Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport

Source: Fyodor Borisov
| IATA: CDG ICAO: LFPG | |
| Airport type | Public |
| Owner/Operator | Groupe ADP |
| Serves | Paris, France |
| Location | 25 km (16 mi) NE of Paris |
| Hub for | Air France |
| Focus city for | Air France HopeasyJetNorwegian Air ShuttleVueling |
| Elevation AMSL | 119 m / 392 ft |
| Coordinates |  49°00′35″N 002°32′52″ECoordinates: 49°00′35″N 002°32′52″ECoordinates:  49°00′35″N 002°32′52″E 49°00′35″N 002°32′52″E |
| Website | parisaeroport.fr |
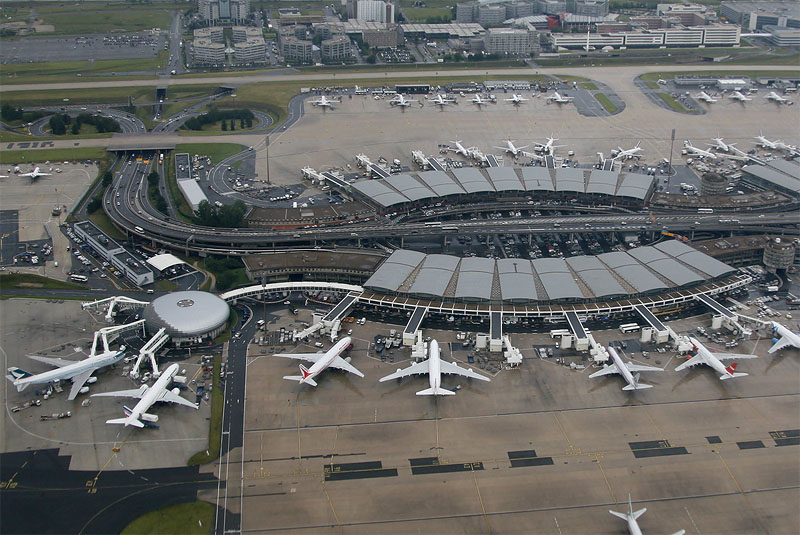
Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport (French: Aéroport de Paris-Charles-de-Gaulle, IATA: CDG, ICAO: LFPG), also known as Roissy Airport, is the largest international airport in France and second-busiest airport in Europe. Opened in 1974, it is located in Roissy-en-France, 23 km (14 mi) northeast of Paris. It is named after Charles de Gaulle (1890–1970).
Charles de Gaulle Airport is located within portions of several communes in Val-d’Oise, Seine-Saint-Denis and Seine-et-Marne. It serves as the principal hub for Air France and a destination for other legacy carriers (from Star Alliance, Oneworld and SkyTeam), as well as a focus city for low-cost carriers easyJet, Vueling, and Norwegian Air Shuttle. The Airport is operated by Groupe ADP under the brand Paris Aéroport.
In 2019, the airport handled 76,150,007 passengers and 498,175 aircraft movements] thus making it the world’s tenth-busiest airport, and Europe’s second-busiest airport (after London Heathrow) in terms of passenger numbers. In terms of cargo traffic, the airport is the twelfth-busiest in the world and the second-busiest in Europe (after Frankfurt Airport), handling 2,150,950 metric tonnes of cargo in 2012.
As of 2017, the airport offers direct flights to the most countries and hosts the most airlines in the world. Marc Houalla has been the director of the airport since 12 February 2018.
Source: CellarDoor85
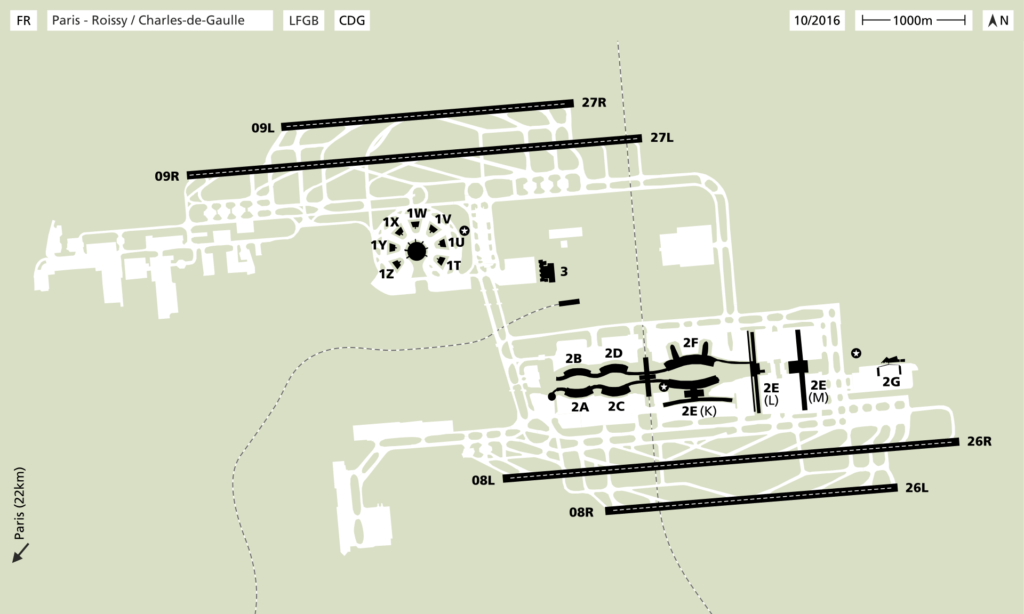
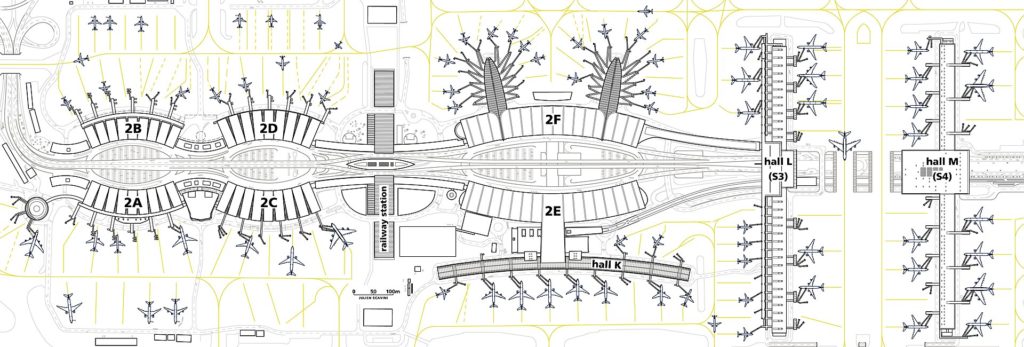
Terminals
Charles de Gaulle Airport has three terminals: Terminal 1 is the oldest and situated opposite to Terminal 3; Terminal 2 is located at another side with 7 sub-terminal buildings (2A to 2G). Terminal 2 was originally built exclusively for Air France; since then it has been expanded significantly and now also hosts other airlines. Terminals 2A to 2F are interconnected by elevated walkways and situated next to each other. Terminal 2G is a satellite building connected by shuttle bus.
Terminal 3 (formerly known as “Terminal 9”) hosts charter and low-cost airlines. The CDGVAL light-rail shuttle connects Terminal 2 to Terminals 1/3 and their parking lots. Refer to Ground Transportation below for inter-terminal transfers and transport to central Paris.
Terminal 1

Source: Dmitry Avdeev, duzik@mail.ru
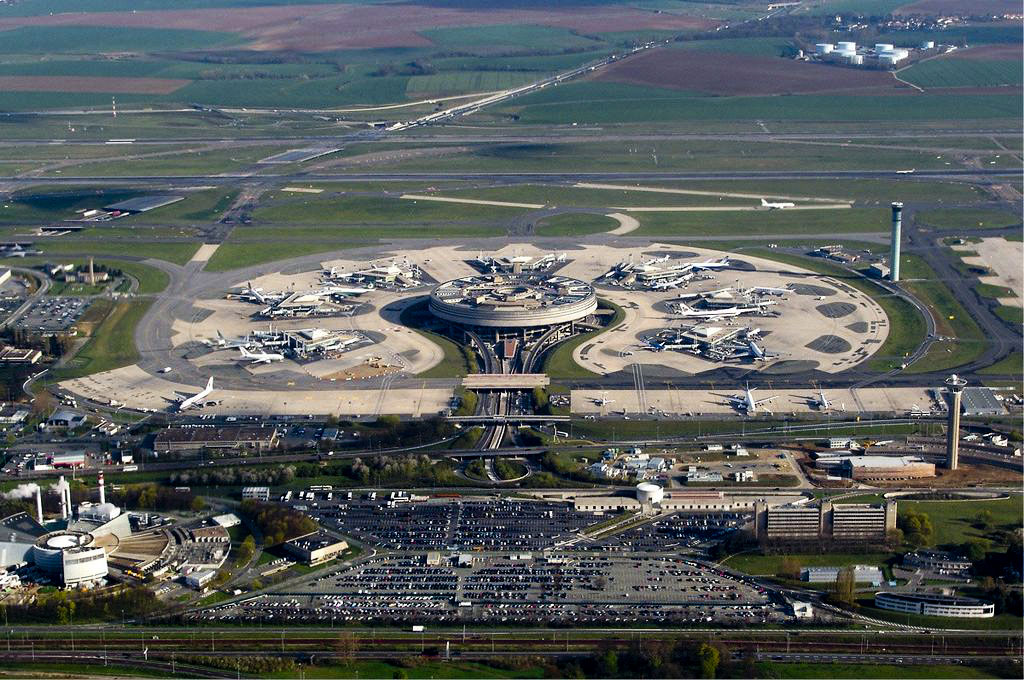
The first terminal, designed by Paul Andreu, was built in the image of an octopus. It consists of a circular terminal building which houses key functions such as check-in counters and baggage claim conveyors. Seven satellites with boarding gates are connected to the central building by underground walkways.
The central building, with a large skylight in its centre, dedicates each floor to a single function. The first floor is reserved for technical operations and not accessible to the public. The second floor contains shops and restaurants, the CDGVAL inter-terminal shuttle train platforms (for Terminal 2 and trains to central Paris) and check-in counters from a recent renovation. The majority of check-in counters, however, are located on the third floor, which also has access to taxi stands, bus stops and special pick-up vehicles. Departing passengers with valid boarding passes can reach the fourth floor, which houses duty-free stores and border control posts, for the boarding gates. The fifth floor contains baggage claim conveyors for arriving passengers. All four upper floors have assigned areas for parking and airline offices.
Passages between the third, fourth and fifth floors are provided by a tangle of escalators arranged through the centre of the building. These escalators are suspended over the central court. Each escalator is covered with a transparent tube to shelter from all weather conditions. These escalators were often used in film shootings (e.g. The Last Gang of Ariel Zeitoun). The Alan Parsons Project album I Robot features these escalators on its cover.
Terminal 2
Terminal 2 is spread across seven sub-terminals: 2A to 2G. Terminals 2A to 2F are connected by inter-terminal walkways, but Terminal 2G is a satellite building 800 m (0.5 mi) away. Terminal 2G can only be accessed by shuttle bus from Terminals 1, 2A to 2F and 3. The CDGVAL inter-terminal shuttle train, Paris RER Regional-Express and high-speed TGV rail station, Aéroport Charles de Gaulle 2 TGV, is located within the Terminal 2 complex and between 2C and 2E (on one side) or 2D and 2F (on the opposite side).
Terminal 2F was used for the filming of the music video for the U2 song “Beautiful Day”. The band also had their picture taken inside Terminal 2F for the album artwork of their 2000 album All That You Can’t Leave Behind.
Collapse of Terminal 2E

Source: Andrewgprout
On 23 May 2004, shortly after the inauguration of terminal 2E, a portion of it collapsed near Gate E50, killing four people.[10] Two of the dead were reported to be Chinese citizens, one Czech and the other Lebanese. Three other people were injured in the collapse. Terminal 2E had been inaugurated in 2003 after some delays in construction and was designed by Paul Andreu. Administrative and judicial enquiries were started. Andreu also designed Terminal 3 at Dubai International Airport, which collapsed while under construction on 28 September 2004.
Before this accident, ADP had been planning for an initial public offering in 2005 with the new terminal as a major attraction for investors. The partial collapse and indefinite closing of the terminal just before the beginning of summer seriously hurt the airport’s business plan.
In February 2005, the results from the administrative inquiry were published. The experts pointed out that there was no single fault, but rather a number of causes for the collapse, in a design that had little margin for safety. The inquiry found the concrete vaulted roof was not resilient enough and had been pierced by metallic pillars and some openings weakened the structure. Sources close to the inquiry also disclosed that the whole building chain had worked as close to the limits as possible, so as to reduce costs. Paul Andreu denounced the building companies for having not correctly prepared the reinforced concrete.
On 17 March 2005, ADP decided to tear down and rebuild the whole part of Terminal 2E (the “jetty”) of which a section had collapsed, at a cost of approximately €100 million. The reconstruction replaced the innovative concrete tube style of the jetty with a more traditional steel and glass structure. During reconstruction, two temporary departure lounges were constructed in the vicinity of the terminal that replicated the capacity of 2E before the collapse. The terminal reopened completely on 30 March 2008.
Source: Julien.scavini
Terminal 2G
Terminal 2, former display screen Air France aircraft on stands at Terminal 2F at Charles de Gaulle Airport.
Terminal 2G, dedicated to regional Air France and HOP! flights and its affiliates, opened in 2008. This terminal is to the east of all terminals and can only be reached by shuttle bus. Terminal 2G is used for passengers flying in the Schengen Area (and thus has no passport control) and handles Air France regional and European traffic and provides small-capacity planes (up to 150 passengers) with a faster turnaround time than is currently possible by enabling them to park close to the new terminal building and boarding passengers primarily by bus, or walking. A bus line called “navette orange” connects the terminal 2G inside the security check area with terminals 2E and 2F. Passengers transferring to other terminals need to continue their trip with other bus shuttles within the security check area if they do not need to get their bags.

Source: Ingolfson
Terminal 2E Hall L (Satellite 3)
The completion of 750 m (2,460 ft) long Satellite 3 (or S3) to the immediate east of Terminals 2E and 2F provides further jetways for large-capacity airliners, specifically the Airbus A380. Check-in and baggage handling are provided by the existing infrastructure in Terminals 2E and 2F. Satellite 3 was opened in part on 27 June 2007 and fully operational in September 2007. It corresponds now to gates L of terminal 2E.
Terminal 2E Hall M (Satellite 4)
The satellite S4, adjacent to the S3 and part of terminal 2E, officially opened on 28 June 2012. It corresponds now to gates M of terminal 2E. Dedicated to long-haul flights, it has the ability to handle 16 aircraft at the same time, with an expected capacity of 7.8 million passengers per year. Its opening has led to the relocation of all SkyTeam airlines to terminals 2E (for international carriers), 2F (for Schengen European carriers) and 2G.
Future
Air France has moved all of its operations previously located at 2C to 2E. In October 2012, 2F closed its international operations and became completely Schengen, allowing for all Air France flights currently operating in 2D to relocate to terminal 2F. Further, in April 2013, Terminal 2B closed for a complete renovation (all airlines relocated to 2D) and will receive upgrades including the addition of a second floor completely dedicated to arrivals. Once 2B is completed, 2D will close and receive similar upgrades, including the addition of a new floor. Low-cost carrier easyJet has shown its interest in being the sole carrier at 2B. To facilitate connections, a new boarding area between 2A and 2C was opened in March 2012. It allows for all security and passport control to be handled in a single area, allows for many new shopping opportunities as well as new airline lounges, and eases transfer restrictions between 2A and 2C.
According to La Tribune newspaper a new Terminal 4 is likely to be built around 2025, when Charles de Gaulle Airport’s maximum capacity of 80 million will be reached. This new Terminal 4, when constructed, will be able to accommodate 30–40 million passengers per year and will most likely be built north of Terminal 2E.
Terminal 3
Terminal 3 is located 1 km (0.62 mi) away from Terminal 1. It consists of one single building for arrivals and departures. The walking distance between Terminals 1 and 3 is 3 km (1.9 mi) long, however, the rail station (named as “CDG Airport Terminal 1”) for RER and CDGVAL trains are only at a distance of 300 m (980 ft). Terminal 3 has no boarding gates constructed and all passengers are ferried via boarding buses to the aircraft stands

Source: Greenboost
Roissypôle
Roissypôle is a complex consisting of office buildings, shopping areas, hotels, and a bus coach and RER B station within Charles de Gaulle Airport. The complex includes the head office of Air France, Continental Square, the Hilton Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport, and le Dôme building. Le Dôme includes the head office of Air France Consulting, an Air France subsidiary. Continental Square has the head office of Air France subsidiary Servair and the Air France Vaccinations Centre.
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
| Aegean Airlines | Athens, Thessaloniki Seasonal: Corfu, Heraklion, Kalamata, Rhodes |
| Aer Lingus | Cork, Dublin Seasonal: Shannon |
| Aeroflot | Moscow–Sheremetyevo |
| Aeroméxico | Mexico City |
| Air Algérie | Algiers, Annaba, Béjaïa, Biskra, Chlef, Constantine, Oran Seasonal: El Oued, Tlemcen |
| Air Arabia Maroc | Fez, Marrakesh, Tangier |
| Air Astana | Almaty (resumes 3 June 2020), Nur-Sultan (ends 31 May 2020) |
| Air Austral | Saint-Denis de la Réunion Seasonal: Dzaoudzi |
| airBaltic | Riga, Tallinn, Vilnius |
| Air Canada | Montréal–Trudeau, Toronto–Pearson Seasonal: Vancouver |
| Air Cairo | Hurghada, Luxor |
| Air China | Beijing–Capital, Chengdu, Shanghai–Pudong |
| Air Corsica | Seasonal: Bastia |
| Air Europa | Málaga, Valencia |
| Air France | Aberdeen, Abidjan, Abuja, Accra, Alicante, Algiers, Amman–Queen Alia, Amsterdam, Antananarivo, Athens, Atlanta, Bamako, Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi, Bangui, Barcelona, Basel/Mulhouse, Beijing–Capital, Beirut, Belgrade, Bengaluru, Bergen, Berlin–Tegel, Biarritz, Bilbao, Billund, Birmingham, Bogotá, Bologna, Bordeaux, Boston, Brazzaville, Bremen, Brest, Bucharest, Budapest, Buenos Aires–Ezeiza, Cairo, Cancún, Cape Town, Caracas, Casablanca, Catania, Chennai (resumes 27 October 2020), Chicago–O’Hare, Clermont-Ferrand, Conakry, Copenhagen, Cotonou, Dakar–Diass, Delhi, Detroit, Djibouti, Douala, Dubai–International, Dublin, Düsseldorf, Edinburgh, Faro, Florence, Fortaleza, Frankfurt, Freetown, Geneva, Genoa, Gothenburg, Hamburg, Hanover, Havana, Ho Chi Minh City, Hong Kong, Houston–Intercontinental, Istanbul, Johannesburg–O. R. Tambo, Kiev–Boryspil, Kinshasa–N’djili, Kraków, Lagos, Libreville, Lima, Lisbon, Ljubljana, Lomé, London–Heathrow, Lorient, Los Angeles, Luanda, Lyon, Madrid, Malabo, Malaga, Manchester, Marrakesh, Marseille, Mauritius, Mexico City, Miami, Milan–Linate, Milan–Malpensa, Monrovia, Montpellier, Montréal–Trudeau, Moscow–Sheremetyevo, Mumbai, Munich, Nairobi–Jomo Kenyatta, Nantes, Naples, N’Djamena, Newcastle upon Tyne, New York–JFK, Niamey, Nice, Nouakchott, Nuremberg, Oran, Osaka–Kansai, Oslo–Gardermoen, Ouagadougou, Palma de Mallorca, Panama City–Tocumen, Papeete, Pau, Pointe-Noire, Port Harcourt, Porto, Prague, Punta Cana, Quito, Rabat, Rennes, Rio de Janeiro–Galeão, Rome–Fiumicino, Saint Petersburg, San Francisco, San José de Costa Rica, Santiago de Chile, Santo Domingo–Las Américas, São Paulo–Guarulhos, Seattle/Tacoma, Seoul–Incheon, Seville (begins 1 June 2020), Shanghai–Pudong, Singapore, St. Maarten, Stockholm–Arlanda, Stuttgart, Taipei–Taoyuan, Tel Aviv, Tokyo–Haneda, Tokyo–Narita, Toronto–Pearson, Toulouse, Tunis, Turin, Valencia, Vancouver, Venice, Vienna, Warsaw–Chopin, Washington–Dulles, Wrocław, Wuhan, Yaoundé, Yerevan, Zagreb, Zurich Seasonal: Ajaccio, Bari, Cagliari, Cork, Dallas/Fort Worth, Djerba (begins 13 July 2020), Dubrovnik, Heraklion, Ibiza, Mahé, Malé, Minneapolis/St. Paul, Mykonos (begins 13 July 2020), Olbia, Palermo, Perpignan, Santorini (begins 13 July 2020), Sofia, Split, Tbilisi, Thessaloniki (begins 13 July 2020) |
| Air India | Delhi |
| Air Madagascar | Antananarivo |
| Air Malta | Malta |
| Air Mauritius | Mauritius |
| Air Saint-Pierre | Seasonal: Saint-Pierre |
| Air Senegal | Dakar–Diass |
| Air Serbia | Belgrade |
| Air Tahiti Nui | Los Angeles, Papeete |
| Air Transat | Montréal–Trudeau, Québec City, Toronto–Pearson |
| Alitalia | Milan–Linate, Rome–Fiumicino |
| All Nippon Airways | Tokyo–Haneda |
| American Airlines | Dallas/Fort Worth, Miami, New York–JFK, Philadelphia Seasonal: Charlotte, Chicago–O’Hare |
| AnadoluJet | Istanbul–Sabiha Gökçen |
| Arkia | Seasonal: Tel Aviv |
| Asiana Airlines | Seoul–Incheon |
| ASL Airlines France | Algiers, Tel Aviv Seasonal: Calvi, Chlef, Djerba (begins 29 June 2020), Oujda |
| Atlantic Airways | Seasonal: Vágar |
| Austrian Airlines | Vienna |
| Azerbaijan Airlines | Baku |
| Belavia | Minsk |
| Blue Air | Bucharest, Turin |
| British Airways | London–Heathrow |
| Brussels Airlines | Brussels |
| Bulgaria Air | Sofia |
| Cabo Verde Airlines | Sal |
| Cathay Pacific | Hong Kong |
| China Eastern Airlines | Beijing–Daxing (begins 14 June 2020), Qingdao, Shanghai–Pudong |
| China Southern Airlines | Guangzhou |
| Corendon Airlines | Antalya |
| Croatia Airlines | Zagreb Seasonal: Dubrovnik, Pula, Split, Zadar |
| Czech Airlines | Prague |
| Delta Air Lines[40] | Atlanta, Boston, Cincinnati, Detroit, Indianapolis, Los Angeles, Minneapolis/St. Paul, New York–JFK, Raleigh/Durham, Salt Lake City, Seattle/Tacoma |
| easyJet[41] | Barcelona, Belfast–International, Berlin–Schönefeld, Berlin–Tegel, Biarritz, Bristol, Budapest, Catania, Copenhagen, Edinburgh, Faro, Glasgow, Kraków, Lanzarote, Lisbon, Liverpool, London–Gatwick, London–Luton, London–Southend, London–Stansted, Madrid, Málaga, Manchester, Marrakesh, Milan–Linate, Milan–Malpensa, Nice, Pau, Porto, Tel Aviv, Toulouse, Venice Seasonal: Ajaccio, Bastia, Bilbao, Corfu, Figari, Fuerteventura, Heraklion, Ibiza, Menorca, Montpellier, Mykonos, Olbia, Palma de Mallorca, Pula, Split, Tenerife–South |
| EgyptAir | Cairo Seasonal: Luxor |
| El Al[42] | Tel Aviv |
| Emirates | Dubai–International |
| Ethiopian Airlines | Addis Ababa |
| Etihad Airways | Abu Dhabi |
| Eurowings | Düsseldorf, Hamburg |
| EVA Air | Taipei–Taoyuan |
| Finnair | Helsinki Seasonal: Kittilä |
| FlyOne | Seasonal: Chișinău |
| Georgian Airways | Tbilisi |
| Gulf Air | Bahrain |
| Hainan Airlines | Chongqing, Guiyang, Shenzhen, Xi’an |
| Iberia Express | Madrid |
| Iberia Regional | Seasonal: Vigo (ends 30 October 2020) |
| Icelandair | Reykjavík–Keflavík |
| Iran Air | Tehran–Imam Khomeini |
| Israir Airlines | Seasonal: Tel Aviv |
| Japan Airlines | Tokyo–Haneda |
| Jet2.com | Leeds/Bradford |
| Kenya Airways | Nairobi–Jomo Kenyatta |
| KLM | Amsterdam |
| Korean Air | Seoul–Incheon |
| Kuwait Airways | Kuwait City |
| LATAM Brasil | São Paulo–Guarulhos |
| Level | Vienna |
| LOT Polish Airlines | Warsaw–Chopin |
| Lufthansa | Frankfurt, Munich |
| Luxair | Luxembourg |
| Middle East Airlines | Beirut |
| Montenegro Airlines | Podgorica Seasonal: Tivat |
| Norwegian Air Shuttle | Copenhagen, Fort Lauderdale, Los Angeles, New York–JFK, Orlando, Oslo–Gardermoen, San Francisco, Stockholm–Arlanda Seasonal: Austin, Bergen, Boston, Chicago–O’Hare, Denver, Helsinki |
| Oman Air | Muscat |
| Pakistan International Airlines | Islamabad, Lahore |
| Pegasus Airlines | Ankara |
| Qatar Airways | Doha |
| Rossiya | Saint Petersburg |
| Royal Air Maroc | Casablanca |
| Royal Jordanian | Amman–Queen Alia |
| Saudia | Jeddah, Riyadh |
| Scandinavian Airlines | Copenhagen, Gothenburg, Oslo–Gardermoen, Stockholm–Arlanda Seasonal: Stavanger |
| Singapore Airlines | Singapore |
| SmartWings | Seasonal: Heraklion, Podgorica (begins 5 June 2020), Prague, Rhodes, Tenerife–South |
| SunExpress | Ankara, Antalya, İzmir |
| Swiss International Air Lines | Zurich |
| TAROM | Bucharest |
| Tassili Airlines | Algiers |
| Thai Airways | Bangkok–Suvarnabhumi |
| TUIfly Belgium | Casablanca Seasonal: Málaga, Oujda, Rabat Seasonal charter: Longyearbyen |
| Tunisair | Djerba, Monastir, Tozeur |
| Turkish Airlines | Ankara, Istanbul |
| Ukraine International Airlines | Kiev–Boryspil |
| United Airlines | Chicago–O’Hare, Newark (resumes 5 June 2020), San Francisco, Washington–Dulles |
| Ural Airlines | Yekaterinburg |
| Uzbekistan Airways | Tashkent, Urgench |
| Vietnam Airlines | Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City |
| Vueling | Alicante, Barcelona, Copenhagen, Fuerteventura, Granada, Gran Canaria, London–Gatwick, Madrid, Menorca, Palma de Mallorca, Porto, Prague, Rome–Fiumicino, Santiago de Compostela, Seville, Venice Seasonal: Dubrovnik, Genoa, Ibiza |
| WestJet | Seasonal: Calgary, Halifax |
| XiamenAir | Fuzhou |

Cargo
| AirBridgeCargo | Moscow–Sheremetyevo |
| Air France Cargo | Algiers, Antananarivo, Atlanta, Bahrain, Bamako, Bangui, Boston, Brazzaville, Cairo, Casablanca, Chicago–O’Hare, Dammam, Djibouti, Douala, Dubai–International, Dublin, Guadalajara, Hanoi, Hong Kong, Houston–Intercontinental, Istanbul–Atatürk, Jeddah, Kuwait, Mexico City, Nairobi–Jomo Kenyatta, N’Djamena, Niamey, New York–JFK, Nouakchott, Ouagadougou, Pointe-Noire, Port Harcourt, Porto, Glasgow-Prestwick, Saint Denis de la Réunion, Seoul–Incheon, Shanghai–Pudong, Tokyo–Narita, Toronto–Pearson, Tripoli, Tunis |
| ASL Airlines Belgium | Liège |
| ASL Airlines France | Bordeaux, Brest, Lorient, Lourdes, Lyon, Nantes, Nice, Pau, Toulouse |
| Cathay Pacific Cargo | Delhi, Frankfurt, Hong Kong, London–Heathrow, Mumbai |
| China Airlines Cargo | Taipei–Taoyuan |
| China Cargo Airlines | Shanghai–Pudong |
| China Southern Cargo | Guangzhou, Vienna |
| DHL Aviation | Casablanca, Cincinnati, Leipzig/Halle, London–Heathrow |
| Emirates SkyCargo | Dubai-Al Maktoum |
| Europe Airpost | Longyearbyen |
| FedEx Express | Amsterdam, Athens, Barcelona, Basel/Mulhouse, Birmingham, Cologne/Bonn, Copenhagen, Delhi, Dubai–International, Guangzhou, Helsinki, Hong Kong, Indianapolis, Istanbul–Atatürk, London–Stansted, Madrid, Memphis, Milan–Malpensa, Mumbai, Munich, Newark, Stockholm–Arlanda, Tel Aviv, Tokyo–Narita, Vienna |
| FedEx Feeder | Belfast–International, Berlin–Schönefeld, Frankfurt, Hamburg, Hanover, Lyon, Manchester, Newcastle upon Tyne, Nice, Prague, Rome–Fiumicino, Shannon, Stuttgart, Toulouse, Warsaw–Chopin |
| Korean Air Cargo | Seoul–Incheon |
| MNG Airlines | Cologne/Bonn, Istanbul–Atatürk, London–Luton |
| Swiftair | Madrid |
| Turkish Airlines Cargo | Istanbul–Atatürk |
| UPS Airlines | Cologne/Bonn, Louisville, Philadelphia |
Ground transportation

Source: Josué Ahoyo

Source: https://www.flickr.com/photos/hdaniel/229262216/

Source: Claude Shoshany
CDGVAL
The airport’s terminals are served by a free automated shuttle rail system, consisting of two lines (CDGVAL and LISA). The shuttle train connects both railway stations for Terminals 1/3 and Terminal 2 in 8 minutes. It is based on the VAL design used in several French cities.
RER
Charles de Gaulle airport is connected to central Paris by the RER B Regional-Express services. During off-peak hours and weekends, there are two types of services:
- 4 trains per hour to Saint-Rémy-lès-Chevreuse calling at all intermediate stations to Cité Universitaire, then Bourg-la-Reine, La Croix de Berny, Antony, Massy–Palaiseau and then all stations to Saint-Rémy-lès-Chevreuse.
- 4 trains per hour to Massy–Palaiseau (on the Saint-Rémy line), non-stop express until Gare du Nord and then all stations to Massy–Palaiseau.
The express RER B only calls at the railway stations of Terminal 1 (also for Terminal 3) and Terminal 2 before Gare du Nord. Journey time is 30–35 minutes. The stopping RER B takes about 35–40 minutes and is sometimes overtaken by the express RER B trains.
- Aéroport Charles de Gaulle 1 station, located inside Roissypôle (an area with hotels and company offices) next to Terminal 3 and is the preferred way to access Terminals 1 and 3;
- Aéroport Charles de Gaulle 2 TGV station, located in the middle of Terminals 2C and 2E or Terminals 2D and 2F.
RER B is jointly operated by SNCF and RATP (Transport for Paris), but the Regional-Express used to suffer from slowness and overcrowding. For these reasons, French authorities have started two projects: CDG Express, which is supposed to link Charles de Gaulle Airport to Paris Gare de l’Est railway station (next to Gare du Nord) from 2023 with trains specifically designed for air travellers; RER B Nord Plus, which modernised and streamlined RER B rail traffic and network north of Gare du Nord from 2008 to 2013 then renovated the trains from 2010 to 2015.
TGV
Terminal 2 includes a TGV station on the LGV Interconnexion Est high-speed line. SNCF operates direct TGV services to several French stations from CDG, including Lille, Strasbourg, Dijon, Lyon, Avignon TGV, Marseille, Montpellier, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Nantes, Poitiers, Rennes, Toulon, as well as services to Brussels in Belgium.
Bus
- Roissybus, operated by the RATP (Transport for Paris), departs from Terminals 1 and 2 and runs non-stop to Palais Garnier.
- “Le Bus Direct” operates to several destinations: line 2 to Place de l’Étoile, Porte Maillot Trocadéro and Eiffel Tower, line 3 to Paris Orly (airport south of Paris), line 4 to Gare Montparnasse and Gare de Lyon railway stations.
- RATP buses 350 and 351 depart from the coach station in Roissypôle (next to Terminal 1’s RER railway station).
- Bus “Magical Shuttle” departs from all three terminals for Disneyland Paris.
After the last RER B service at 23:50, the Noctilien (Night Lines) N143 and N140 depart every 30 minutes and hour respectively from Terminal 1 Door D12, Terminal 2F Door 2 and Roissypôle coach station. Both bus lines run to Paris Gare de l’Est railway station.
Long-distance bus
Since 17 December 2012, SNCF’s national and international coach network, OUIBUS, serves Charles de Gaulle Airport, by terminal 3, station CDG 1 to London, Lyon, Lille and Brussels. Flixbus serves CDG from at least Brussels and Amsterdam.
Car
Charles de Gaulle Airport is directly connected to Autoroute A1 which connects Paris and Lille
Source: Mazta2012
Alternative airports
The two other airports serving Paris are Orly Airport (south of Paris, the other major airport in Paris) and Le Bourget Airport (for general aviation and private jets).
Several low-cost airlines also advertise Beauvais–Tillé Airport and Châlons Vatry Airport, respectively 85 kilometres (53 mi) and 165 kilometres (103 mi) from Paris proper, as serving “Paris” with Paris–Beauvais and Paris–Vatry. Beauvais airport has no railway connections, but there is a shuttle bus to central Paris 15 times daily.
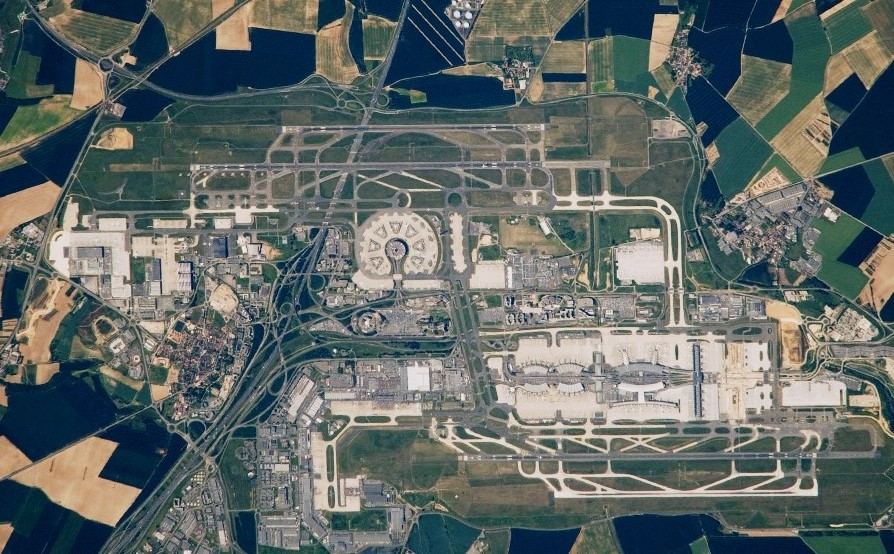
Source: NASA/JSC
Accidents and incidents
- On 6 January 1993, Lufthansa Flight 5634 from Bremen to Paris, which was carried out under the Lufthansa CityLine brand using a Contact Air Dash 8–300 (registered D-BEAT), hit the ground 1,800 metres (5,900 ft) short of the runway of Charles de Gaulle Airport, resulting in the death of four out of the 23 passengers on board. The four crew members survived. The accident occurred after the pilot had to abort the final approach to the airport because the runway had been closed: the aircraft immediately ahead, a Korean Air Boeing 747, had suffered a blown tire upon landing.
- On 25 July 2000, a Concorde, Air France Flight 4590 from Charles de Gaulle to John F. Kennedy International Airport in New York, crashed into Les Relais Bleus Hotel in Gonesse, killing everyone on the aircraft and four people on the ground. Investigations concluded that a tire burst on take-off due to metal left on the runway from a McDonnell Douglas DC-10-30 that departed shortly before, leading to a ruptured fuel tank and resulting in engine failure and other damage. Concorde was conducting a charter flight for a German tour company.
- On 25 May 2001, a freight-carrying Short SH36 (operated as Streamline flight 200), departing to Luton, England, collided on the runway with departing Air Liberté flight 8807, an MD-83 jet. The first officer of the SH36 was killed when the wing tip of the MD-83 tore through his side of the flight deck. The captain was slightly injured and all others aboard survived.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Charles_de_Gaulle_Airport



















