat, Ufa, Varadero, Volgograd, Yekaterinburg, Yerevan Seasonal: Karshi, Namangan, Omsk, Samarkand, Urgench, Yakutsk Seasonal charter: Amman–Queen Alia, Antalya, Aqaba, Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Barcelona, Burgas, Camagüey, Cancún, Cayo Coco, Dalaman, Djerba, Dubai–Al Maktoum, Girona, Heraklion, Holguín, Izmir, Krabi, Larnaca, Monastir, Montego Bay, Nha Trang, Palma de Mallorca, Phuket, Puerta Plata, Punta Cana, Reus, Salalah, Samaná, Santa Clara, Santa Domingo, Surat Thani, Zanzibar |
| Pegas Fly | Blagoveshchensk, Cheboksary, Guangzhou, Kazan, Krasnodar, Kurgan, Nizhnekamsk, Orenburg, Orsk, Samara, Saransk, Simferopol, Ufa, Volgograd, Yekaterinburg Seasonal: Antalya, Aqaba, Dalaman, Fuzhou, Hangzhou, Istanbul–Sabiha Gökçen, Izmir, Jinan, Larnaca, Monastir, Nanning, Nanjing, Shijiazhuang, Taiyuan, Xi’an, Zhengzhou |
| Rossiya Airlines | Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Khabarovsk, Krasnodar, Mineralnye Vody, Orenburg, Paris–Orly, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Rostov-on-Don, Saint Petersburg, Simferopol, Sochi, Vladivostok, Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk Seasonal charter: Antalya, Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Barcelona, Dubai–International, Eilat, Enfidha, Goa, Larnaca, Paphos, Phuket, Punta Cana, Rimini, Tivat, Zanzibar |
| Royal Flight | Seasonal charter: Agadir, Antaya, Barcelona, Bodrum, Catania, Colombo–Bandaranaike, Corfu, Dalaman, Djerba, Dubai–Al Maktoum, Enfidha, Gazipaşa, Goa, Guiyang, Hefei, Jiangbei, Kos, Malé, Nanning, Nha Trang, Phuket, Phu Quoc, Punta Cana, Reus, Rhodes, Sharjah, Taipei–Taoyuan, Varadero, Yinchuan |
| Severstal Air | Apatity/Kirovsk, Cherepovets |
| Sichuan Airlines | Chengdu |
| Smartwings | Prague |
| TAROM | Bucharest |
| Tianjin Airlines | Seasonal: Hohhot |
| Ural Airlines | Simferopol, Sochi, Yekaterinburg |
| Vietnam Airlines | Hanoi Seasonal charter: Nha Trang (begins 2 July 2020), Phu Quoc (begins 11 September 2020) |
| Yamal Airlines | Salekhard |
Cargo
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| AirBridgeCargo | Amsterdam, Anchorage, Atyrau, Beijing–Capital, Chengdu, Chicago–O’Hare, Frankfurt, Hanoi, Helsinki, Ho Chi Minh City, Hong Kong, Jakarta–Soekarno–Hatta, Leipzig/Halle, London–Heathrow, Los Angeles, Milan–Malpensa, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Phnom Penh, Seoul–Incheon, Shanghai–Pudong, Singapore, Taipei, Tokyo–Narita, Zaragoza, Zhengzhou |
| Air Koryo | Pyongyang |
| ASL Airlines Belgium | Liège |
| DHL Aviation | Leipzig/Halle |
| Korean Air Cargo | Frankfurt, Seoul–Incheon |
| Lufthansa Cargo | Frankfurt, Seoul–Incheon, Tokyo–Narita |
| Silk Way Airlines | Baku, Maastricht/Aachen |
| Turkish Airlines Cargo | Istanbul–Atatürk |
Public access
Rail

Moscow‘s Belorussky station.
Source: SVO_Aeroexpress_
Terminal_station_01.jpg
Aeroexpress, a subsidiary of Russian Railways[74] operates a nonstop line, connecting the airport to Belorussky station in downtown Moscow. A one-way journey takes 35 minutes. The trains offer adjustable seats, luggage compartments, restrooms, electric outlets. Business-class coaches available.
The service started in November 2004, when express train connection was established from Savyolovsky station to Lobnya station, which is 7 km (4.3 mi) from the airport, with the remainder of the journey served by bus or taxi. On 10 June 2008, a 60,000 square meter (645,000 ft2) rail terminal opened in front of Terminal F, with direct service from Savyolovsky station. A shuttle bus service ferried passengers to terminals B and C.[75] From 28 August 2009, the line was extended to Belorussky station with plans to serve all three of Moscow’s main airports from a single point of boarding, and service to Savyolovsky station terminated.
Interterminal underground

Source: A.Savin (Wikimedia Commons · WikiPhotoSpace)
The airport’s Automated Passenger Transportation System (APTS) connects the Terminal B with the Terminals D, E, F and the Aeroexpress railway station.
At the 1st floor of the Terminal B there is an entrance to Sheremetyevo 1 — the northern station. The entrance to Sheremetyevo 2 — the southern station — is at the passage between the terminals D and E.
The APTS is a part of the Interterminal underground passage — a dual tunnel transportation system in the airport. One of the tunnels is dedicated to the transportation of people and featuring an automated people mover (APM). The other tunnel is used for automated baggage transportation.
Bus
Moscow can be reached by the municipal Mosgortrans bus lines: 817 to station Planernaya of Moscow Metro Tagansko-Krasnopresnenskaya Line (#7), 851 to station Rechnoy Vokzal of Zamoskvoretskaya Line (#2), departures every 10 minutes, travel time 33–55 minutes by schedule depending on the terminal served. At night time bus N1 (Russian: Н1) (departures every 30 minutes between 3am and 5:40am) connects the airport to Moscow’s Leningradsky Avenue, downtown area and Leninsky Avenue. Travel time 30–90 minutes, fare is 50 rubles (as of September, 2016).
Other buses serve the connections to the nearby cities: Lobnya (route 21), Zelenograd, Khimki (routes 43,62), Dolgoprudny.
Road
The main road leading to the airport—Leningradskoye Highway—has experienced large traffic jams. Since 23 December 2014, a toll road to the airport has been opened. It connects with MKAD near Dmitrovskoe Highway. Now it is possible to reach the airport in ten minutes, avoiding traffic jams.
Official airport taxis are available from taxi counters in arrivals. Prices to the city are fixed based on zones.
Accidents and incidents
- On 26 September 1960, Austrian Airlines Flight 901 crashed 11 km (6.8 mi) short of the runway at Sheremetyevo Airport. Of the 37 people on board, 31 died.
- On 27 November 1972, Japan Airlines Flight 446, a DC-8-62, crashed while in an initial climb on a route from Sheremetyevo International Airport to Haneda Airport. There were 14 crew members and 62 passengers on board the aircraft. A total of 9 crew and 52 passengers died, with a total of 61 of 76 occupants dead.
- On 28 November 1976, Aeroflot Flight 2415, a Tupolev Tu-104 crashed shortly after takeoff as result of artificial horizon failure. All 67 passengers and six crew members died in the crash.
- On 6 July 1982, Aeroflot Flight 411, an Ilyushin Il-62, crashed on takeoff; all 90 on board died.
- On 22 July 2002, Pulkovo Aviation Enterprise Flight 9560, an Ilyushin Il-86, crashed on takeoff; 14 of the 16 occupants on board died.
- On 3 June 2014, Ilyushin Il-96 RA-98010 of Aeroflot was damaged beyond economical repair in a fire whilst parked.
- On 5 May 2019, Aeroflot Flight 1492, a Sukhoi Superjet 100, crash-landed and caught fire after returning to the airport due to an on-board malfunction shortly after takeoff, killing 41 of the 78 passengers and crew on board and injuring 11 others.
Awards and accolades
In 2018, Sheremetyevo International Airport has been recognized for the best customer service in the busiest airports in Europe category by ACI’s global Airport Service Quality (ASQ) program. In 2018, Sheremetyevo enter the list of the world’s best airports – ACI Director General’s Roll of Excellence. The Official Aviation Guide (OAG) ranked Sheremetyevo International Airport as the most punctual major airport (20 – 30 million departing seats) in the world for 2018 with an on-time performance of 87%.
In February 2019, SVO won an award for strengthening Russia’s national security with its perimeter protection system. In February 2019, Sheremetyevo on top in on-time departure performance in the Major Airports category for February 2019, with 93.65% flights departed on time. In March 2019, Sheremetyevo International Airport was officially awarded a 5-star terminal rating from Skytrax, with Terminal B receiving the 5-star rating after a comprehensive audit.
In January 2020, Sheremetyevo International Airport has been named by the travel data and analytics expert Cirium as the world’s most punctual airport in the annual On-Time Performance (OTP) review, with 95% of its flights departing on-time.
Source: wikipedia



















