Aviation
Amsterdam Airport Schiphol

Source: Ikreis
| IATA: AMS ICAO: EHAM | |
| Airport type | Public |
| Owner/Operator | Royal Schiphol Group |
| Serves | Amsterdam, Netherlands |
| Location | Haarlemmermeer, North Holland |
| Hub for | KLM KLM Cityhopper Martinair Transavia TUI fly Netherlands |
| Focus city for | Corendon Dutch Airlines easyJet Level |
| Elevation AMSL | −11 ft / −3 m |
| Coordinates | |
| Website | schiphol.nl |
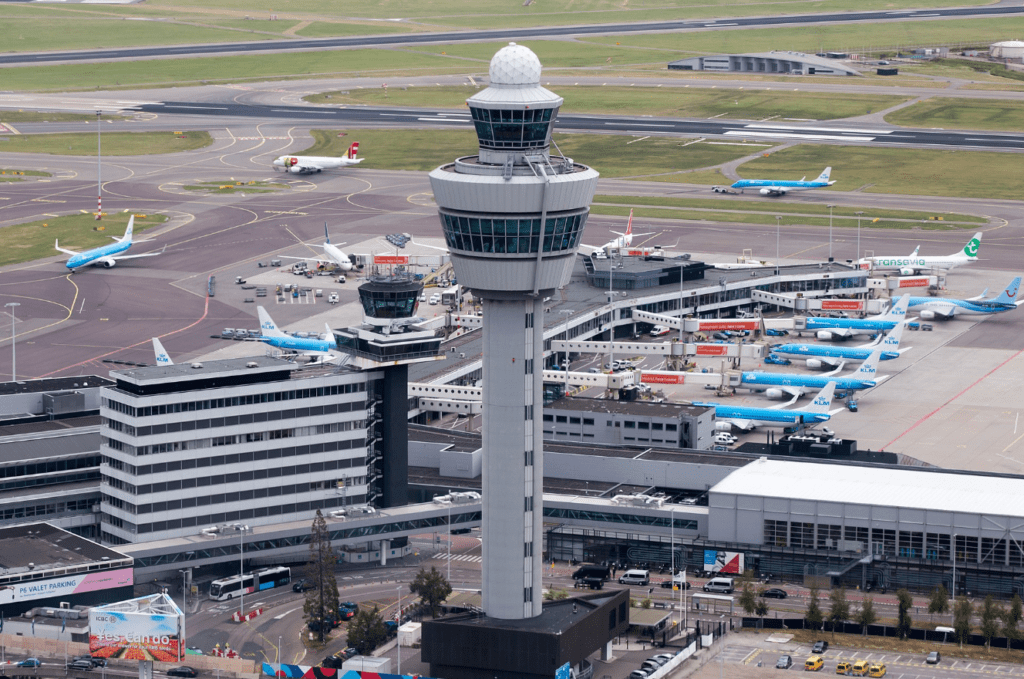
Amsterdam Airport Schiphol (IATA: AMS, ICAO: EHAM), known informally as Schiphol Airport (Dutch: Luchthaven Schiphol, pronounced [ˌlʏxtɦaːvə(n) ˈsxɪp(ɦ)ɔl]), is the main international airport of the Netherlands. It is located 9 kilometres (5.6 miles)southwest of Amsterdam, in the municipality of Haarlemmermeer in the province of North Holland. With almost 72 million passengers in 2019, it is the third-busiest airport in Europe in terms of passenger volume and the busiest in Europe in terms of aircraft movements. With a annual cargo tonnage of 1.74 million, it is the 4th busiest in Europe. The airport is built as a single-terminal concept: one large terminal split into three large departure halls.
Schiphol is the hub for KLM and its regional affiliate KLM Cityhopper as well as for Corendon Dutch Airlines, Martinair, Transavia and TUI fly Netherlands. The airport also serves as a base for EasyJet and LEVEL.
Schiphol opened on 16 September 1916 as a military airbase. The end of the First World War also saw the beginning of civilian use of Schiphol Airport and the airport eventually lost its military role completely. By 1940, Schiphol had four asphalt runways at 45-degree angles. The airport was captured by the German military that same year and renamed Fliegerhorst Schiphol. The airport was destroyed through bombing but at the end of the war, the airfield was soon rebuilt. In 1949, it was decided that Schiphol was to become the primary airport of the Netherlands. Schiphol Airport was voted the Best Airport in Western Europe in 2020.

Source: NielsB
Description
Schiphol Airport is an important European airport, ranking as Europe’s third busiest and the world’s eleventh busiest by total passenger traffic in 2017 (12th in 2016, 14th in 2015, 2014 and 2013 and 16th in 2012). It also ranks as the world’s fifth busiest by international passenger traffic and the world’s sixteenth busiest for cargo tonnage. 63,625,664 passengers passed through the airport in 2016. Schiphol’s main competitors in terms of passenger traffic and cargo throughput are London-Heathrow, Frankfurt, Paris–Charles de Gaulle and Istanbul. In 2010, 65.9% of passengers using the airport flew to and from Europe, 11.7% to and from North America and 8.8% to and from Asia; cargo volume was mainly between Schiphol and Asia (45%) and North America (17%).
In 2010, 106 carriers provided a total of 301 destinations on a regular basis. Passenger destinations were offered by 91 airlines. Direct (non-stop) destinations grew by nine to a total of 274. Regular destinations serviced exclusively by full freighters (non-passenger) grew by eight to a total of twenty-seven.
The airport is built as one large terminal (a single-terminal concept), split into three large departure halls, which connect again once airside. The most recent of these was completed in 1994 and expanded in 2007 with a new section, called Terminal 4, although it is not considered a separate building. A new pier is to be opened in 2019 with a terminal extension planned to be operational by 2023. Plans for further terminal and gate expansion exist, including the construction of a separate new terminal between the Zwanenburgbaan and Polderbaan runways that would end the one-terminal concept.
Because of intense traffic and high landing fees (due to the limit of 500,000 flights a year), some low-cost carriers decided to move their flights to smaller airports, such as Rotterdam The Hague Airport and Eindhoven Airport. Many low-cost carriers, such as EasyJet and Transavia, however, continue to operate at Schiphol, using the low-cost H pier. Lelystad Airport is currently being expanded aimed at accommodating some of the low-cost and leisure flights currently operating out of Schiphol, eventually taking up to 45,000 flights a year.


Source: Amin
Infrastructure
Terminal
Schiphol uses a one-terminal concept, where all facilities are located under a single roof, radiating from the central plaza, Schiphol Plaza. The terminal is divided into three sections or halls designated 1, 2 and 3. The piers and concourses of each hall are connected so that it is possible, on both sides of security or border inspection, to walk between piers and halls, although border control separates Schengen from non-Schengen areas. The exception to this is the low-cost pier M: once airside (past security), passengers cannot access any other areas.
Schiphol Airport has approximately 223 boarding gates including eighteen double jetway gates used for widebody aircraft. The airport adopted a distinctive design, with the second jetway extending over the aircraft wing hanging from a steel cantilever structure. Recent refurbishments have seen most of these jetways being replaced with a more conventional layout. Two gates feature a third jetway for handling of the Airbus A380. Emirates was the first airline to fly the A380 to Schiphol in August 2012, deploying the aircraft on its double daily Dubai–Amsterdam service. During the summer, China Southern Airlines also uses the A380 on its Beijing–Amsterdam route.
Schiphol has large shopping areas as a source of revenue and as an additional attraction for passengers. Schiphol Plaza not only connects the three halls but also houses a large shopping centre and the railway station, also attracting general visitors.
Departure Hall 1
Departure Hall 1 consists of Piers B and C, both of which are dedicated Schengen areas and shares D-pier with Departure hall 2. Pier B has 14 gates and Pier C has 21 gates.
Departure Hall 2
Departure Hall 2 consists of Piers D and E.
Pier D is the largest pier and has two levels. The lower floor houses non-Schengen flights and the upper floor is used for Schengen flights. By using stairs, the same jetways are used to access the aircraft. Schengen gates are numbered beginning with D-59; non-Schengen gates are numbered from D-1 to D-57.
Pier E is a dedicated non-Schengen area and has 14 gates. It is typically home to SkyTeam hub airlines Delta Air Lines and KLM, along with other members, such as China Airlines and China Southern Airlines. Other Middle Eastern and Asian airlines such as Air Astana, EVA Air, Etihad Airways and Iran Air also typically operate out of Pier E.
Departure Hall 3
Departure Hall 3 consists of three piers: F, G, and H/M. Pier F has 8 gates and is typically dominated by SkyTeam members such as primary airline KLM, Kenya Airways, China Airlines and China Southern Airlines, and other members. Pier G has 13 gates. Piers F and G are non-Schengen areas.
Piers H and M are physically one concourse consisting of 7 shared gates and are home to low-cost airlines. Operating completely separately, H handles non-Schengen flights while M is dedicated to flights within the Schengen area.
A380
Gates G9, E18 and E22 (E22 refurbished in 2019) are equipped to handle daily Airbus A380 service by Emirates and China Southern Airlines.
General aviation terminal
A new general aviation terminal was opened in 2011 on the east side of the airport, operated as the KLM Jet Center. The new terminal building has a floorspace of 6,000 m2 (65,000 sq ft); 1,000 m2 (11,000 sq ft) for the actual terminal and lounges, 4,000 m2 (43,000 sq ft) for office space and 1,000 m2 (11,000 sq ft) for parking.
Other facilities
The Rijksmuseum operates an annex at the airport, offering a small overview of both classical and contemporary art. Admission to the exhibits is free.
In summer 2010, Schiphol Airport Library opened alongside the museum, providing passengers access to a collection of 1,200 books (translated into 29 languages) by Dutch authors on subjects relating to the country’s history and culture. The 89.9 m2 (968 sq ft) library offers e-books and music by Dutch artists and composers that can be downloaded free of charge to a laptop or mobile device.
For aviation enthusiasts, Amsterdam Airport Schiphol has a large rooftop viewing area, called the Panoramaterras. It is not accessible to connecting passengers unless they first exit the airport. Enthusiasts and the public can enter, free of charge, from the airport’s landside. Since June 2011, it is the location for a KLM Cityhopper Fokker 100, modified to be a viewing exhibit.[26] Besides the Panoramaterras, Schiphol has other spotting sites, especially along the newest Polderbaan runway and at the McDonald’s restaurant at the north side of the airport.
Schiphol has its own mortuary, where the dead can be handled and kept before departure or after arrival. Since October 2006, people can also hold a wedding ceremony at Schiphol.
Schiphol also has a new state-of-the-art cube-shaped Hilton Amsterdam Airport Schiphol with 433 rooms, rounded corners and diamond-shaped windows. The spacious atrium has a 41-metre-high (135 ft) ceiling made of glass and is in the heart of the building. A covered walkway connects the hotel directly to the terminal. The hotel was completed in 2015.


Source: Wolfgang Pehlemann
Future expansions
In 2012, Schiphol Group announced an expansion of Schiphol, featuring a new pier, an expansion of the terminal, and a new parking garage Pier A will be part of Departure Hall 1, which already has Pier B (14 gates) and Pier C (21 gates). The new Pier A will have 5 narrow-body gates and will initially have 3 wide-body gates, with two more planned for a later phase. The first activities are expected to start in 2017 and to be completed in 2023. The expansions will cost about 500 million euros.
First, the new Pier A will be built to the southwest of Pier B, in an area currently used as a freight platform. Expected to be operational by the end of 2019, pier A will mainly be used for flights within Europe. To handle future growth in passengers, Schiphol will further expand the terminal and build a fourth departure hall with facilities for both departures and arrivals. From this new building, direct access will be made to Schiphol Plaza, continuing the one-terminal concept. When finished in 2023, Schiphol will be able to handle over 70 million passengers. Due to rapid growth of Schengen passengers during 2016, Schiphol was however forced to rapidly build a temporary departure hall which opened in March 2017.

Tower
The Schiphol air traffic control tower, with a height of 101 m (331 ft), was the tallest in the world when constructed in 1991. Schiphol is geographically one of the world’s lowest major commercial airports. The entire airport is below sea level. The lowest point sits at 3.4 m (11 ft) below sea level: 1.4 m (4.5 ft) below the Dutch Normaal Amsterdams Peil (NAP). The runways are around 3 m (9.8 ft) below NAP.
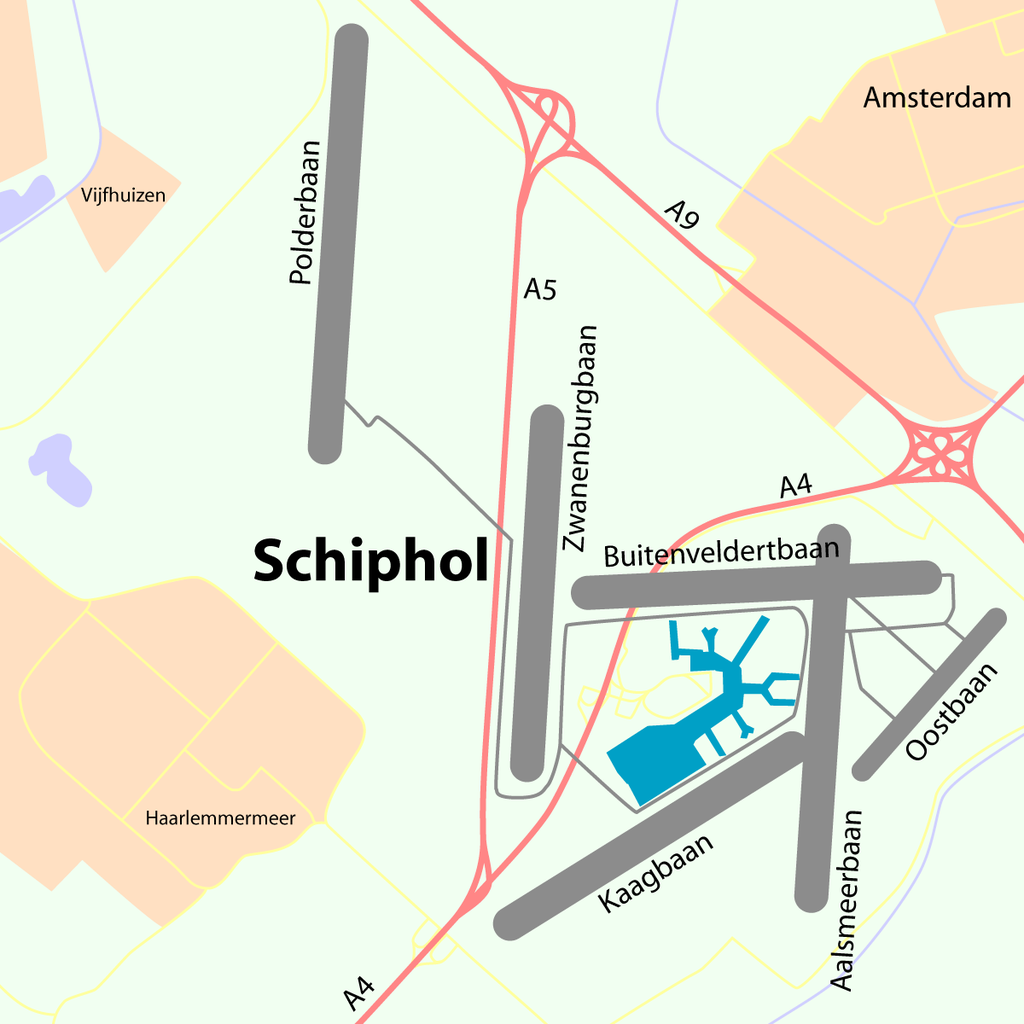
Runways
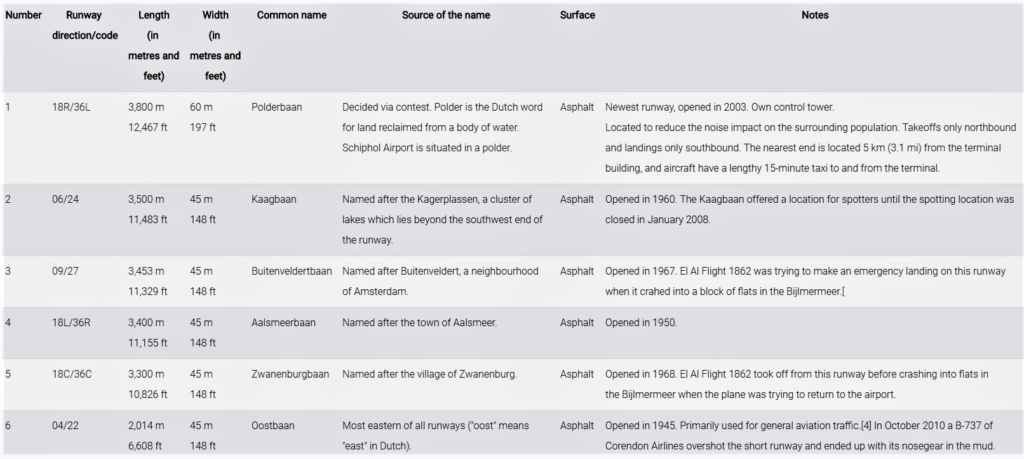

Schiphol has six runways, one of which is used mainly by general aviation. AMS covers a total area of 6,887 acres (2,787 ha) of land.


Source: MartinD
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
| Aegean Airlines | Athens |
| Aer Lingus | Cork, Dublin |
| Aeroflot | Moscow–Sheremetyevo |
| Aeroméxico | Mexico City |
| Air Arabia Maroc | Fez, Nador, Tangier |
| Air Astana | Atyrau |
| airBaltic | Riga, Tallinn, Vilnius |
| Air Canada | Toronto–Pearson |
| Air Europa | Madrid |
| Air France | Nantes, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Rennes, Strasbourg Seasonal: Marseille |
| Air Malta | Malta |
| Air Serbia | Belgrade |
| Air Transat | Seasonal: Toronto–Pearson, Vancouver |
| Alitalia | Milan–Linate, Rome–Fiumicino |
| American Airlines | Philadelphia Seasonal: Dallas/Fort Worth |
| AnadoluJet | Istanbul–Sabiha Gökçen |
| Arkia | Tel Aviv |
| Austrian Airlines | Vienna |
| Belavia | Minsk |
| British Airways | London–City, London–Gatwick, London–Heathrow |
| Bulgaria Air | Sofia |
| Cathay Pacific | Hong Kong |
| China Airlines | Taipei–Taoyuan |
| China Eastern Airlines | Shanghai–Pudong |
| China Southern Airlines | Beijing–Capital, Guangzhou |
| Corendon Airlines Europe | Seasonal: Heraklion |
| Corendon Dutch Airlines | Antalya, Fuerteventura, Funchal, Gran Canaria, Hurghada, Lanzarote, Tenerife–South Seasonal: Alghero, Alicante, Banjul, Bodrum, Burgas, Catania, Corfu, Dalaman, Enfidha, Ercan, Faro, Heraklion, Ibiza, İzmir, Kos, Málaga, Mytilene, Natal, Ohrid, Palma de Mallorca, Preveza (begins 25 April 2020), Rhodes, Sal (begins 3 July 2020), Trapani, Zakynthos |
| Croatia Airlines | Zagreb |
| Czech Airlines | Prague |
| Delta Air Lines | Atlanta, Boston, Detroit, Minneapolis/St. Paul, New York–JFK, Orlando, Portland (OR), Salt Lake City, Seattle/Tacoma Seasonal: Los Angeles (resumes 1 June 2020), Tampa |
| easyJet | Agadir, Alicante, Basel/Mulhouse, Belfast–International, Berlin–Schönefeld, Berlin-Tegel, Bordeaux, Bristol, Budapest, Copenhagen, Edinburgh, Fuerteventura, Geneva, Glasgow, Lisbon, Liverpool, London–Gatwick, London–Luton, London–Southend, London–Stansted, Málaga, Manchester, Milan–Linate, Milan–Malpensa, Naples, Nice, Prague, Rome–Fiumicino, Tel Aviv, Venice, Vienna, Zürich Seasonal: Catania, Corfu, Dubrovnik, Genoa, Hurghada, Ibiza, Lanzarote, Marseille, Olbia, Palma de Mallorca, Pula, Rhodes, Salzburg, Split, Tenerife–South, Toulouse, Verona, Zadar (begins 23 June 2020) |
| EgyptAir | Cairo |
| El Al | Tel Aviv |
| Emirates | Dubai–International |
| Etihad Airways | Abu Dhabi |
| Eurowings | Hamburg, Stuttgart |
| EVA Air | Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Taipei–Taoyuan |
| Finnair | Helsinki |
| Garuda Indonesia | Jakarta–Soekarno-Hatta |
| Georgian Airways | Tbilisi |
| Iberia Express | Madrid |
| Icelandair | Reykjavík–Keflavík |
| Iran Air | Tehran–Imam Khomeini |
| Jet2.com | Leeds/Bradford |
| Kenya Airways | Nairobi–Jomo Kenyatta |
| KLM | Aalborg, Aberdeen, Abu Dhabi, Accra, Ålesund, Alicante, Aruba, Athens, Atlanta, Austin (begins 29 March 2021), Bahrain, Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Barcelona, Basel/Mulhouse, Beijing–Capital, Belfast–City, Bengaluru, Bergen, Berlin–Tegel, Bilbao, Billund, Birmingham, Bogotá, Bologna, Bonaire, Bordeaux, Boston, Bremen, Bristol, Brussels, Bucharest, Budapest, Buenos Aires–Ezeiza, Cagliari, Calgary, Cape Town, Cardiff, Cartagena, Catania, Chengdu, Chicago–O’Hare, Copenhagen, Cork, Curaçao, Dammam, Dar es Salaam, Delhi, Denpasar, Dresden, Dubai–International, Dublin, Düsseldorf, Edinburgh, Edmonton, Entebbe, Florence, Fortaleza, Frankfurt, Gdańsk, Geneva, Genoa, Glasgow, Gothenburg, Graz, Guayaquil, Hamburg, Hangzhou, Hanover, Helsinki, Hong Kong, Houston–Intercontinental, Humberside, Inverness, Istanbul, Jakarta–Soekarno-Hatta, Johannesburg–O.R. Tambo, Kiev–Boryspil, Kigali, Kilimanjaro, Kraków, Kristiansand, Kuala Lumpur–International, Kuwait, Lagos, Las Vegas, Leeds/Bradford, Lima, Linköping, Lisbon, London–City, London–Heathrow, Los Angeles, Luanda, Luxembourg, Lyon, Madrid, Málaga, Manchester, Manila, Marseille, Mexico City, Milan–Linate, Milan–Malpensa, Minneapolis/St. Paul, Montpellier, Montréal–Trudeau, Moscow–Sheremetyevo, Mumbai, Munich, Muscat, Nairobi–Jomo Kenyatta, Nantes, Naples, Newcastle upon Tyne, New York–JFK, Nice, Norwich, Nuremberg, Osaka–Kansai, Oslo–Gardermoen, Panama City, Paramaribo, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Porto, Prague, Quito, Rio de Janeiro–Galeão, Rome–Fiumicino, Saint Petersburg, Sandefjord, San Francisco, Santiago de Chile, São Paulo–Guarulhos, Seoul–Incheon, Shanghai–Pudong, Singapore, St. Maarten, Stavanger, Stockholm–Arlanda, Stuttgart, Taipei–Taoyuan, Tel Aviv, Teesside, Tokyo–Narita, Toronto–Pearson, Toulouse, Trondheim, Turin, Valencia, Vancouver, Växjö, Venice, Vienna, Warsaw–Chopin, Washington–Dulles, Windhoek–Hosea Kutako, Wrocław, Xiamen, Zagreb, Zürich Seasonal: Havana, Ibiza, Liberia, Miami, Salt Lake City, San José de Costa Rica, Split |
| Korean Air | Seoul–Incheon |
| Level | Barcelona, Fuerteventura, Lisbon, London–Luton, Milan–Malpensa, Rome–Fiumicino, Vienna |
| LOT Polish Airlines | Warsaw–Chopin |
| Lufthansa | Frankfurt, Munich |
| Norwegian Air Shuttle | Copenhagen, New York–JFK, Oslo–Gardermoen, Stockholm–Arlanda |
| Pegasus Airlines | Antalya, Istanbul–Sabiha Gökçen Seasonal: Bodrum, İzmir, Kayseri, Konya |
| Qatar Airways | Doha |
| Royal Air Maroc | Casablanca, Nador, Tangier Seasonal: Al Hoceima, Oujda |
| Royal Jordanian | Amman–Queen Alia |
| Ryanair | Dublin, Málaga |
| Scandinavian Airlines | Copenhagen, Oslo–Gardermoen, Stockholm–Arlanda |
| Singapore Airlines | Singapore |
| Sun d’Or | Seasonal: Tel Aviv |
| SunExpress | İzmir Seasonal: Ankara, Antalya, Kayseri, Konya |
| Surinam Airways | Paramaribo |
| Swiss International Air Lines | Zürich |
| TAP Air Portugal | Lisbon, Porto |
| TAROM | Bucharest |
| Transavia | Agadir, Alicante, Almería, Amman–Queen Alia, Athens, Barcelona, Bari, Beirut, Belgrade, Casablanca, Catania, Dubai–International, Faro, Fuerteventura, Funchal, Gran Canaria, Ibiza, Innsbruck, Katowice, Lanzarote, La Palma, Larnaca, Lisbon, Ljubljana, Málaga, Marrakesh, Naples, Nice, Paris–Orly, Pisa, Porto, Reykjavík–Keflavík, Seville, Tel Aviv, Tenerife–South, Thessaloniki, Valencia Seasonal: Ajaccio, Antalya, Bodrum, Chambéry, Chania, Chios, Corfu, Dalaman, Dubrovnik, Eilat, Girona, Heraklion, İzmir, Kalamata, Kefalonia, Kos, Menorca, Mykonos, Olbia, Palermo, Palma de Mallorca, Paphos, Preveza, Rhodes, Sal, Salzburg, Samos, Santorini, Varna, Verona, Zakynthos |
| Transavia France | Paris–Orly |
| TUI fly Belgium | Seasonal: Marrakesh |
| TUI fly Netherlands | Aruba, Banjul, Boa Vista, Bonaire, Cancún, Curaçao, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Holguín, Hurghada, Lanzarote, Málaga, Marsa Alam, Miami, Montego Bay, Orlando/Sanford, Paramaribo, Praia, Punta Cana, Sal, São Vicente, Tenerife–South, Varadero Seasonal: Alicante, Antalya, Baltimore, Bodrum, Burgas, Catania, Chania, Corfu, Dakar–Diass, Dalaman, Djerba, Enfidha, Faro, Funchal, Gazipaşa, Heraklion, Ibiza, Innsbruck, Ivalo, İzmir, Karpathos, Kavala (begins 12 May 2020), Kefalonia, Kittilä, Kos, Kuusamo, La Palma, Menorca, Mombasa, Mykonos, Mytilene, Ohrid, Olbia, Palma de Mallorca, Paphos, Ponta Delgada, Preveza, Pula, Rhodes, Rovaniemi, Samos, Santorini, Sharm El Sheikh, Skiathos, Split, Terceira, Tivat, Varna, Zakynthos, Zanzibar |
| Tunisair | Tunis |
| Turkish Airlines | Istanbul |
| Ukraine International Airlines | Kiev–Boryspil |
| United Airlines | Chicago–O’Hare, Houston–Intercontinental, Newark, Washington–Dulles Seasonal: San Francisco |
| Ural Airlines | Moscow–Zhukovsky |
| Vueling | Alicante, Barcelona, Bilbao, Florence, Málaga, Santiago de Compostela, Valencia Seasonal: Ibiza, Palma de Mallorca |
| XiamenAir | Xiamen |


Source: Vmzp85
Cargo
| Air China Cargo | Shanghai–Pudong, Tianjin |
| AirBridgeCargo | Anchorage, Chengdu, Chicago–O’Hare, Khabarovsk, Los Angeles, Moscow–Domodedovo, Moscow–Sheremetyevo, Novosibirsk, Shanghai–Pudong, Zhengzhou |
| Cargolux | Luxembourg |
| Cathay Pacific Cargo | Chennai, Dubai–Al Maktoum, Frankfurt, Hong Kong |
| China Airlines Cargo | Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Dubai–Al Maktoum, Prague, Taipei–Taoyuan |
| China Cargo Airlines | Copenhagen, Ningbo, Shanghai–Pudong, Tianjin, Xi’an, Zaragoza, Zhengzhou |
| China Southern Airlines Cargo | Chongqing, Guangzhou, Shanghai–Pudong |
| Coyne Airways | Tbilisi |
| DHL Aviation | East Midlands, London–Heathrow |
| Emirates SkyCargo | Barcelona, Chicago O’Hare, Columbus–Rickenbacker, Dubai–Al Maktoum, Houston–Intercontinental, Los Angeles, Luxembourg, Oslo–Gardermoen |
| Etihad Cargo | Abu Dhabi, Bridgetown, Bogotá |
| FedEx Express | Oslo–Gardermoen, Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| Iran Air Cargo | Tehran–Imam Khomeini |
| Kalitta Air | Bahrain |
| Korean Air Cargo | Seoul–Incheon |
| LATAM Cargo Chile | Frankfurt, Campinas–Viracopos, Santiago |
| Martinair | Bogotá, Buenos Aires–Ezeiza, Campinas–Viracopos, Cairo, Dar es Salaam, Guatemala City, Harare, Johannesburg–OR Tambo, Lima, London–Stansted, Miami, Nairobi–Jomo Kenyatta, Quito, Santiago |
| MNG Airlines | Istanbul, Munich, Tripoli–Mitiga |
| Nippon Cargo Airlines | Tokyo–Narita, Milan–Malpensa |
| Qatar Airways Cargo | Chicago–O’Hare, Doha |
| Saudia Cargo | Dammam, Jeddah, Johannesburg–OR Tambo, Nairobi–Jomo Kenyatta |
| Silk Way Airlines | Baku |
| Singapore Airlines Cargo | Bengaluru, Chennai, Chicago–O’Hare, Cincinnati, London–Heathrow, Mumbai, Sharjah, Singapore |
| Suparna Airlines | Hahn, Shanghai–Pudong, Tianjin, Zhengzhou |
| Turkish Cargo | Istanbul-Atatürk, London–Stansted |
Other users
Other regular users of Schiphol are the Netherlands Coastguard whose aircraft are operated by the Royal Netherlands Air Force, the Dienst Luchtvaart Politie and the Dutch Dakota Association.
Other facilities


Source: MartinD
The TransPort Building on the Schiphol Airport property houses the head offices of Martinair and Transavia. Construction of the building, which has 10,800 m2 (116,000 sq ft) of rentable space, began on 17 March 2009. Schiphol Group and the architect firm Paul de Ruiter designed the building, while De Vries and Verburg, a firm of Stolwijk, constructed the building.
The World Trade Center Schiphol Airport houses the head office of SkyTeam, the Netherlands office of China Southern Airlines, and the Netherlands offices of Iran Air. The head office of Schiphol Group, the airport’s operator, is located on the airport property. The Convair Building, with its development beginning after a parcel was earmarked for its development in 1999, houses KLM offices, including KLM Recruitment Services and the head office of KLM Cityhopper. The original control tower of Schiphol Airport, which the airport authorities had moved slightly from its original location, now houses a restaurant. The area Schiphol-Rijk includes the head offices of TUI fly Netherlands and Amsterdam Airlines.
At one time, KLM had its head office briefly on the grounds of Schiphol Airport. Its current head office in nearby Amstelveen had a scheduled completion at the end of 1970. Previously Martinair had its head office in the Schiphol Center (Dutch: Schiphol Centrum) at Schiphol Airport. Formerly, the head office of Transavia was in the Building Triport III at Schiphol Airport. NLM Cityhopper and later KLM Cityhopper previously had their head offices in Schiphol Airport building 70.
Nippon Cargo Airlines has its Europe regional headquarters at Schiphol. The National Aerospace Museum Aviodome–Schiphol was previously located at Schiphol. In 2003, the museum moved to Lelystad Airport and was renamed the “Aviodrome.”


Ground transport
Rail


Source: Michiel1972 at nl.wikipedia
The Nederlandse Spoorwegen (NS), the national Dutch train operator, has a major passenger railway station directly underneath the passenger terminal complex that offers transportation 24 hours a day into the four major cities Amsterdam, Utrecht, The Hague and Rotterdam. There are efficient and often direct services to many other cities in the country. There are intercity connections to Almere, Lelystad, Amsterdam Centraal, Utrecht Centraal, both The Hague Centraal and The Hague HS, Rotterdam Centraal, Eindhoven, ‘s-Hertogenbosch, Leeuwarden, Groningen, Amersfoort Centraal, Apeldoorn, Deventer, Enschede, Arnhem Centraal, Nijmegen and Venlo. Schiphol is also a stop for the Thalys international high-speed train, connecting the airport directly to Antwerp, Brussels and Paris Gare du Nord, as well as to Bourg St Maurice (winter) and Marseille (summer). The Intercity-Brussel (also named “beneluxtrein”) to Antwerp and Brussels stops at the airport.
Bus
Amsterdam Airport Schiphol is also easily accessible by bus, as many services call or terminate at the bus station located outside in front of the terminal building.
| Destination | Service(s) |
|---|---|
| Aalsmeer | 342, night bus N42 |
| Alphen aan den Rijn | 470 |
| Amstelveen | 186, 199, 300, night bus N30 |
| Amsterdam, Leidseplein/city centre | 397, night bus N97 “Amsterdam Airport Express” |
| Amsterdam, Osdorp | 69, 194, 195, night bus N95 |
| Amsterdam, Slotervaart | 69 |
| Amsterdam, Amsterdam–Zuid and Buitenveldert | 341 |
| Amsterdam Bijlmer Arena | 300, night bus N30 |
| Haarlem | 300, night bus N30 |
| Hoofddorp | 300, 397, 341, night bus N30, night bus N97 |
| IJmuiden | Night bus N30 |
| Keukenhof Gardens | 858 (seasonal) |
| Lisse | 361 |
| Leiden | 365 |
| Leimuiden | 370 |
| Nieuw-Vennep | 397, night bus N97 |
| Ouderkerk aan de Amstel | 300, night bus N30 |
| Sassenheim | 361 |
| Schiphol | 180, 181, 185, 186, 187, 190, 191, 193, 194, 195, 198, 199 |
| Uithoorn | 342, night bus N42 |
| Vijfhuizen | 300, night bus N30 |
| Zoetermeer | 365 |
The Taiwanese EVA Air provides private bus services from Schiphol to Belgium for its Belgium-based customers. The service, which departs from and arrives at bus stop C11, goes to Sint-Gillis, Brussels (near the Brussels-South (Midi) railway station) and Berchem, Antwerp (near Antwerp-Berchem bus station). The service is co-operated with Reizen Lauwers NV.
Car
Schiphol Airport can easily be reached by car via the A4 and A9 motorways.
Accidents and incidents


Source: Author
Jos Wiersema. The original uploader was Maaike98 at Dutch Wikipedia., modified by Simeon87.


Source: English: originally posted to Flickr as Crash Turkish Airlines TK 1951
- On 14 November 1946, a Douglas C-47 operated by KLM from London approached Schiphol during bad weather conditions. The first two attempts to land failed. During the third attempt, the pilot realized that the airplane was not lined up properly with the runway. The aircraft made a sharp left turn at low speed, causing the left wing to hit the ground. The airplane crashed and caught fire, killing all 26 people on board.
- On 4 October 1992, El Al Flight 1862, a Boeing 747-200F cargo jet en route to Tel Aviv, lost both right-wing engines (#3 and #4) just after taking off from Schiphol and crashed into an apartment building in the Bijlmer neighbourhood of Amsterdam while attempting to return to the airport. A total of 43 people were killed, including the plane’s crew of three and a non-revenue passenger. In addition to these fatalities, 11 persons were seriously injured and 15 persons received minor injuries.
- On 4 April 1994, KLM Cityhopper Flight 433, a Saab 340 to Cardiff, returned to Schiphol after setting the number two engine to flight idle because the crew mistakenly believed that the engine suffered from low oil pressure because of a faulty warning light. On final approach at a height of 90 ft (27 m), the captain decided to go-around and gave full throttle on only the number one engine leaving the other in flight idle. The airplane rolled to the right, pitched up, stalled and hit the ground at 80 degrees bank. Of the twenty-four people on board, three were killed including the captain. Nine others were seriously injured.
- On 27 October, 2005, a fire at a detention center for drug smugglers and asylum seekers waiting for deportation killed 11 and injured 15.
- On 25 February 2009, Turkish Airlines Flight 1951, a Boeing 737-800 from Istanbul crashed on approach, just 1 km (0.6 mi) short of the airport’s Polderbaan runway. The plane carried 128 passengers and 7 crew on board. 9 people were killed and a further 86 were injured, including six with serious injuries. Four of the dead were employees of Boeing, involved in an advanced radar deal with Turkey. An initial report from the Dutch Safety Board revealed that the left radio altimeter had failed to provide the correct height above the ground and suddenly reported −8 ft (−2.4 m). As a result of this the autothrottle system closed the thrust levers to idle, as it is programmed to reduce thrust when below 27 ft (8.2 m) radio altitude. This eventually resulted in a dropping airspeed that was not acted upon until it was too late to recover, and the aircraft stalled and crashed in a field.
Source: wikipedia















