Aviation
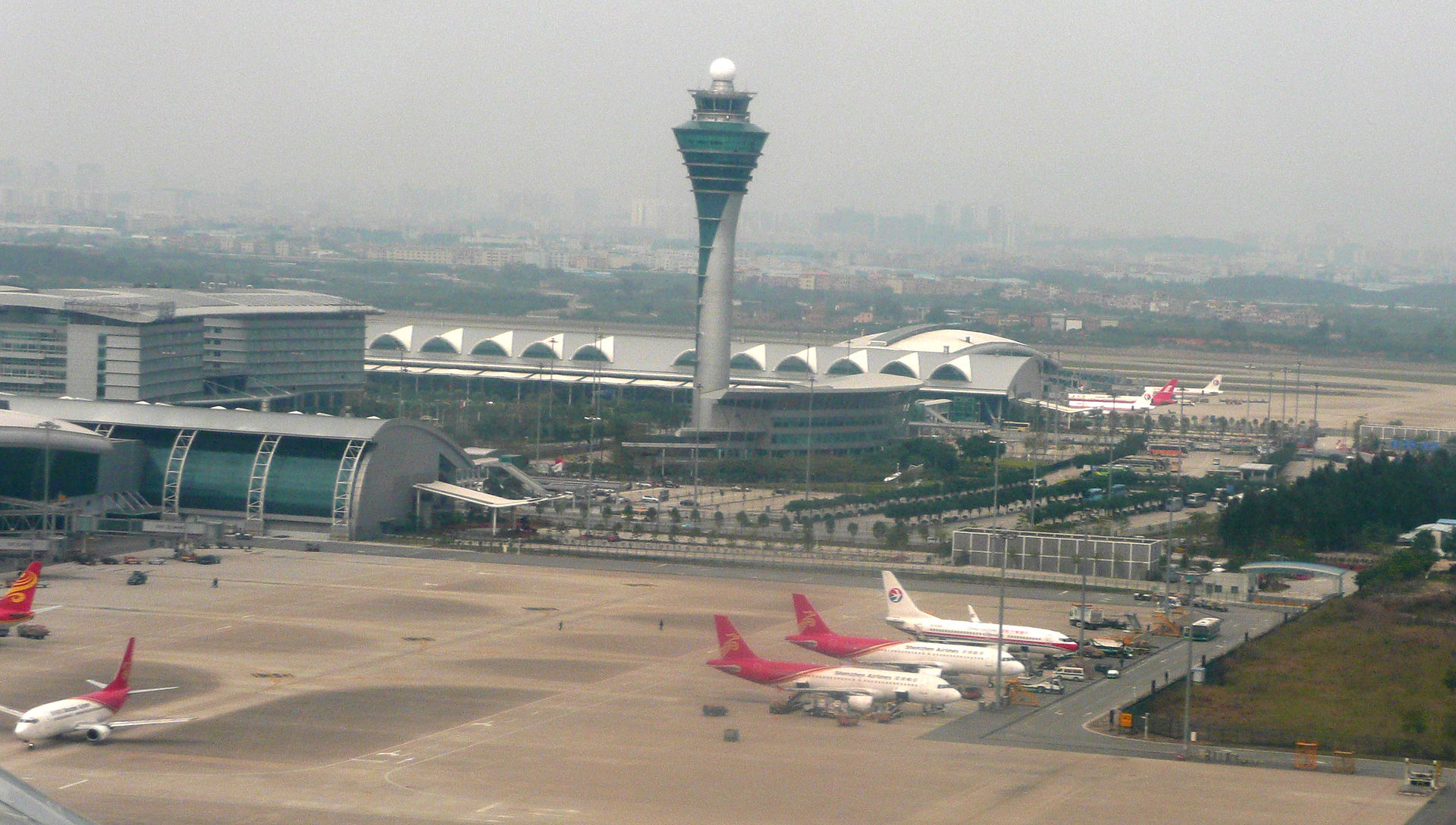
Toronto Pearson International Airport

Source: Buffyjossdollhouse
| IATA: YYZ ICAO: CYYZ WMO: 71624 | |
| Airport type | Public |
|---|---|
| Owner | Transport Canada |
| Operator | Greater Toronto Airports Authority |
| Serves | Greater Toronto |
| Location | Mississauga and Toronto, Ontario, Canada |
| Hub for | Air Canada Air Canada Express Air Canada Rouge FedEx Express WestJet WestJet Encore |
| Focus city for | Air Transat Sunwing Airlines |
| Time zone | EST (UTC−05:00) |
| • Summer (DST) | EDT (UTC−04:00) |
| Elevation AMSL | 569 ft / 173 m |
| Coordinates | |
| Website | www.torontopearson.com |
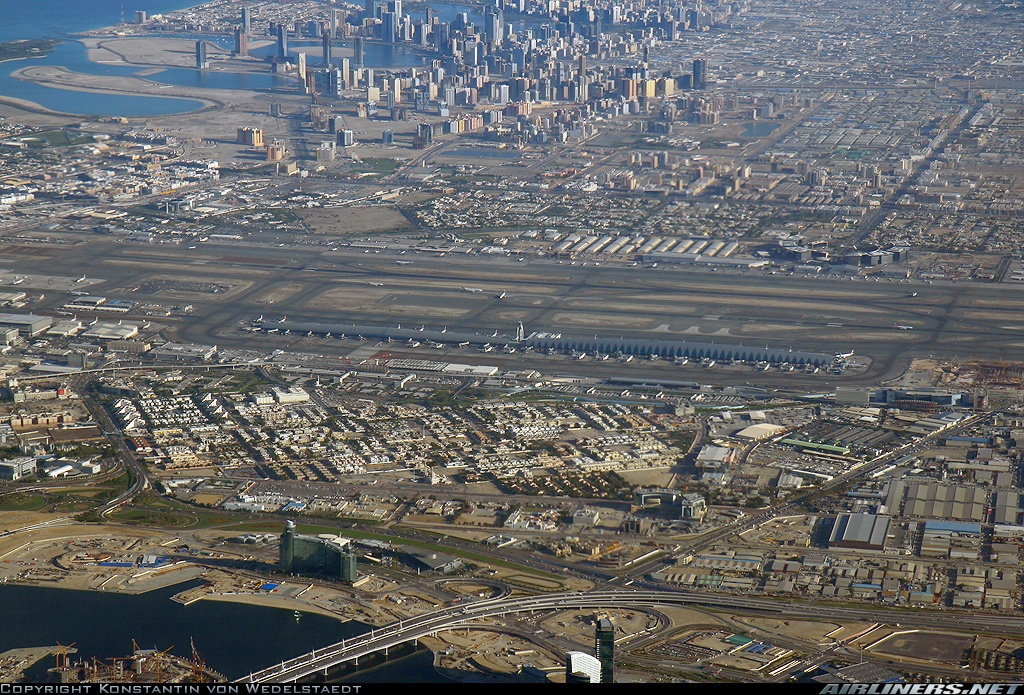
Lester B. Pearson International Airport (IATA: YYZ, ICAO: CYYZ), branded as Toronto Pearson International Airport (simply known as Toronto Pearson, Pearson Airport or Pearson), is the primary international airport serving Toronto, its metropolitan area, and its surrounding region known as the Golden Horseshoe. It is the largest and busiest airport in Canada, the second-busiest international air passenger gateway in the Americas, and the 30th-busiest airport in the world by passenger traffic, handling 50.5 million passengers in 2019. The airport is named in honour of Lester B. Pearson, Nobel Peace Prize laureate and 14th Prime Minister of Canada.
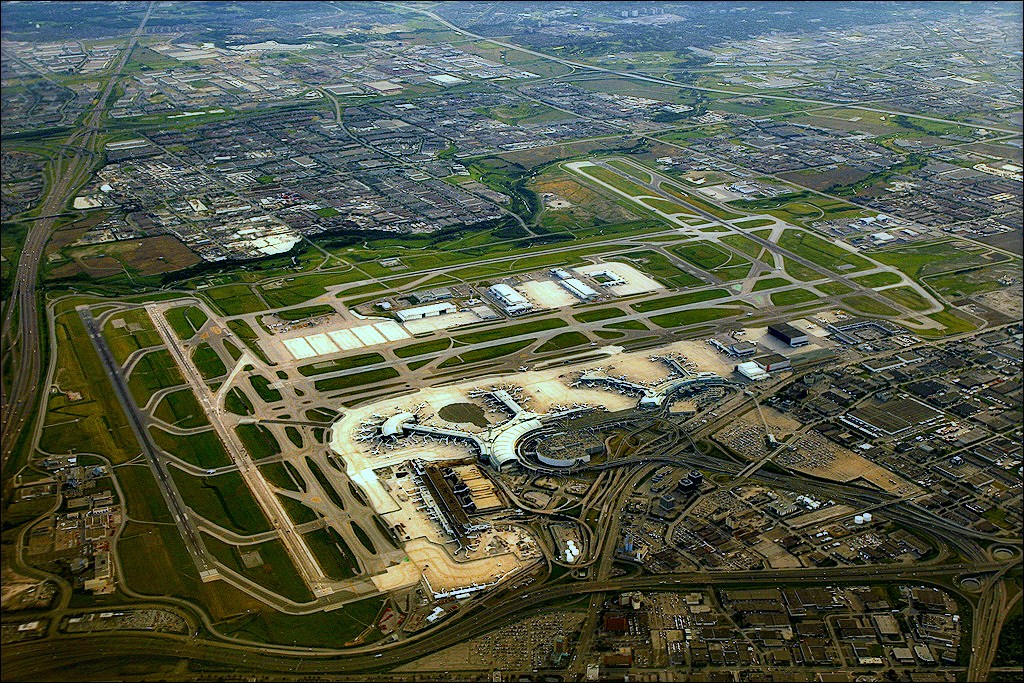
Toronto Pearson is located 22.5 kilometres (14.0 mi) northwest of Downtown Toronto with the majority of the airport situated in the city of Mississauga and a small portion of the airfield extending into Toronto’s western district of Etobicoke. It features five runways and two passenger terminals along with numerous cargo and maintenance facilities on a site that covers 1,867 hectares (4,613 acres).
Toronto Pearson is the primary hub for Air Canada. It also serves as a hub for WestJet, cargo airline FedEx Express, and as a base of operations for Air Transat and Sunwing Airlines. Pearson is operated by the Greater Toronto Airports Authority (GTAA) as part of Transport Canada’s National Airports System, and is the largest airport in the world with facilities for United States border preclearance.
An extensive network of non-stop domestic flights is operated from Toronto Pearson by several airlines to all major and many secondary cities across all provinces of Canada. As of 2019, over 75 airlines operate around 1,250 daily departures from the airport to more than 180 destinations across all six of the world’s inhabited continents.


Terminals
Toronto Pearson International Airport has two active public terminals, Terminal 1 and Terminal 3. Both terminals are designed to handle all three sectors of travel (domestic, transborder, and international), which results in terminal operations at Pearson being grouped for airlines and airline alliances, rather than for domestic and international routes.
A third public terminal, the Infield Concourse (IFC), currently acts as an extension of Terminal 3 providing additional bridged gates.
Terminal 2 was permanently closed and demolished in 2007, replaced by an expanded Terminal 1.
Terminal 1
Measuring over 346,000 square metres (3,724,000 sq ft), Terminal 1 is the largest airport terminal in Canada and the 12th largest in the world by floor space. Air Canada and all other Star Alliance airlines that serve Pearson are based at Terminal 1. Emirates is the only non-alliance airline that uses the terminal.
Terminal 1 was designed by a joint venture known as Airports Architects Canada made up of Skidmore, Owings & Merrill LLP, Adamson Associates Architects and Moshe Safdie and Associates. It contains 58 gates: D1, D3, D5, D7-D12, D20, D22, D24, D26, D28, D31–D45 (D32, D34, D36 also serve US flights and carry F designation), D51, D53, D55, D57 (also carry F designation), F60–F63, F64A–F64B, F65, F66A–F66B, F/E67–F/E81 (F68-F73 and F78-F81 serve both US and international flights but E74-E77 are international only), F59, F82-F83, and F84-F99. Two of the gates, E73 and E75, can accommodate the Airbus A380.
Along with the standard customs and immigration facilities, Terminal 1 also contains special customs “B” checkpoints along the international arrivals walkway. Passengers connecting from an international or trans-border arrival to another international (non-U.S.) departure in Terminal 1 go to one of these checkpoints for passport control and immigration checks, then are immediately directed to Pier E for departure. This alleviates the need to recheck bags, pass through security screening, and relieves congestion in the primary customs hall. International-to-domestic passengers use the same corridor and a bus for one-stop security procedures, which avoids having to re-clear security if coming from another country with a mutual agreement.


Source: Robert Linsdell from St. Andrews, Canada


Source: 天王星
The terminal has a total of eight lounges, with five of the lounges being Air Canada operated lounges (3 Maple Leaf Lounges, one Maple Leaf Express Lounge and one Signature Suite) and three being Plaza Premium operated. Both Air Canada and Plaza Premium have lounges in the Domestic, International and Transborder zones, with the Signature Suite being in the International Zone.
In addition to the eight lounges, Air Canada operates the Air Canada Cafe, in which premium passengers have the ability to enter into the zone and get premium coffee and grab-and-go snacks.
An eight-level parking garage with 8,400 public parking spaces (including 700 rental car spaces) across from Terminal 1 is connected to the terminal by several elevated and enclosed pedestrian walkways.
Terminal 1 is home to the ThyssenKrupp Express Walkway, the world’s fastest moving walkway.
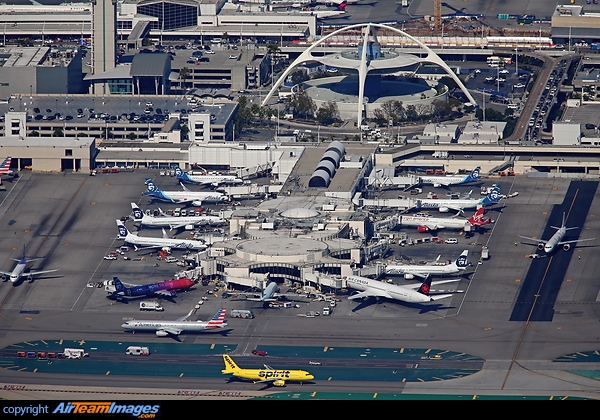
Terminal 3


Source: Martin Kraft (1979–)


Source: Jeff Hitchcock
Terminal 3 is a 178,000-square-metre (1,916,000 sq ft) facility designed by B+H Architects and Scott Associates Architects Inc. It is used by all SkyTeam and Oneworld airlines that serve Pearson, along with Air Transat, Etihad Airways, Pakistan International Airlines, Philippine Airlines, Sunwing Airlines, WestJet and all other airlines that are unaffiliated with an airline alliance (except Emirates, which uses Terminal 1). Terminal 3 has 46 gates: B1a-B1d, B2a, B2c, B3-B5, A6d-A6f, A7–A16, B17-B20 (also, A17-A20 for transborder flights), B22-B29, C30-C36 and B37–B41.
A five-level parking garage with 3,800 public parking spaces (including 600 rental car spaces) is located directly across from the terminal along with the Sheraton Hotel, both of which are connected to Terminal 3 by an elevated pedestrian walkway.
Since June 2018, the GTAA has used the Infield Terminal to act as an extension of Terminal 3 to provide additional bridged gates. Passengers on flights arriving or departing from gates at the Infield Terminal are transported by bus to/from Terminal 3.
Infield Concourse
The Infield Concourse (IFC) was originally built to handle traffic displaced during the development and construction of the current Terminal 1. Its 11 gates (521 to 531) were opened gradually throughout 2002 and 2003,[37] and a business lounge was opened in 2005. In 2009, the Infield Concourse was closed for regular operations in conjunction with the official opening of the newly constructed Terminal 1. However, the GTAA retained plans to reactivate the IFC for regular operations whenever necessary to accommodate seasonal or overflow demand.
The terminal was substantially renovated in late 2015 to serve as a dedicated terminal for incoming government-sponsored refugees of the Syrian Civil War. Further renovations were completed at the Infield Concourse in early 2018 and on June 5, 2018, the terminal was reactivated for summer operations by the GTAA to act as an extension of Terminal 3 with the purpose of providing required additional bridged gates. Passengers are transported by bus between Terminal 3 and the IFC. Effective December 2019, Sunwing Airlines moved their operations from terminal 3 to the IFC.
Due to its intermittent usage for passenger traffic, the Infield Concourse is frequently used as a location to film major motion pictures and television productions.
VIP Terminal
Skyservice FBO operates an 800-square-metre (8,611 sq ft) private VIP terminal at Toronto Pearson on Midfield Road in the infield area of the airport. The terminal handles most private aircraft arriving and departing at Pearson, providing passenger services that include 24/7 concierge, private customs and immigration facilities, personalized catering, showers, direct handling of baggage, and VIP ground transportation services.
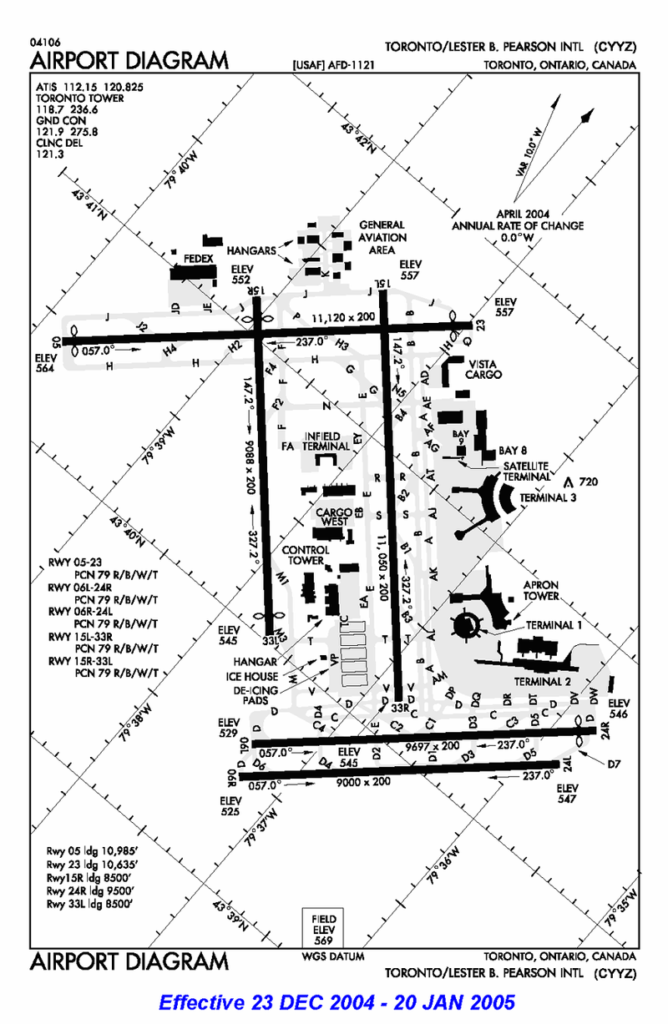

Secondary source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Cyyz_arpt_diagram.png en:User:Gwk
Infrastructure and operations
Runways
Toronto Pearson has five runways, three of which are aligned in the east–west direction, and two in the north–south direction. A large network of taxiways, collectively measuring over 40 km (25 mi) in length, provides access between the runways and the passenger terminals, air cargo areas, and airline hangar areas.
| Number | Length | Width | ILS | Alignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05/23 | 11,120 ft (3,390 m) | 200 ft (61 m) | Cat. IIIa (05), Cat. I (23) | East–West |
| 06L/24R | 9,697 ft (2,956 m) | 200 ft (61 m) | Cat. IIIa (6L), Cat. I (24R) | East–West |
| 06R/24L | 9,000 ft (2,700 m) | 200 ft (61 m) | Cat. I (both directions) | East–West |
| 15L/33R | 11,050 ft (3,370 m) | 200 ft (61 m) | Cat. I (both directions) | North–South |
| 15R/33L | 9,088 ft (2,770 m) | 200 ft (61 m) | Cat. I (both directions) | North–South |
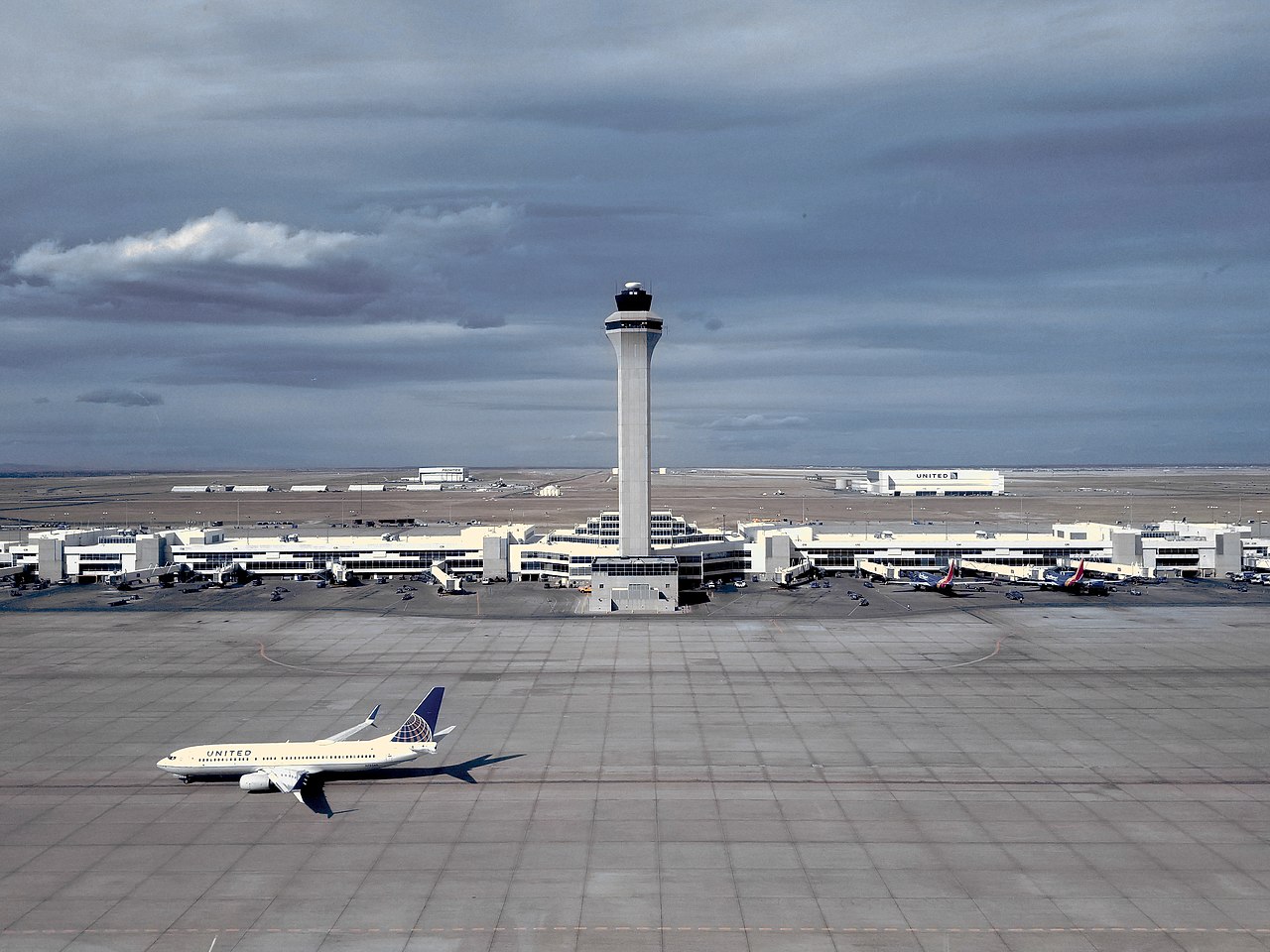
Airfield operations


Source: Jiaqian AirplaneFan
Toronto Pearson is home to the Toronto Area Control Centre, one of seven area control centres in Canada operated by Nav Canada. The airport uses a Traffic Management Unit (TMU), located in the apron control tower at Terminal 1, to control the movement of aircraft and other airport traffic on the ground. The main air traffic control tower at Pearson is located within the infield operations area of the airport.
The airfield maintenance unit is responsible for general maintenance and repairs at Pearson. During the winter months, the unit expands into a dedicated 24-hour snow removal team of more than 200 workers tasked with ensuring normal operations at the airport, as Pearson regularly experiences 110 to 130 centimetres (43 to 51 in) of total snow accumulation in a typical winter season. The airport employs over 94 pieces of snow removal equipment, including 11 Vammas PSB series, 4 Oshkosh HT-Series snowplow units, and 14 snowmelters.
Pearson Airport’s Central De-icing Facility is the largest in the world, servicing over 10,500 aircraft each winter. The six de-icing bays, covering a total area of 24 hectares (60 acres), can handle 12 aircraft simultaneously and take between 2 and 19 minutes to de-ice each aircraft dependent on factors such as active weather and aircraft specifications.
The Greater Toronto Airports Authority (GTAA) Fire and Emergency Service maintains three stations at the airport, with more than 80 firefighters providing fire and rescue operations at Pearson. They are equipped with six crash tenders as well as several pumpers, aerial ladders, and heavy rescue units. The GTAA Fire and Emergency Service operates in conjunction with the Fire and Emergency Services Training Institute (FESTI), located at the northwest end of the airport grounds.
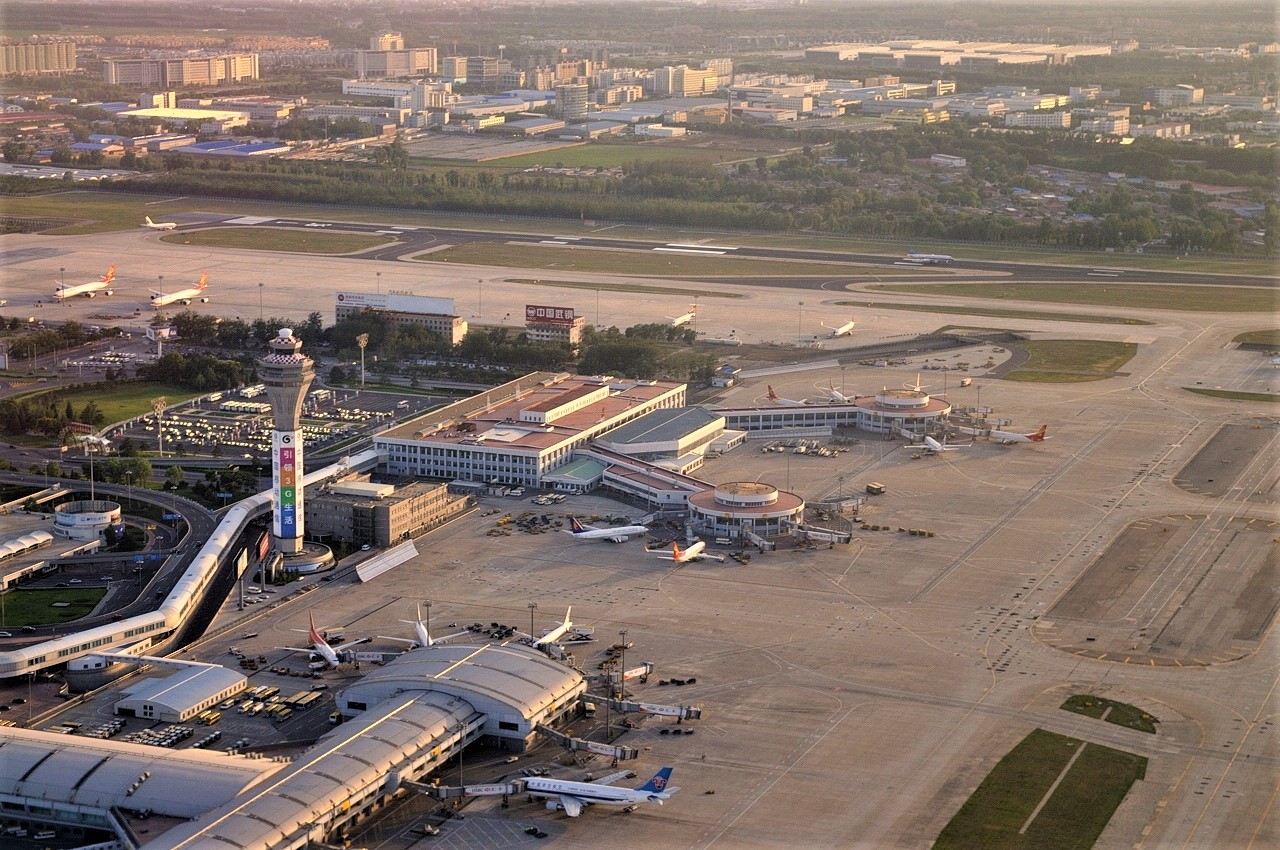
Cargo facilities


Source: N169UP
Toronto Pearson handles over 50% of total international air cargo in Canada. The airport has three main cargo facilities, known as Cargo West (Infield), Cargo East (VISTA), and Cargo North (FedEx).
The Cargo West facility (also known as the Infield Cargo Area) is located between runways 15L/33R and 15R/33L. It is a multi-tenant facility including three large buildings with 52,600 square metres (566,000 sq ft) of warehouse space, a common use cargo apron, vehicle parking, and a truck maneuvering area. A four-lane vehicle tunnel connects the Infield Cargo Area to the passenger terminal area of the airport.
The Cargo East facility (also known as the VISTA cargo area) is located north of Terminal 3. The VISTA cargo area is a multi-tenant facility of several buildings organised in a U-shape, with 29,500 square metres (318,000 sq ft) of warehouse space and an adjacent common use cargo apron.
The Cargo North facility is the Canadian hub for FedEx Express. The site occupies an area on the north side of the airport lands near runway 05/23, and is home to two buildings operated exclusively by FedEx with 32,100 square metres (346,000 sq ft) of warehouse space and a dedicated cargo apron.
Security
The Peel Regional Police is the primary law enforcement agency at Toronto Pearson. The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) also maintain a Toronto Airport Detachment at Pearson, which provides federal law enforcement services.
The Canadian Air Transport Security Authority (CATSA) is responsible for security screening procedures at Pearson Airport. Other government agencies with security operations at Pearson include the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA), Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC), and Transport Canada. In addition, U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) and United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) also conduct operations at the airport to facilitate United States border preclearance.
Other facilities
Pearson Airport has seven aircraft maintenance hangars, operated by Air Canada, Air Transat, WestJet, and the GTAA, which are used for line maintenance and routine aircraft inspections. At the north end of the airfield are numerous independently operated hangars for charter aircraft and personal private aircraft based at Pearson, along with passenger and maintenance facilities to service them.
The Greater Toronto Airports Authority maintains administrative offices on Convair Drive, near the southeast corner of the airfield. Gate Gourmet and CLS Catering Services both operate dedicated flight kitchen facilities at Pearson for airline catering services. Aviation fuel (Jet A-1) is supplied by Esso Avitat and Shell Aerocentre, both located in the infield operations area of the airport.

Airlines and destinations
Passenger
| Airlines | Destinations | |
|---|---|---|
| Aer Lingus | Dublin | |
| Aeroméxico | Mexico City | |
| Air Canada | Amsterdam, Antigua, Aruba, Beijing–Capital, Bermuda, Bogotá (resumes September 1, 2020), Brussels (begins October 25, 2020), Buenos Aires–Ezeiza, Calgary, Copenhagen, Curaçao, Delhi, Denver, Dubai–International, Dublin, Edmonton, Frankfurt, Geneva, Grand Cayman, Grenada, Halifax, Hong Kong, Houston–Intercontinent London–Heathrow, Los Angeles, Madrid, Montréal–Trudeau, Munich, New York–LaGuardia, Ottawa, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Providenciales, Regina, Rome–Fiumicino, St. John’s (NL), San Francisco, San Jose (CA), Santiago de Chile, São Paulo–Guarulhos, Saskatoon, Seattle/Tacoma, Seoul–Incheon, Shanghai–Pudong, Tel Aviv, Tokyo–Haneda, Vancouver, Vienna, Winnipeg, Zürich Seasonal: Athens, Barcelona (resumes March 28, 2021), Boston, Edinburgh (resumes June 4, 2021), Fort McMurray, George Town/Exuma, Honolulu, Huatulco, Ixtapa/Zihuatanejo, Lisbon (resumes March 29, 2021), Manchester (UK) (resumes June 4, 2021), Mumbai, Reykjavík–Keflavík, St. Maarten, San Juan, Shannon, Tokyo–Narita (resumes October 2, 2020), West Palm Beach | |
| Air Canada Express | Atlanta, Austin, Baltimore, Boston, Charlotte, Chicago–O’Hare, Cincinnati, Cleveland, Columbus–Glenn, Dallas/Fort Worth, Detroit, Hartford, Indianapolis, Kansas City, London (ON), Memphis, Milwaukee, Minneapolis/St. Paul, Montréal–Trudeau, Nashville, Newark, New Orleans, Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, Raleigh/Durham, St. Louis, Sault Ste. Marie (ON), Sudbury, Sydney (NS), Timmins, Washington–Dulles, Washington–National, Windsor Seasonal: Gander, Mont Tremblant, Providence (RI), Savannah | |
| Air Canada Rouge | Barbados, Cancún, Cayo Coco, Charlottetown, Deer Lake, Fort Lauderdale, Fort Myers, Fredericton, Havana, Holguín, Kelowna, Kingston–Norman Manley, Las Vegas, Liberia, Mexico City, Miami, Moncton, Montego Bay, Nassau, Orlando, Panama City–Tocumen, Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Port of Spain, Puerto Plata, Puerto Vallarta, Punta Cana, Québec City, St. Lucia–Hewanorra, St. Vincent–Argyle, Saint John (NB), Samaná, San Diego, San José de Costa Rica, Santa Clara, Tampa, Thunder Bay, Varadero, Victoria Seasonal: Abbotsford, Belize City, Berlin–Tegel, Bucharest, Budapest, Cartagena, Cozumel, Glasgow, Kamloops, Nanaimo, Palm Springs, Portland (OR), Porto, Prague, St. Kitts, San José del Cabo, Sarasota, Venice, Warsaw–Chopin, Zagreb | |
| Air France | Paris–Charles de Gaulle | |
| Air India | Delhi | |
| Air Transat | Cancún, Cayo Coco, Fort Lauderdale, Glasgow, Holguín, Lisbon, London–Gatwick, Manchester (UK), Montego Bay, Montréal–Trudeau, Orlando, Porto, Puerto Plata, Punta Cana, Samaná, Santa Clara, Vancouver, Varadero Seasonal: Amsterdam, Athens, Cartagena, Dublin, Faro, Fort-de-France, Lamezia Terme, La Romana, Paris–Charles de Gaulle, Puerto Vallarta, Roatán, St. Maarten, Venice, Zagreb | |
| Alitalia | Seasonal: Rome–Fiumicino | |
| American Airlines | Charlotte, Chicago–O’Hare, Dallas/Fort Worth, Miami | |
| American Eagle | Charlotte, Chicago–O’Hare, Dallas/Fort Worth, New York–JFK, New York–LaGuardia, Philadelphia, Washington–National | |
| Avianca Costa Rica | San Salvador | |
| Azores Airlines | Ponta Delgada Seasonal: Terceira | |
| British Airways | London–Heathrow Seasonal: London–Gatwick | |
| Caribbean Airlines | Kingston–Norman Manley, Port of Spain | |
| Cathay Pacific | Hong Kong | |
| China Eastern Airlines | Shanghai–Pudong | |
| China Southern Airlines | Guangzhou | |
| Condor | Seasonal: Frankfurt | |
| Copa Airlines | Panama City–Tocumen (resumes October 2, 2020) | |
| Delta Air Lines | Atlanta, Salt Lake City | |
| Delta Connection | Cincinnati, Detroit, Minneapolis/St. Paul, New York–JFK | |
| EgyptAir | Cairo | |
| El Al | Tel Aviv | |
| Emirates | Dubai–International | |
| Ethiopian Airlines | Addis Ababa | |
| Etihad Airways | Abu Dhabi | |
| EVA Air | Taipei–Taoyuan | |
| Flair Airlines | Calgary, Edmonton, Fort McMurray (begins August 26, 2020), Regina (begins August 24, 2020), Saskatoon (begins August 27, 2020), Vancouver, Winnipeg Seasonal: Charlottetown, Halifax, Ottawa, Saint John (NB) | |
| Hainan Airlines | Beijing–Capital | |
| Icelandair | Reykjavík–Keflavík | |
| Interjet | Cancún, Mexico City (both suspended) | |
| KLM | Amsterdam | |
| Korean Air | Seoul–Incheon | |
| LOT Polish Airlines | Warsaw–Chopin | |
| Lufthansa | Frankfurt Seasonal: Munich | |
| OWG | Cayo Coco (begins November 1, 2020), Holguín (begins November 5, 2020), Santa Clara (begins November 6, 2020), Varadero (begins November 7, 2020) | |
| Pakistan International Airlines | Islamabad, Karachi, Lahore | |
| Philippine Airlines | Manila | |
| Sunwing Airlines | Antigua, Aruba, Cancún, Cayo Coco, Fort Lauderdale, Freeport, Holguín, Mazatlán, Montego Bay, Orlando, Puerto Plata, Puerto Vallarta, Punta Cana, Río Hato, St. Lucia–Hewanorra, St. Maarten, San José del Cabo, Santa Clara, Varadero Seasonal: Acapulco, Bonaire, Camagüey, Cayo Largo del Sur, Cienfuegos, Cozumel, Curaçao, Daytona Beach, Gander, Grand Cayman, Grenada, Huatulco, Ixtapa/Zihuatanejo, La Romana, Liberia, Manzanillo (Cuba), Miami, Nassau, Roatán, St. John’s (NL), St. Petersburg/Clearwater, Stephenville, Tobago, Vancouver | |
| TAP Air Portugal | Lisbon, Ponta Delgada | |
| Turkish Airlines | Istanbul | |
| Ukraine International Airlines | Kyiv–Boryspil | |
| United Airlines | Chicago–O’Hare, Denver, Houston–Intercontinental, San Francisco | |
| United Express | Chicago–O’Hare, Houston–Intercontinental, Newark, Washington–Dulles | |
| WestJet | Antigua, Aruba, Barbados, Bermuda, Calgary, Cancún, Cayo Coco, Charlottetown, Edmonton, Fort Lauderdale, Fort Myers, Grand Cayman, Halifax, Kelowna, Kingston–Norman Manley, Las Vegas, Liberia, London–Gatwick, Los Angeles, Montego Bay, Montréal–Trudeau, Nassau, New York–LaGuardia, Orlando, Ottawa, Port of Spain, Providenciales, Puerto Plata, Puerto Vallarta, Punta Cana, Regina, St. John’s (NL), St. Lucia–Hewanorra, St. Maarten, San José de Costa Rica, Santa Clara, Samaná, Saskatoon, Tampa, Vancouver, Varadero, Winnipeg Seasonal: Barcelona, Belize City, Cozumel, Curaçao, Deer Lake, Holguín, Huatulco, Mérida, Miami, Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Roatán, San Juan, Sydney (NS), Victoria | |
| WestJet Encore | Boston, Fredericton, London (ON), Moncton, Montréal–Trudeau, Nashville, Ottawa, Québec City, Thunder Bay Seasonal: Myrtle Beach |
Cargo
| Cathay Pacific Cargo | Anchorage, Hong Kong, New York–JFK | VISTA |
| FedEx Express | Calgary, Edmonton, Indianapolis, Memphis, Minneapolis/St. Paul, Montréal–Mirabel, North Bay, Sault Ste. Marie (ON), Sudbury, Timmins, Vancouver, Winnipeg | FedEx |
| Korean Air Cargo | Anchorage, New York–JFK, Seoul–Incheon | Cargo West |
| Lufthansa Cargo | Frankfurt | Cargo West |
| Turkish Cargo | Istanbul–Atatürk, New York–JFK | VISTA |
| UPS Airlines | Louisville | VISTA |
Ground transportation
Bus
Public transit


Source: Toronto501
Several public transit bus services operate bus routes to Toronto Pearson International Airport. Toronto Transit Commission (TTC) operates daily, 24-hour public transit bus service from Pearson Airport to various stations in Toronto, with route 900 Airport Express being the main express bus service to the airport from Kipling station on Line 2 Bloor–Danforth subway line, and route 52 Lawrence West providing rush hour service to Lawrence and Lawrence West stations on Line 1 Yonge–University subway line. The TTC Blue Night Network operates local night bus routes to Warden Avenue, Eglinton station and Sunnybrook Hospital. Although the airport terminals are situated outside of the Toronto city limits, TTC services at Pearson do not require a supplementary fare. TTC buses serve both Terminal 1 and Terminal 3.
Two public transit operators based in Peel Region also operate routes to the airport, Brampton Transit, and MiWay. Brampton Transit operates all-day public transit bus service from Pearson Airport to the city of Brampton, with express service operating to Bramalea Terminal. Brampton Transit buses arrive and depart from Terminal 1. MiWay operates all-day public transit bus service from Pearson Airport to the city of Mississauga, with express service to City Centre Transit Terminal, Humber College, and Winston Churchill Transitway Station, and local routes to Westwood Square Terminal, Renforth station, and Meadowvale Town Centre Terminal. MiWay buses arrive and depart from Terminal 1, Terminal 3, Toronto Pearson Viscount station, and the infield operations area of the airport.


Source: JPark99
GO Transit is another daily, 24-hours public transit service that operates coaches from the airport to cities across the Greater Toronto Area with express service to Richmond Hill Terminal and Hamilton GO Centre and local service to Finch Terminal. GO Transit coaches arrive and depart from Terminal 1.
Private
Greyhound Canada operates daily intercity coach service from Pearson Airport to the Toronto Coach Terminal, cities across Southern Ontario, and select cities in the U.S. states of New York and Michigan. Greyhound Canada coaches arrive and depart from Terminal 1.
The airport is also served by several long-distance van and minibus shuttle operators, which provide transportation from the airport to various municipalities and regional airports throughout Southern Ontario and to select cities and towns in the U.S. states of New York and Michigan.
Car


Toronto Pearson is directly accessible from Highway 427 and Highway 409 with Airport Road and Dixon Road providing local access to the airport. There are 12,200 parking spaces available in parking garages adjacent to Terminal 1 and Terminal 3, in addition to several other parking lots located in the immediate area.
Car rentals are available from various major car rental agencies located in the parking garages adjacent to both terminals. Car rentals are also available from off-airport car rental agencies located near Toronto Pearson Viscount station, accessible from both terminals via the Link Train.
Taxi
Taxicabs and limousines can be accessed at designated taxi stands located outside of both Terminal 1 and Terminal 3. Only official airport-licensed taxis and limousines can legally pick up passengers at Pearson, and all airport-licensed taxi and limo companies use GTAA authorized flat rate fares for travel from the airport.
Rideshare
Ridesharing services Uber and Lyft are available at Pearson Airport. Designated rideshare pickup zones are located at both Terminal 1 and Terminal 3. Terminal 1 pickup is from the ground level, while Terminal 3 pickup is from the arrivals level.
Train


Source: Craig James White


Source: Secondarywaltz
Two train services have stops at the airport. Union Pearson Express airport rail link that runs to downtown Toronto; whereas the LINK Train is a localized people mover (within airport property).
Presently two train services operate from the airport, one serving as an airport rail link, the other as a localized people mover.
Union Pearson Express
The Union Pearson Express (UP Express) is an airport rail link running between Pearson Airport and Union Station in Downtown Toronto, with intermediate stops at Weston and Bloor GO Stations. Trains depart every 15 minutes from Toronto Pearson Terminal 1 station and provide a 25-minute travel time to Union Station, the busiest intermodal transportation facility in Canada. Union Station offers connections to numerous GO Transit regional rail and bus services as well as inter-city rail links on Via Rail’s Québec City–Windsor Corridor. The UP Express operates daily between 5:27 am and 12:57 am.
Link Train
Link Train is an automated people mover that facilitates inter-terminal transportation at Pearson Airport. It runs between Terminal 1, Terminal 3, and the Viscount Value Park Lot, connecting to the airport terminals at Toronto Pearson Terminal 1 station and Toronto Pearson Terminal 3 station. The Link train operates daily, 24-hour service with trains departing all stations every 4 to 8 minutes.
Future
In February 2017, the GTAA announced a proposed transit hub to be located across from Terminal 3 that would connect with Union Pearson Express and may connect with other transit lines extended to the airport like Line 5 Eglinton LRT and GO Transit Regional Express Rail. This proposal would eliminate the Link Train connecting Terminals 1 and 3 with a bridge from the transit hub to Terminal 3 and another bridge connecting Terminal 3 to Terminal 1.
Metrolinx is currently planning the Eglinton Crosstown West Extension, which is a western extension of the under-construction Line 5 Eglinton to a proposed transit hub at Pearson Airport across the terminals at the site of Viscount Station. The extension is scheduled to open in 2030-31. As of 2020, the segment to Pearson is under study by Metrolinx and the GTAA. The line will connect the airport to Midtown Toronto with additional transfers to Downtown Toronto. Metrolinx is also studying a potential connection with Line 6 Finch West to the transit hub. Other connections like the Mississauga Transitway are being studied.
Incidents and accidents
- On October 3, 1959, Vickers Viscount CF-TGY of Trans-Canada Air Lines was written off when it landed short of the runway. No fatalities among the 38 on board.
- On February 10, 1960, a Super Constellation of Trans-Canada Air Lines was seriously damaged when it overran the runway after landing in bad weather. None of the 59 passengers and crew were injured.
- On June 13, 1964, Vickers Viscount CF-THT of Air Canada was damaged beyond economical repair when it crash-landed after the failure of two engines on approach.
- The airport’s deadliest accident occurred on July 5, 1970, when Air Canada Flight 621, a DC-8 jet, flew on a Montreal–Toronto–Los Angeles route. The pilots inadvertently deployed spoilers before the plane attempted landing, forcing the pilots to abort landing and takeoff. Damage to the aircraft that was caused during the failed landing attempt caused the plane to break up in the air during the go-around, killing all 100 passengers and nine crew members on board when it crashed into a field southeast of Brampton. Controversy remains over the cleanup effort following the crash, as both plane wreckage debris and human remains from the crash are still found on the site.
- On August 30, 1970, Douglas C-47 CF-JRY of D G Harris Productions was damaged beyond economic repair in a storm.
- On June 21, 1973, Air Canada Flight 890, a DC-8-53 (CF-TIJ), was destroyed by fire during refueling at the gate.
- On June 26, 1978, Air Canada Flight 189 to Winnipeg overran the runway during an aborted takeoff, and crashed into the Etobicoke Creek ravine. Two of the 107 passengers on board the DC-9 were killed.
- On June 22, 1983, Douglas C-47A C-GUBT of Skycraft Air Transport crashed on takeoff roll at Toronto International Airport while on an international cargo flight from Cleveland Hopkins International Airport in northeastern Ohio. Both of the crew members were killed.
- On August 2, 2005, Air France Flight 358, an Airbus A340-300 (registration F-GLZQ) inbound from Paris, landed on runway 24L during a severe thunderstorm, failed to stop, and ran off of the runway into the Etobicoke Creek ravine. The rear third of the plane burst into flames, eventually engulfing the whole plane except the cockpit and wings. There were 12 serious injuries, but no fatalities. The investigation predominantly blamed pilot error when faced with the severe weather conditions.
- On July 25, 2014, Sunwing Airlines Flight 772, which had taken off from Toronto bound for Scarlett Martínez International Airport, was forced to return to Toronto after a passenger made a bomb threat; the plane landed safely and the passenger was arrested.
- On May 10, 2019, Air Canada Flight 8615, a Bombardier DHC-8-300, was struck by a fuel truck while taxiing on the tarmac. Five persons were injured and the plane was deemed a write-off.
Source: wikipedia















