Berlin Tegel Airport
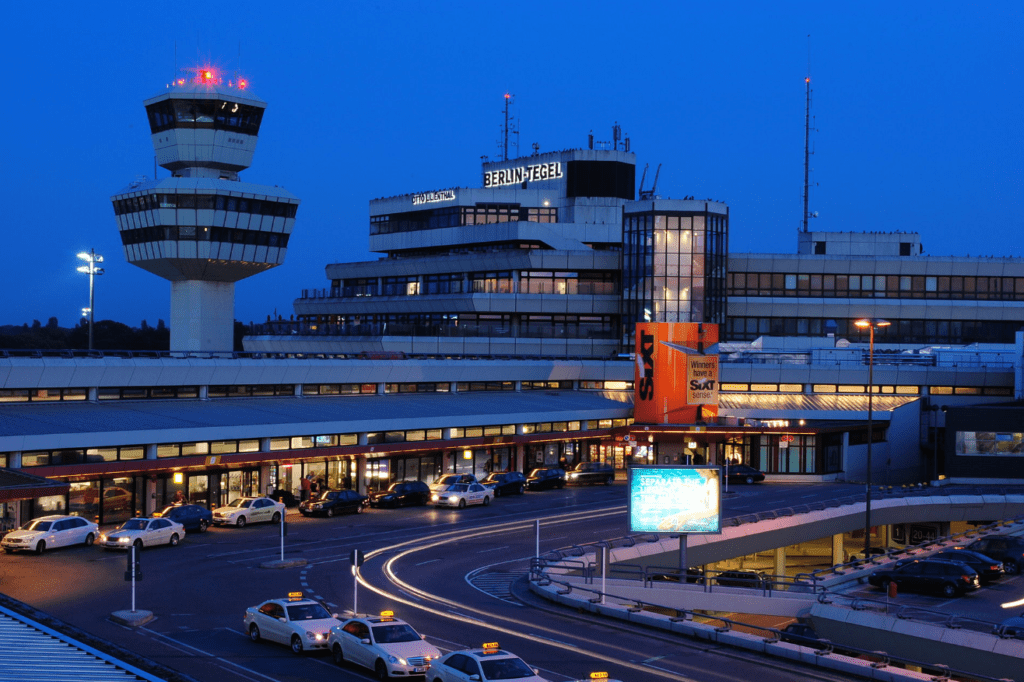

Source: Hans Knips
| IATA: TXL ICAO: EDDT | |
| Airport type | Public |
| Operator | Flughafen Berlin Brandenburg GmbH |
| Serves | Berlin, Germany |
| Location | Reinickendorf borough, Berlin, Germany |
| Opened | 1948 |
| Focus city for | easyJet Eurowings Ryanair Sundair |
| Elevation AMSL | 122 ft / 37 m |
| Coordinates | |
| Website | berlin-airport.de |
Berlin Tegel “Otto Lilienthal” Airport (German: Flughafen Berlin-Tegel „Otto Lilienthal“) (IATA: TXL, ICAO: EDDT) is the main international airport of Berlin, the federal capital of Germany. The airport is named after Otto Lilienthal and is the fourth busiest airport in Germany, with 20.5 million passengers in 2017 and about 22 million in 2018. The airport is a hub for Eurowings as well as a base for EasyJet. It features flights to several European metropolitan and leisure destinations as well as some intercontinental routes.
It is situated in Tegel, a section of the northern borough of Reinickendorf, 8 km (5.0 mi) northwest of the city centre of Berlin. Tegel Airport is notable for its hexagonal main terminal building around an open square, which makes walking distances as short as 30 m (98 ft) from the aircraft to the terminal exit. As of June 2020, Tegel is scheduled to be replaced by Berlin Brandenburg Airport after several delays.

Future development
The airport was scheduled to close in June 2012 after Berlin Brandenburg Airport (BER) opened, but due to ongoing delays with BER, the future of Tegel has long remained uncertain. A campaign was launched to keep Tegel Airport open, which gathered signatures for a referendum for voters to decide on the future of the airport. In September 2017, a public quorum was held parallel to the German federal election to decide whether Tegel Airport should remain open once Berlin Brandenburg Airport starts its operations. The majority of voters voted in favour of Tegel remaining open; however, the federal authorities and the state of Brandenburg, which together hold a majority against Berlin over the airport’s ownership, already declined that wish shortly afterwards, so the shutdown of Tegel is still planned.
Future plans also involve the redevelopment of Berlin Tegel Airport into the Urban Tech Republic, 221 hectares (550 acres) of building land will be available for up to 800 companies with some 17,500 employees in the Research and Industrial Park alone. In the central airport terminal, the Beuth University of Applied Sciences Berlin will establish the scientific core of the new technology park, with up to 2,500 students. It is envisaged that the adjoining areas will be used both for research and development and for manufacturing companies. Berlin TXL will also make 80 hectares (200 acres) available for industrial uses – the largest single inner-city development area in Berlin.
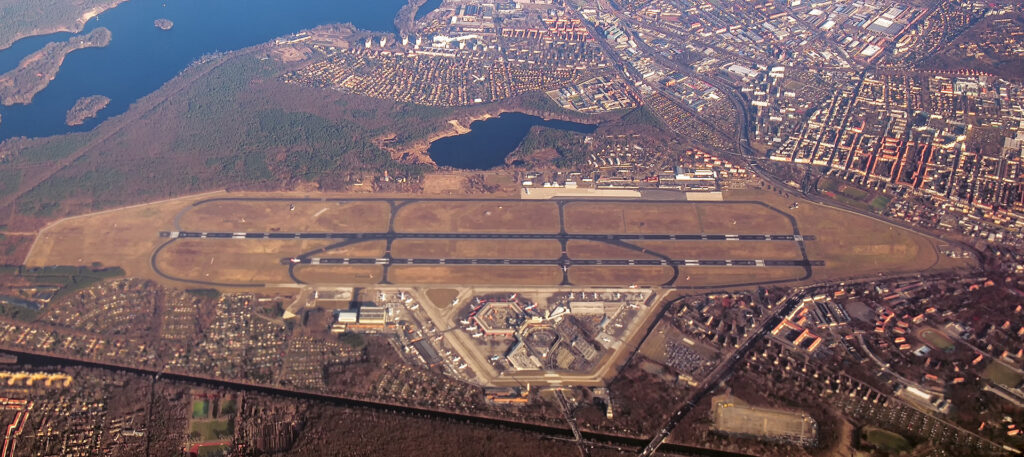

Source: © Ralf Roletschek
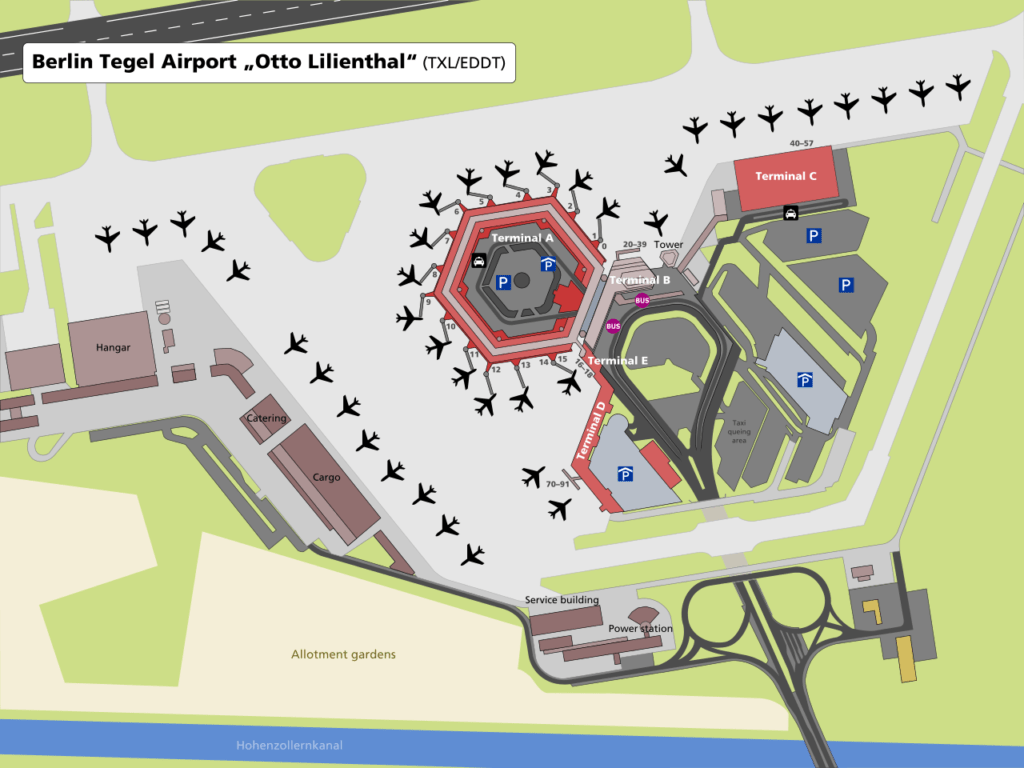
Terminals
Tegel consists of five terminals. As the airport is small compared to other major airports, these terminals might be regarded as “halls” or “boarding areas”; nevertheless, they are officially referred to as “terminals”, even if they share the same building.
Terminals A and B

Source: Matti Blume
The main building is the original part of the airport. It consists of two parts:
- Terminal A is a hexagon-shaped ring concourse with a parking area, taxi stands and bus stops in its middle. It features 14 jet bridges which correspond to 16 respective check-in counters (A00–A15), with jetways 1 and 14 each serving two check-in counters. There is no transit zone, which means that each gate has its own security clearance checkpoint and exit for arriving passengers. Therefore, direct flight connections without leaving the airside area are not possible. Most major airlines arrive and depart here, especially “prestigious” flights like intercontinental services or flights to the busy European hub airports; for example United Airlines flights to Newark and Lufthansa services to Munich and Frankfurt are handled here. The whole rooftop works as a visitor platform. Terminal A is capable of handling wide-bodied aircraft up to the size of a Boeing 767-400ER or Airbus A330-300 on two positions but with only one jet bridge attached to each.
- Terminal B (also called “Nebel-Hall” after German spaceflight pioneer Rudolf Nebel) is a converted former waiting area in a side wing of the main building and features check-in counters B20–B39. There is only one walk-boarding aircraft stand directly serving it. This single stand however can handle widebody aircraft up to the size of the Boeing 777-300ER – currently operated into Tegel by Qatar Airways – and Boeing 747-400.
Source: Michael F. Mehnert
Terminal C
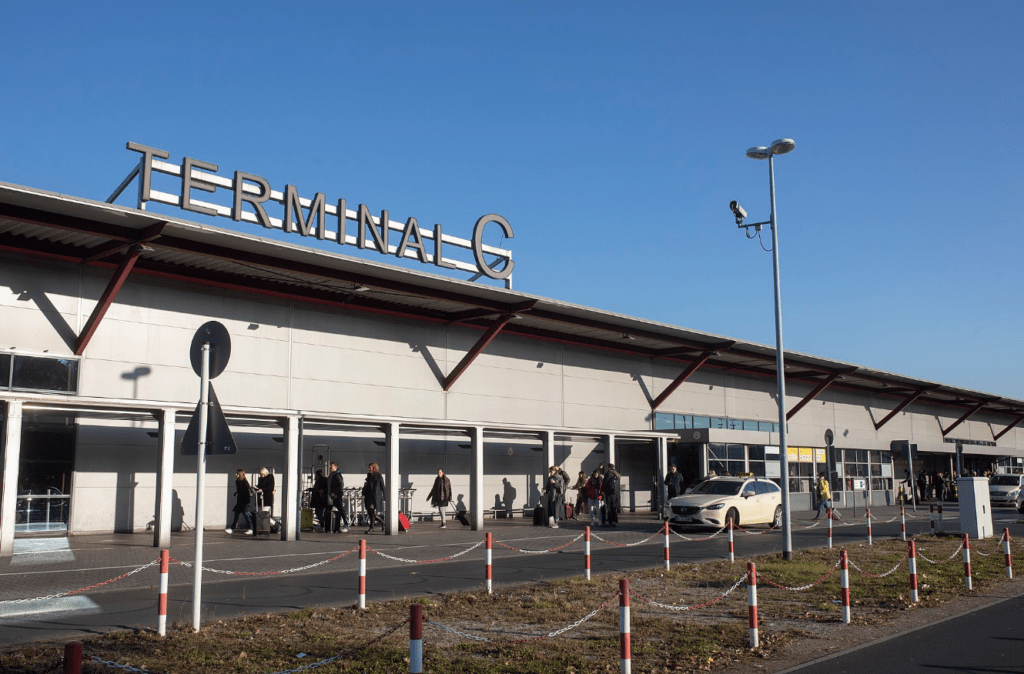

Source: Arne Müseler
Terminal C was opened in May 2007 as a temporary solution because all other terminals operated on their maximum capacity. It was largely used by Air Berlin until its demise. It features 26 check-in counters and the gates numbered C38-C51, C60–C67 (Section C2) and C80-C89 (in the newest addition Section C3). From 2008 until August 2009, 5 additional aircraft stands were constructed and the building was expanded by approximately 50% of its original size, in order to handle another 1.5 million passengers per year. The extended terminal now houses a transit zone for connecting passengers which does not exist at any other terminal at Tegel Airport. Due to noise protection treaties, the overall number of aircraft stands at the airport is restricted, thus aircraft stands on the apron (serving Terminals A and D) had to be removed for compensation. Terminal C is able to handle widebody-aircraft like formerly Air Berlin’s Airbus A330-200s up to the size of a Boeing 747-400 but features no jet bridges.
Terminal D
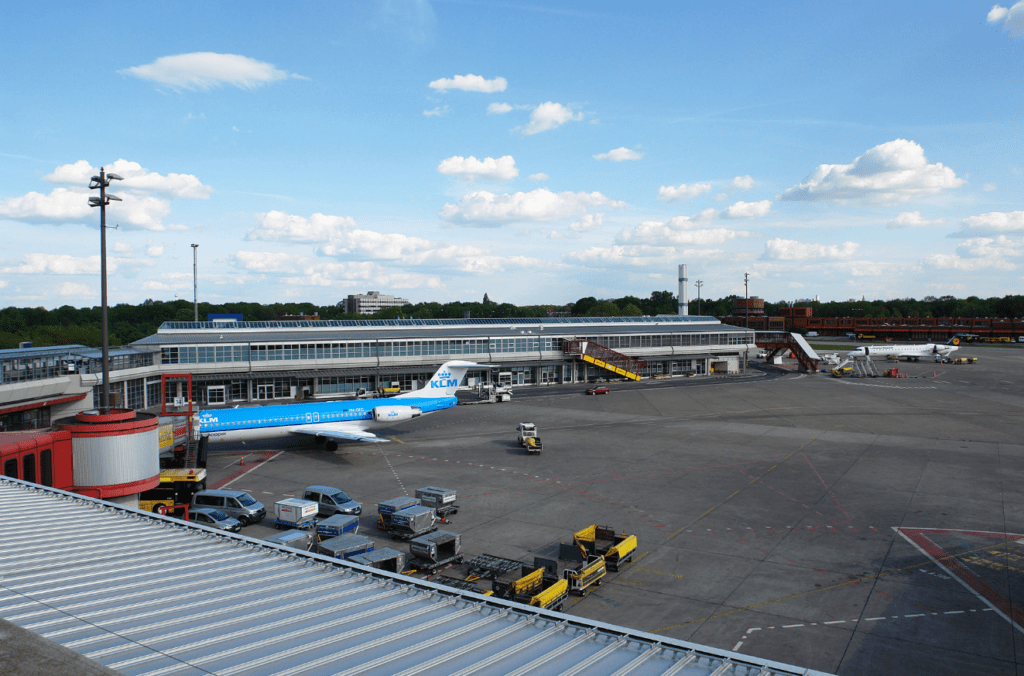

Source: Michael F. Mehnert
Terminal D was opened in 2001 and is a converted car park. It features 22 check-in counters (D70–D91), with one bus-boarding gate and two walk-boarding gates. Most passengers of airlines operating smaller aircraft (like Embraer 190s for example) are brought to the remote aircraft stands by bus from here. Terminal D is the only part of the airport that remains open all night long. The lower level arrival area is called Terminal E (Gates E16-E18).
Tegel Airport was originally planned to have a second hexagonal terminal like the main building right next to it. The second terminal ring was never built because of Berlin municipal budgetary constraints and the post-reunification decision to replace the former West Berlin airports with the new Berlin Brandenburg Airport.
Airlines and destinations
The following airlines operate regular scheduled and charter flights at Berlin Tegel Airport:
| Airlines | Destinations |
|---|---|
| Aegean Airlines | Athens Seasonal: Thessaloniki |
| Aer Lingus | Dublin |
| airBaltic | Riga, Tallinn, Vilnius |
| Air France | Paris–Charles de Gaulle |
| Air Malta | Malta |
| Air Serbia | Belgrade |
| AIS Airlines | Münster/Osnabrück |
| Alitalia | Rome–Fiumicino |
| American Airlines | Seasonal: Philadelphia |
| AnadoluJet | Istanbul–Sabiha Gökçen |
| Austrian Airlines | Vienna |
| Azerbaijan Airlines | Baku |
| British Airways | London–City, London–Heathrow Seasonal: London–Stansted |
| Brussels Airlines | Brussels |
| Bulgaria Air | Sofia |
| Bulgarian Air Charter | Seasonal charter: Burgas, Varna |
| Corendon Airlines | Seasonal: Antalya, İzmir |
| Corendon Airlines Europe | Seasonal: Heraklion, Hurghada |
| Croatia Airlines | Seasonal: Split |
| DAT | Saarbrücken Seasonal: Bornholm (begins 2 July 2020) |
| Delta Air Lines | Seasonal: New York–JFK |
| easyJet | Aarhus, Agadir, Amsterdam, Athens, Basel/Mulhouse, Belgrade, Brussels, Budapest, Catania, Cologne/Bonn, Copenhagen, Düsseldorf, Edinburgh, Faro, Fuerteventura, Funchal, Gothenburg, Granada, Graz, Helsinki, Hurghada, Innsbruck, London–Gatwick, Madrid, Manchester, Marsa Alam, Milan–Malpensa, Munich, Nantes, Oslo, Palma de Mallorca, Paphos, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Paris–Orly, Rome–Fiumicino, Sofia, Stockholm–Arlanda, Stuttgart, Tel Aviv, Toulouse, Venice,Vienna, Zürich Seasonal: Alghero, Alicante, Bari, Biarritz, Brindisi, Cagliari, Chania, Corfu, Dubrovnik, Jerez de la Frontera, Kefalonia, Kos, Menorca, Montpellier, Naples, Nice, Östersund, Preveza, Pula, Rhodes, Sylt, Zadar |
| Eurowings | Cologne/Bonn, Düsseldorf, Palma de Mallorca, Salzburg, Stuttgart Seasonal: Bastia, Dubrovnik, Gran Canaria, Heraklion, Lanzarote, Rijeka, Sarajevo, Split, Tenerife–South, Zadar |
| Finnair | Helsinki |
| Hainan Airlines | Beijing–Capital |
| Iberia Express | Madrid |
| Icelandair | Reykjavík–Keflavík |
| Iraqi Airways | Baghdad, Erbil |
| KLM | Amsterdam |
| LOT Polish Airlines | Warsaw–Chopin |
| Lufthansa | Frankfurt, Munich |
| Luxair | Luxembourg |
| MIAT Mongolian Airlines | Moscow–Sheremetyevo, Ulaanbaatar |
| Nouvelair | Seasonal: Djerba (resumes 30 June 2020) |
| Onur Air | Seasonal: Antalya, Istanbul |
| Pobeda | Moscow–Vnukovo |
| Qatar Airways | Doha |
| Rhein-Neckar Air | Mannheim |
| Royal Air Maroc | Casablanca |
| Royal Jordanian | Amman–Queen Alia |
| Ryanair | Alicante, Faro, Málaga, Milan–Malpensa, Naples, Palma de Mallorca, Tel Aviv Seasonal: Corfu, Heraklion, Ibiza, Kos, Paphos, Pula, Rhodes |
| S7 Airlines | Moscow–Domodedovo |
| Scandinavian Airlines | Copenhagen, Gothenburg, Oslo–Gardermoen, Stockholm–Arlanda |
| Sundair | Beirut Seasonal charter: Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Hurghada, Lanzarote, Tenerife-South |
| SunExpress | Ankara, Antalya, Izmir Seasonal: Bodrum, Dalaman, Gaziantep |
| Swiss International Air Lines | Zürich |
| TAP Air Portugal | Lisbon (resumes 1 August 2020) |
| TUI fly Deutschland | Cairo, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Hurghada, Tenerife–South Seasonal: Heraklion, Kos, Marsa Alam, Rhodes Seasonal charter: Dubai–Al Maktoum |
| Turkish Airlines | Ankara, Istanbul Seasonal: Adana, Antalya, Bodrum (begins 19 June 2020), Diyarbakır (begins 27 June 2020), Gaziantep, Hatay (begins 28 June 2020), Izmir, Kayseri (begins 22 June 2020), Samsun, Trabzon |
| Ukraine International Airlines | Kiev–Boryspil |
| United Airlines | Newark |
| Utair | Moscow–Vnukovo |
| Vueling | Barcelona Seasonal: Bilbao |
Ground transportation
Tegel Airport doesn’t have a direct rail connection but is connected by several bus routes and motorways.
An underground station directly serving the airport had been planned since the 1960s but it was never built due to the expected closure of Tegel Airport. Note that the Alt-Tegel U-Bahn station and Tegel S-Bahn station do not serve Tegel Airport, but rather the Tegel-quarter of Berlin. Currently (2017) an extension of the Berlin Straßenbahn from Hauptbahnhof to Tegel Airport / and the U6 branch from Kurt-Schumacher Platz to Tegel Airport is being discussed but it is unclear whether this extension will open before the closure of the airport.
Car
The airport has a direct connection to motorway A111 (Exit Flughafen Tegel) which further links it to motorways A10, A110 and A115 (via A110) reaching out in all directions. Taxis and car hire are available at the airport, the city center (Alexanderplatz) can be reached within 25 minutes.[citation needed]
Bus
The airport is linked by several BVG bus lines, which offer connection to the U-Bahn and S-Bahn, as well as to Regional Express trains and long distance trains:
- The TXL express bus runs to Beusselstraße S-Bahn station, Berlin Central station (within 20 minutes). It has frequent departures between 7 am and 10 pm.
- The X9 express bus runs to Jakob-Kaiser Platz U-Bahn station (within 5 minutes), Jungfernheide S-Bahn and Regional Express station, and Zoologischer Garten U-Bahn/S-Bahn/Regional Express station (within 20 minutes).
- The 109 bus runs to Jakob-Kaiser Platz U-Bahn station, Charlottenburg S-Bahn and Regional Express station (within 20 minutes), and Zoologischer Garten U-Bahn/S-Bahn/Regional Express station (within 30 minutes) (runs via Kurfürstendamm).
- The 128 bus runs to Kurt-Schumacher-Platz U-Bahn station (within 10 minutes) and Osloer Straße U-Bahn station (within 25 minutes).
Tegel Airport is in regular tariff area B. There is no additional fee for the BVG services from and to the airport.

Source: Avda
Incidents and accidents
There are no recorded fatal accidents involving commercial airline operations at Berlin Tegel itself. However, two commercial flights, one of which was due to arrive at Tegel Airport and the other of which had departed the airport, were involved in fatal accidents. These accidents are listed below:
- On 15 November 1966, Clipper München, a Pan Am Boeing 727–21 (registration N317PA) operating the return leg of the airline’s daily cargo flight to Berlin from Frankfurt Rhein-Main Airport (flight number PA 708) was due to land that night at Tegel Airport, rather than Tempelhof, due to runway resurfacing work taking place at that time at the latter. Berlin Control had cleared flight 708 for an Instrument Landing System (ILS) approach to Tegel Airport’s runway 08, soon after the crew had begun its descent from Flight Level (FL) 090 to FL 030 before entering the southwest air corridor over East Germany on the last stretch of its journey to Berlin. The aircraft impacted the ground near Dallgow, East Germany, almost immediately after the crew had acknowledged further instructions received from Berlin Control, just 10 mi (16 km) from Tegel Airport. All three crew members lost their lives in this accident. Visibility was poor, and it was snowing at the time of the accident. Following the accident, the Soviet military authorities in East Germany returned only half of the aircraft’s wreckage to their US counterparts in West Berlin. This excluded vital parts, such as the flight data recorder (FDR), the cockpit voice recorder (CVR) as well as the plane’s flight control systems, its navigation and communication equipment. The subsequent National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) investigation report concluded that the aircraft’s descent below its altitude clearance limit was the accident’s probable cause. However, the NTSB was unable to establish the factors that had caused the crew to descend below its cleared minimum altitude.
The following notable, non-fatal incidents involving airline operations occurred at Tegel. These include commercial flights that were about to depart or had actually departed/arrived as well as unscheduled stopovers:
- Between 1969 and 1982, Berlin Tegel was the destination of several aircraft hijackings involving LOT Polish Airlines domestic flights within Poland. The hijackings were a means of forcing the authorities in communist Poland to let the hijackers emigrate from the Eastern Bloc. Once the aircraft had landed at Tegel, the French military authorities in charge of the airport during the Cold War era let the hijackers and anyone else who did not wish to return to Poland disembark and claim political asylum in West Berlin. The aircraft, its crew and those passengers who did not want to disembark were subsequently returned to Poland.
- Upon completing the repair and run-up of the faulty engine that had caused a rejected takeoff due to an engine oil warning at Berlin Tegel during the late 1980s, a Dan-Air Boeing 727-200 Adv collided with a jetway at the airport’s terminal building while maintenance engineers taxied the aircraft back to its stand. This badly injured the ground crew member manning the jetway and ruptured the fully refuelled aircraft’s centre wing tank at the left wing root. As a result, a large quantity of jet fuel spilled onto the tarmac. The maintenance engineers’ failure to pressurise the aircraft’s hydraulics had resulted in a complete loss of hydraulic pressure just before reaching the stand, making it impossible to steer the aircraft and rendering the brakes ineffective.
- On 7 January 1997, Austrian Airlines flight 104, a McDonnell Douglas MD-87 en route to Vienna International Airport, was hijacked shortly after takeoff from Tegel Airport by a Bosnian male carrying a knife (which was small enough to be allowed on board under then valid safety regulations). The pilots were forced to return to Berlin, where the perpetrator was overpowered by German police forces.
- On 6 November 1997, an Air France Boeing 737-500 skidded off the runway while landing at Berlin Tegel due to a suspected brake defect. There were no injuries.
There were also two Cold war era incidents relating to an American and a British airliner that had departed Tegel on international non-scheduled passenger services. Both of these occurred in Bulgarian airspace. The former was a charter flight carrying German holidaymakers to the Bulgarian Black Sea coast, the latter a migrant charter en route to Turkey:
- On 28 May 1971, a Modern Air CV-990A with 45 passengers on board en route from Berlin Tegel to Bulgaria was unexpectedly denied permission to enter Bulgarian airspace, as a result of a new policy adopted by that country’s then communist government to deny any aircraft whose flight had originated or was going to terminate at a West Berlin airport the right to take off and land at any of its airports. This resulted in the aircraft having to turn back to Berlin, where it landed safely at the city’s Tegel Airport.
- The same year, a Dan-Air Comet carrying Turkish migrant workers from Berlin Tegel to Istanbul was “escorted” by Bulgarian fighter planes into Sofia. The crew flying the aircraft was attempting to take the shortest route to Istanbul when leaving Yugoslav airspace by entering Bulgarian airspace, instead of taking the longer route through Greek airspace. They were not aware of the then communist government of Bulgaria’s decision not to let any aircraft enter its airspace whose flight had originated or was going to terminate at a West Berlin airport, without stopping en route at another airport outside West Berlin. The aircraft landed safely at Sofia. It was released along with its crew and passengers when the flight’s commander paid with the company’s credit card the fine the Bulgarian authorities had imposed for violating their country’s airspace.
Source: wikipedia



















